Emancipation is when a minor has achieved independence from his or her parents, such as by getting married before reaching age 18 or by becoming fully self-supporting. It may be possible for a child to petition a court for emancipation to free the minor child from the control of parents and allow the minor to live on his/her own or under the control of others. It usually applies to adolescents who leave the parents' household by agreement or demand.
Some of the most common methods for a minor to become emancipated include marriage, reaching the age of majority, entering military service, or by court order. A parent may also formally or informally agree to give up some or all of his/her parental control. For example, a parent might consent to allowing a child to establish a separate household. In other cases, a parent may force the minor to leave and support him/herself. Generally, parental consent is required, except in cases of parental misconduct that causes the minor to leave the home.
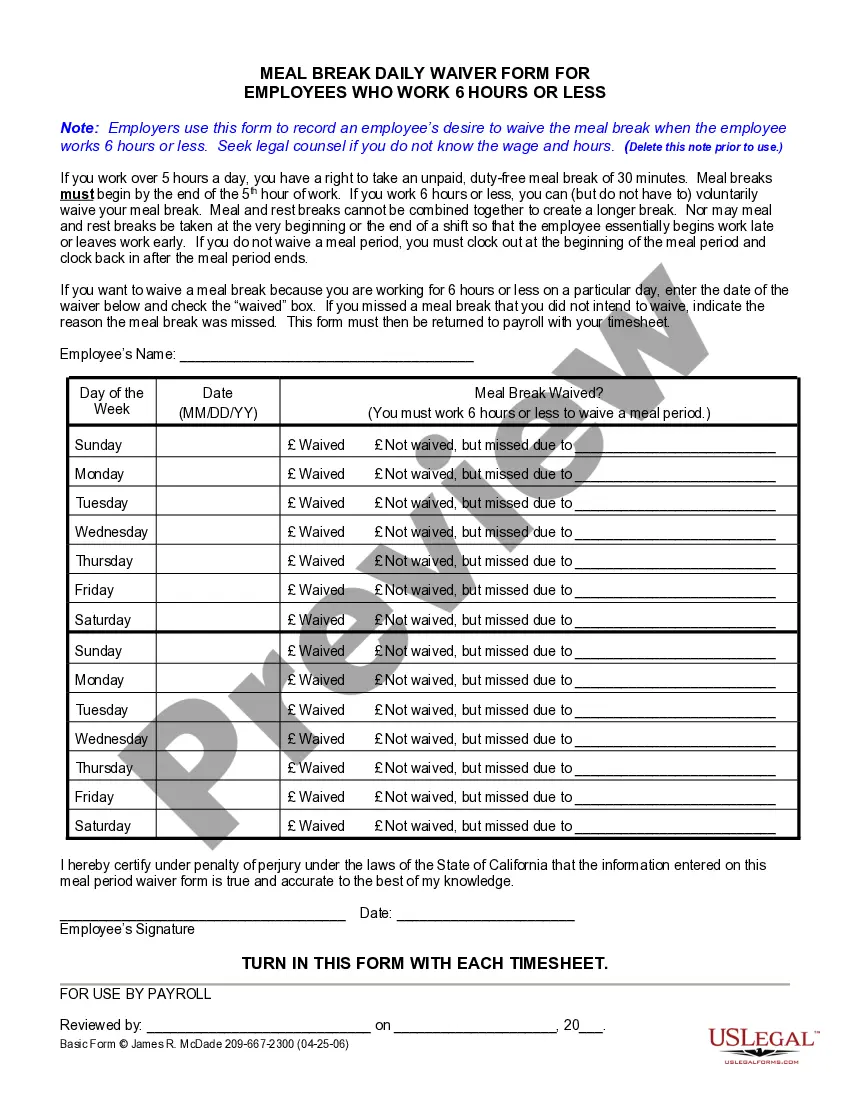
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.