North Dakota Limitations on Additional Proposals
Description
How to fill out Limitations On Additional Proposals?
Are you presently inside a situation that you need papers for sometimes company or specific purposes nearly every time? There are a lot of authorized file web templates available on the Internet, but finding ones you can depend on isn`t simple. US Legal Forms offers a large number of kind web templates, just like the North Dakota Limitations on Additional Proposals, which are created in order to meet federal and state requirements.
When you are already familiar with US Legal Forms internet site and get a merchant account, simply log in. Following that, you can obtain the North Dakota Limitations on Additional Proposals template.
If you do not come with an account and would like to start using US Legal Forms, abide by these steps:
- Obtain the kind you want and make sure it is for the correct area/county.
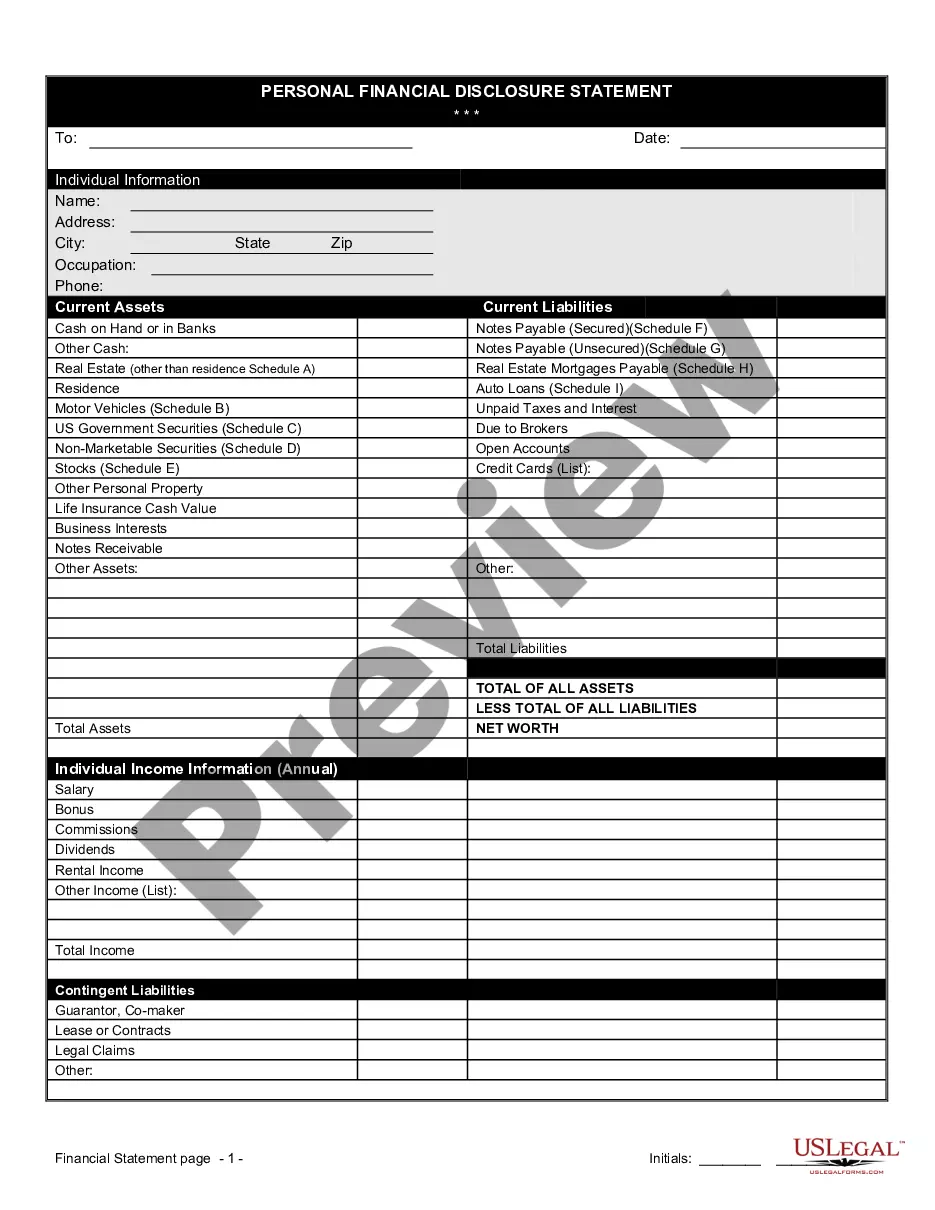
- Make use of the Preview switch to check the form.
- Browse the explanation to ensure that you have chosen the right kind.
- In case the kind isn`t what you are trying to find, make use of the Research discipline to discover the kind that meets your needs and requirements.
- Once you find the correct kind, click on Purchase now.
- Pick the pricing strategy you desire, complete the necessary information to create your bank account, and pay for an order making use of your PayPal or charge card.
- Pick a convenient file format and obtain your version.
Discover all of the file web templates you possess purchased in the My Forms menu. You can obtain a additional version of North Dakota Limitations on Additional Proposals at any time, if needed. Just click the essential kind to obtain or printing the file template.
Use US Legal Forms, the most extensive variety of authorized kinds, to save time as well as stay away from mistakes. The service offers professionally made authorized file web templates that can be used for a selection of purposes. Generate a merchant account on US Legal Forms and initiate producing your daily life easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
A bill is a proposed law as introduced in the Legislature. The bill does not become a law (an "act"or "statute") until passed by the Legislature and signed by the Governor or passed over the Governor's veto.
[¶5] Section 28-01-18, N.D.C.C., provides that an action for libel or slander must be commenced within two years after the claim for relief has accrued. A cause of action accrues on a defamation claim when the publication of the false statement is made to a third party.
North Dakota Civil Statute of Limitations: At a Glance Time limits for filing civil lawsuits in North Dakota range from two to 10 years, with a six-year statute of limitations for most civil actions.
A bill to create a new law can be introduced in either chamber of Congress by a senator or representative who sponsors it. Once a bill is introduced, it is assigned to a committee whose members will research, discuss, and make changes to the bill. The bill is then put before that chamber to be voted on.
The Legislative Process. The first step in the legislative process is the introduction of a bill to Congress. Anyone can write it, but only members of Congress can introduce legislation. Some important bills are traditionally introduced at the request of the President, such as the annual federal budget.
80-day limit - Section 7, Article IV of the Constitution of North Dakota states "No regular session of the legislative assembly may exceed eighty natural days during the biennium." Interim preparations - Studies from session bills and resolutions are prioritized and assigned to committees.
Bills may be introduced by members of the Legislative Assembly, standing committees, or the Legislative Management. A state executive agency or the North Dakota Supreme Court can have bills automatically introduced in the name of the standing committee to which the bill will be referred.
Every bill passed by the legislative assembly must be presented to the governor for the governor's signature. If the governor signs the bill, it becomes law. The governor may veto a bill passed by the legislative assembly. The governor may veto items in an appropriation bill.