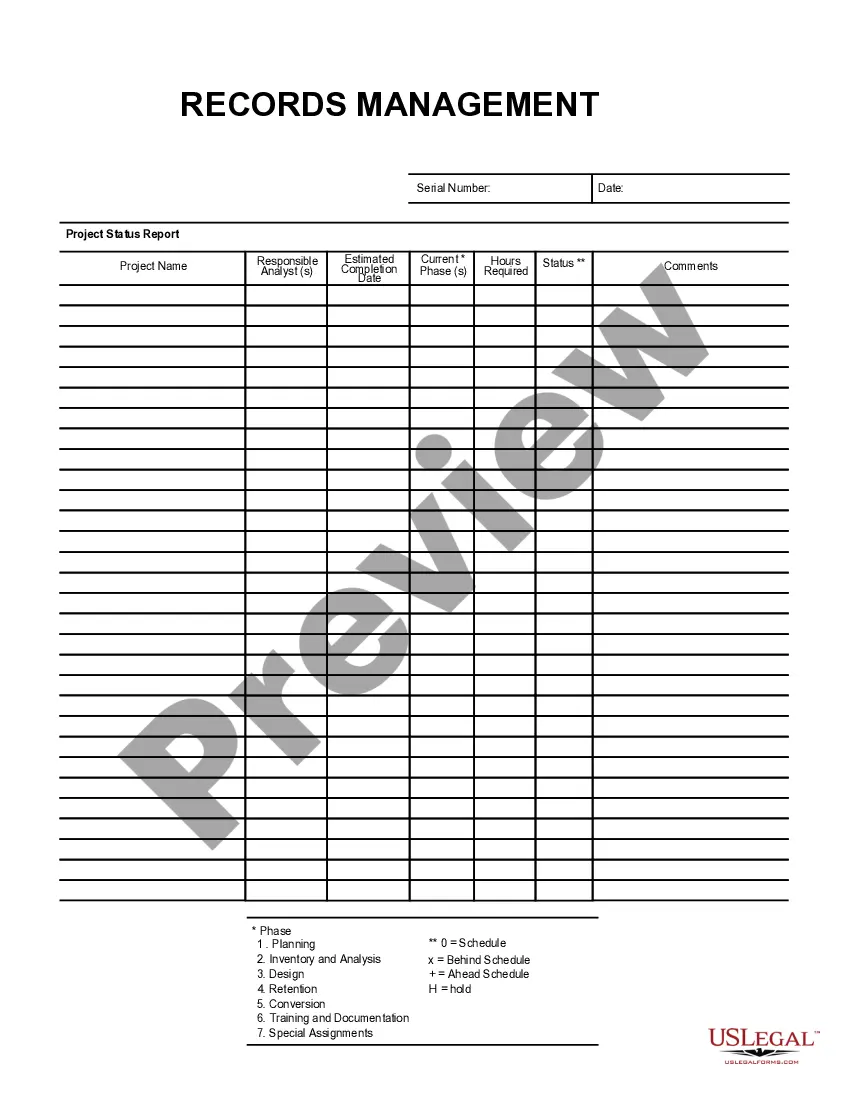
New Hampshire Filing System for a Business
Description
How to fill out Filing System For A Business?
You might spend hours online searching for the official document template that fulfills the federal and state requirements you need.
US Legal Forms offers a vast array of legal forms that are vetted by professionals.
It is easy to obtain or print the New Hampshire Filing System for a Business from my service.
If available, utilize the Review button to examine the document template as well.
- If you possess a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and hit the Download button.
- Then, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the New Hampshire Filing System for a Business.
- Every legal document template you purchase is yours permanently.
- To obtain another copy of any acquired form, visit the My documents tab and click the relevant button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the simple instructions below.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct document template for the area/city of your choice.
- Check the form description to confirm you have picked the right form.
Form popularity
FAQ
Does New Hampshire Have Income Tax? No, but New Hampshire businesses are responsible for filing and paying Business Profits Tax and Business Enterprise Tax. Owners may also be subject to the 5% Interest/Dividends tax from distributions they received from their corporations.
If you had no income, you must file the corporation income tax return, regardless of whether you had expenses or not. The bottom line is: No income, no expenses = Filing Form 1120 / 1120-S is necessary.
Individuals: Individuals who are residents or inhabitants of New Hampshire for any part of the tax year must file a return if they received more than $2,400 of gross interest and/or dividend income for a single individual or $4,800 of such income for a married couple filing a joint New Hampshire return.
All business organizations, including single member Limited Liability Companies (SMLLC), taxed as a corporation federally must file a Form NH-1120 return provided they have conducted business activity in New Hampshire and their gross business income from everywhere is in excess of $50,000.
New Hampshire does not tax individuals' earned income, so you are not required to file an individual New Hampshire tax return. The state only taxes interest and dividends at 5% on residents and fiduciaries whose gross interest and dividends income, from all sources, exceeds $2,400 annually ($4,800 for joint filers).
All business organizations, including corporations, fiduciaries, partnerships, proprietorships, combined groups, and homeowners' associations must file a Business Profits Tax return provided they are carrying on business activity within New Hampshire and their gross business income from everywhere is in excess of
New Hampshire does not tax individuals' earned income, so you are not required to file an individual New Hampshire tax return. The state only taxes interest and dividends at 5% on residents and fiduciaries whose gross interest and dividends income, from all sources, exceeds $2,400 annually ($4,800 for joint filers).
The state of New Hampshire requires all New Hampshire corporations, LLCs, and LLPs to file an annual report each year. New Hampshire nonprofits must file a report every five years. All reports must be submitted to the New Hampshire Department of State, Corporations Division.
All business organizations, including corporations, fiduciaries, partnerships, proprietorships, combined groups, and homeowners' associations must file a Business Profits Tax return provided they are carrying on business activity within New Hampshire and their gross business income from everywhere is in excess of