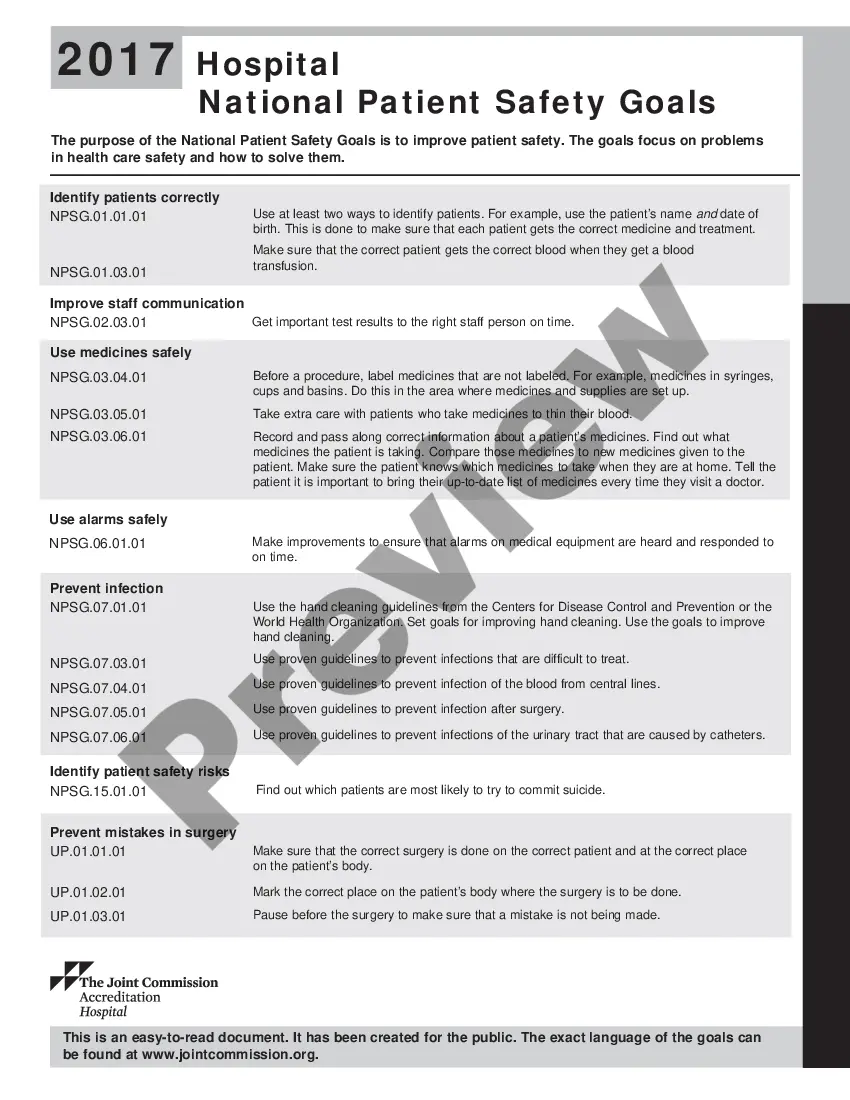
The New Jersey Hospital National Patient Safety Goals (NJH-NPSGs) comprise a set of guidelines established by the New Jersey Department of Health (NJ DOH) to ensure patient safety and prevent medical errors within hospitals across the state. These goals are aligned with the broader National Patient Safety Goals (Nests) developed by The Joint Commission, a leading healthcare accrediting organization. The NJH-NPSGs are designed to address specific areas of potential harm and enhance patient care standards in New Jersey hospitals. By adhering to these goals, healthcare providers strive to enhance the overall quality and safety of healthcare delivery. Below are some key components of the NJH-NPSGs: 1. Identification verification: Accurately identifying patients to prevent errors and ensure correct procedures and medications are administered. This goal emphasizes using at least two patient identifiers, such as name and date of birth, before providing care. 2. Improve communication: Enhancing communication across multidisciplinary teams to prevent errors, miscommunications, and misunderstandings. This involves clear and concise exchange of information about patients' conditions, treatment plans, and medication orders. 3. Medication safety: Ensuring safe medication practices by conducting medication reconciliations, correctly labeling medications, and reducing the risk of adverse drug interactions. Hospitals are encouraged to establish protocols for safe prescribing, administration, and monitoring of medications. 4. Infection prevention: Implementing strategies to prevent healthcare-associated infections (His) and promoting proper hand hygiene. Hospitals are required to assess and manage risks associated with infections, encourage vaccination, and follow evidence-based practices for infection control. 5. Surgical safety: Reducing the potential for surgical errors and complications by implementing surgical-site verification processes, conducting comprehensive preoperative assessments, and preventing wrong-site, wrong-procedure, or wrong-patient surgeries. 6. Fall prevention: Implementing strategies to minimize the risk of patient falls and related injuries. This includes assessing patients' fall risk, implementing preventive measures (e.g., bed alarms, frequent rounding), and educating both patients and their families about fall prevention. 7. Emergency preparedness: Ensuring hospitals are well-prepared for emergencies and disasters. This includes implementing effective emergency response plans, conducting drills and exercises, and ensuring staff is trained in disaster management. These are some primary NJH-NPSGs, but various additional goals and measures may be incorporated based on updates, emerging trends, or specific hospital settings. It is crucial for healthcare organizations to stay updated with the latest goals and guidelines specified by the NJ DOH to improve patient safety and provide quality care.
New Jersey Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out New Jersey Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
Are you presently in a position that you need to have files for either company or specific reasons almost every day? There are a variety of lawful papers layouts available on the Internet, but finding kinds you can rely on is not straightforward. US Legal Forms delivers a huge number of kind layouts, like the New Jersey Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, which can be created to satisfy federal and state specifications.
When you are already informed about US Legal Forms internet site and get a free account, simply log in. Afterward, it is possible to obtain the New Jersey Hospital National Patient Safety Goals format.
Unless you come with an bank account and need to begin using US Legal Forms, adopt these measures:
- Get the kind you will need and ensure it is for that correct metropolis/area.
- Take advantage of the Preview button to analyze the form.
- See the explanation to actually have chosen the proper kind.
- In case the kind is not what you are searching for, make use of the Search area to obtain the kind that suits you and specifications.
- Once you get the correct kind, simply click Get now.
- Pick the prices plan you would like, fill in the required details to create your money, and pay for an order with your PayPal or Visa or Mastercard.
- Decide on a convenient data file structure and obtain your duplicate.
Find every one of the papers layouts you possess bought in the My Forms menu. You may get a further duplicate of New Jersey Hospital National Patient Safety Goals anytime, if necessary. Just go through the needed kind to obtain or produce the papers format.
Use US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive collection of lawful varieties, to save time as well as avoid blunders. The assistance delivers expertly produced lawful papers layouts which can be used for a range of reasons. Create a free account on US Legal Forms and initiate producing your life easier.