New Hampshire Ratification
Description
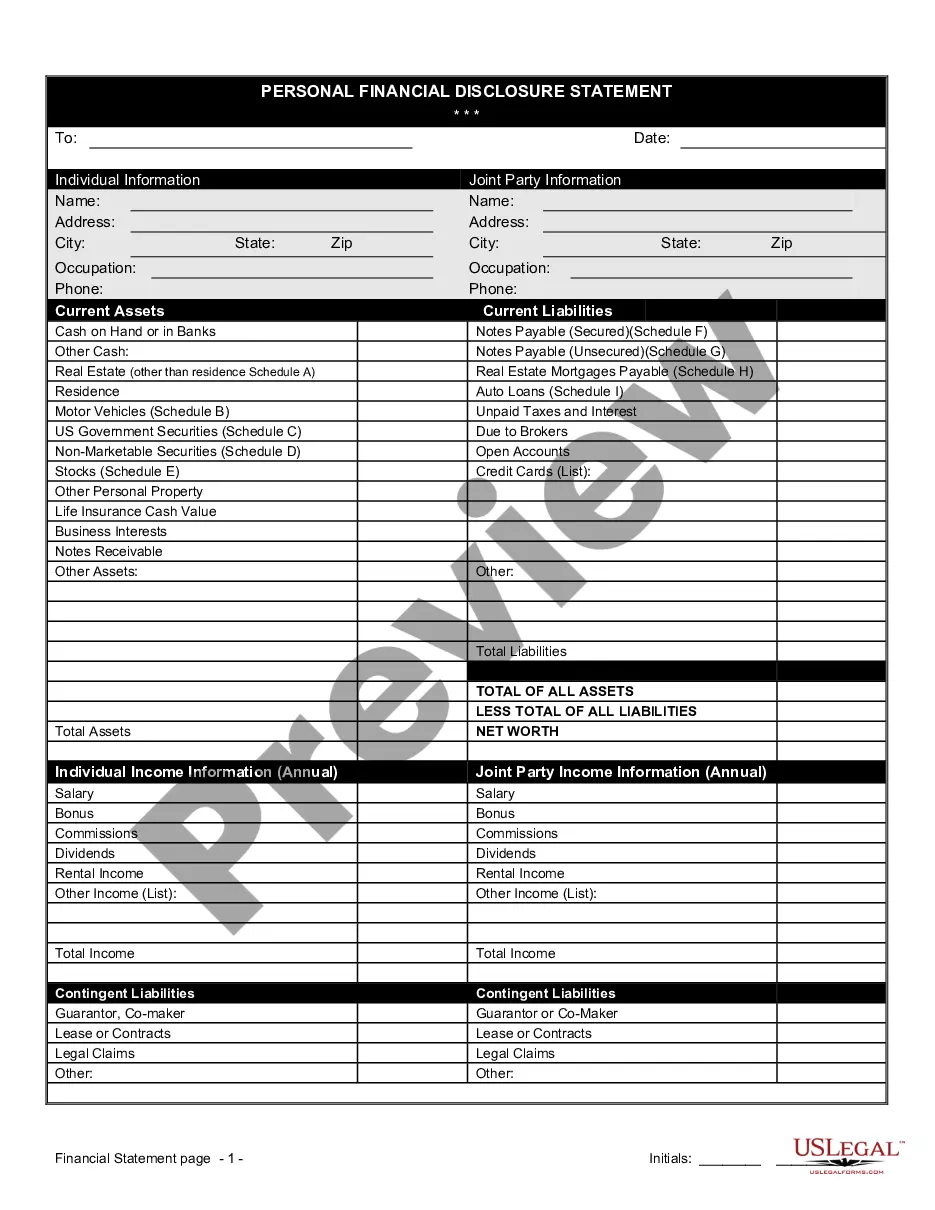
How to fill out Ratification?
You can spend time online trying to find the legitimate record design that fits the state and federal requirements you require. US Legal Forms gives thousands of legitimate varieties that are examined by professionals. You can actually obtain or produce the New Hampshire Ratification from the assistance.
If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you are able to log in and then click the Down load switch. Afterward, you are able to comprehensive, modify, produce, or signal the New Hampshire Ratification. Every single legitimate record design you acquire is your own for a long time. To acquire one more copy of any bought develop, proceed to the My Forms tab and then click the corresponding switch.
If you are using the US Legal Forms site the very first time, follow the easy guidelines beneath:
- First, ensure that you have selected the right record design for that state/city that you pick. Look at the develop outline to make sure you have selected the right develop. If available, use the Review switch to check with the record design as well.
- In order to get one more variation of your develop, use the Search area to obtain the design that meets your needs and requirements.
- After you have located the design you would like, just click Buy now to move forward.
- Find the rates plan you would like, type in your qualifications, and sign up for a free account on US Legal Forms.
- Comprehensive the purchase. You may use your bank card or PayPal account to purchase the legitimate develop.
- Find the structure of your record and obtain it in your system.
- Make adjustments in your record if necessary. You can comprehensive, modify and signal and produce New Hampshire Ratification.
Down load and produce thousands of record templates utilizing the US Legal Forms website, which offers the biggest selection of legitimate varieties. Use skilled and status-distinct templates to handle your business or specific requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
The founders set the terms for ratifying the Constitution. They bypassed the state legislatures, reasoning that their members would be reluctant to give up power to a national government. Instead, they called for special ratifying conventions in each state. Ratification by 9 of the 13 states enacted the new government.
The Constitution was not ratified by all states until , when Rhode Island finally approved the document, and the Bill of Rights was not ratified to become part of the Constitution until the end of the following year.
Ratification. The process set out in the Constitution for its ratification provided for much popular debate in the States. The Constitution would take effect once it had been ratified by nine of the thirteen State legislatures; unanimity was not required.
The founders set the terms for ratifying the Constitution. They bypassed the state legislatures, reasoning that their members would be reluctant to give up power to a national government. Instead, they called for special ratifying conventions in each state. Ratification by 9 of the 13 states enacted the new government.
The states and the dates of ratification are listed here, in order of ratification: Delaware: December 7, 1787. Pennsylvania: December 12, 1787. New Jersey: December 18, 1787. Georgia: January 2, 1788. Connecticut: January 9, 1788. Massachusetts: February 6, 1788. Maryland: April 28, 1788. South Carolina: .
Each state holds a ratifying convention. Each state convention debate vote to ratify/ reject. Once a states approve constitution is officially ratified (New Hampshire)
Mode 1: Constitutional Ratification Process (Article V) Congress must pass a proposed amendment by a two-thirds majority vote in both the Senate and the House of Representatives and send it to the states for ratification by a vote of the state legislatures.