New Hampshire Issuance of Common Stock in Connection with Acquisition
Description
How to fill out Issuance Of Common Stock In Connection With Acquisition?
Are you presently in the situation where you need papers for either business or person reasons just about every day time? There are tons of authorized file templates available on the Internet, but discovering types you can trust is not effortless. US Legal Forms gives a huge number of form templates, just like the New Hampshire Issuance of Common Stock in Connection with Acquisition, which are created in order to meet state and federal requirements.
Should you be already informed about US Legal Forms internet site and get a merchant account, basically log in. Next, you are able to acquire the New Hampshire Issuance of Common Stock in Connection with Acquisition format.
If you do not provide an profile and wish to start using US Legal Forms, abide by these steps:
- Obtain the form you will need and make sure it is for your proper town/county.
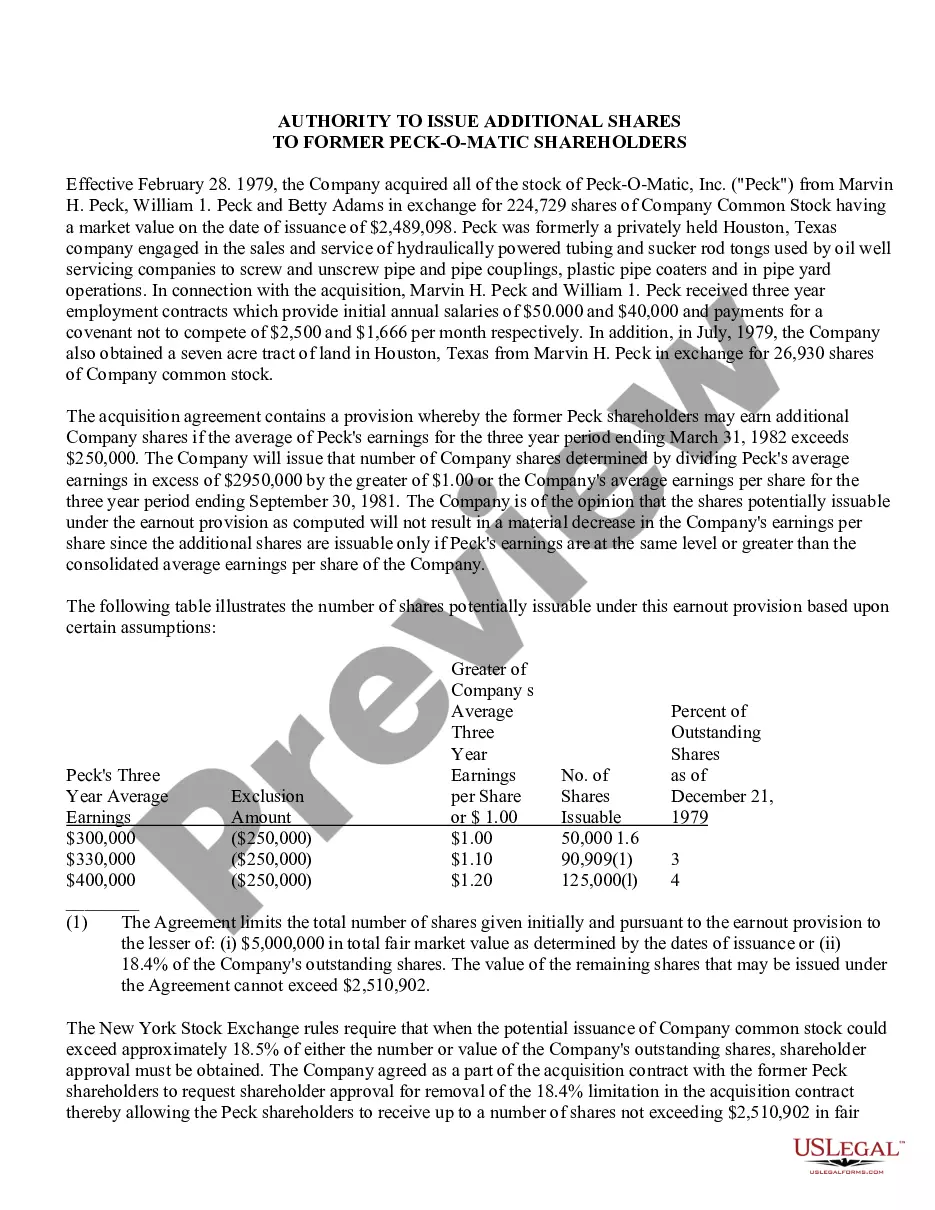
- Take advantage of the Preview button to review the form.
- Read the information to ensure that you have chosen the right form.
- When the form is not what you are searching for, make use of the Lookup field to discover the form that fits your needs and requirements.
- Once you find the proper form, click on Purchase now.
- Opt for the prices strategy you would like, submit the specified details to produce your money, and purchase the order utilizing your PayPal or bank card.
- Pick a hassle-free file formatting and acquire your backup.
Locate each of the file templates you have bought in the My Forms menus. You can aquire a further backup of New Hampshire Issuance of Common Stock in Connection with Acquisition at any time, if necessary. Just go through the essential form to acquire or print the file format.
Use US Legal Forms, by far the most considerable assortment of authorized forms, to conserve efforts and avoid blunders. The support gives appropriately created authorized file templates that you can use for a selection of reasons. Make a merchant account on US Legal Forms and begin making your lifestyle a little easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
An agreement setting out steps of a merger of two or more entities including the terms and conditions of the merger, parties, the consideration, conversion of equity, and information about the surviving entity (such as its governing documents).
Parts of merger and acquisition contracts ?Parties and recitals. ?Price, currencies, and structure. ?Representations and warranties. ?Covenants. ?Conditions. ?Termination provisions. ?Indemnification. ?Tax.
?parties? means Parent, Merger Sub and the Company.
Common Per Share Merger Consideration means an amount equal to the quotient of (x) the Common Stock Merger Consideration, divided by (y) the sum of (i) the total number of shares of Common Stock outstanding as of immediately prior to the Effective Time, (ii) the total number of shares of Common Stock that would be ...
Merger Termination Date means the date on which the Merger Agreement terminates pursuant to a final and non-appealable judgment, injunction, order or decree of the Federal Trade Commission prohibiting the consummation of the Merger.
In a merger, two separate legal entities come together to form a new joint legal entity. In an acquisition, one company (the acquirer) buys another company (the target) and takes control of its assets and operations.
Every M&A transaction involves at least one purchaser, or buyer, the party that will be making the acquisition. This is the person (i.e., individual or company) that signs the purchase agreement, pays the purchase price and which, after closing, directly or indirectly, owns or controls the target company or its assets.
There are two basic merger structures: direct and indirect. In a direct merger, the target company and the buying company directly merge with each other. In an indirect merger, the target company will merge with a subsidiary company of the buyer.