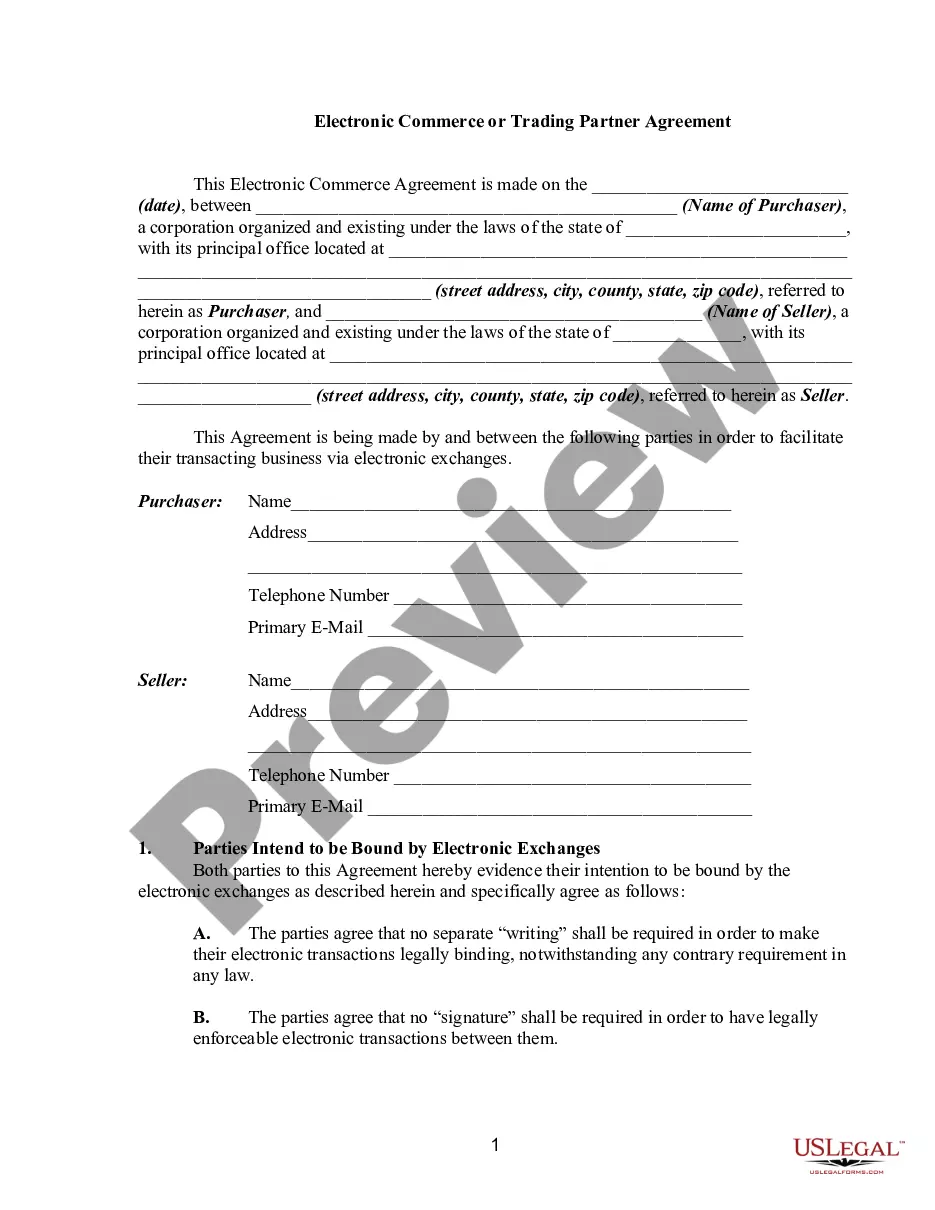
Nebraska Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement
Description
How to fill out Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement?
You may commit hrs on the web attempting to find the authorized document design that meets the state and federal requirements you will need. US Legal Forms supplies a large number of authorized forms that happen to be reviewed by experts. It is simple to acquire or print out the Nebraska Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement from your support.
If you currently have a US Legal Forms profile, you may log in and click the Acquire key. After that, you may full, edit, print out, or indication the Nebraska Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement. Each authorized document design you buy is your own for a long time. To acquire yet another duplicate of any bought type, visit the My Forms tab and click the corresponding key.
If you use the US Legal Forms website the first time, keep to the straightforward directions beneath:
- First, be sure that you have selected the best document design for the region/metropolis of your choosing. See the type information to ensure you have chosen the appropriate type. If accessible, utilize the Preview key to check from the document design too.
- If you want to locate yet another variation in the type, utilize the Look for discipline to obtain the design that meets your needs and requirements.
- When you have discovered the design you want, click on Purchase now to carry on.
- Choose the prices program you want, enter your credentials, and sign up for a free account on US Legal Forms.
- Complete the transaction. You can utilize your charge card or PayPal profile to pay for the authorized type.
- Choose the structure in the document and acquire it for your gadget.
- Make alterations for your document if possible. You may full, edit and indication and print out Nebraska Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement.
Acquire and print out a large number of document web templates while using US Legal Forms Internet site, which provides the largest collection of authorized forms. Use skilled and state-distinct web templates to handle your company or personal needs.