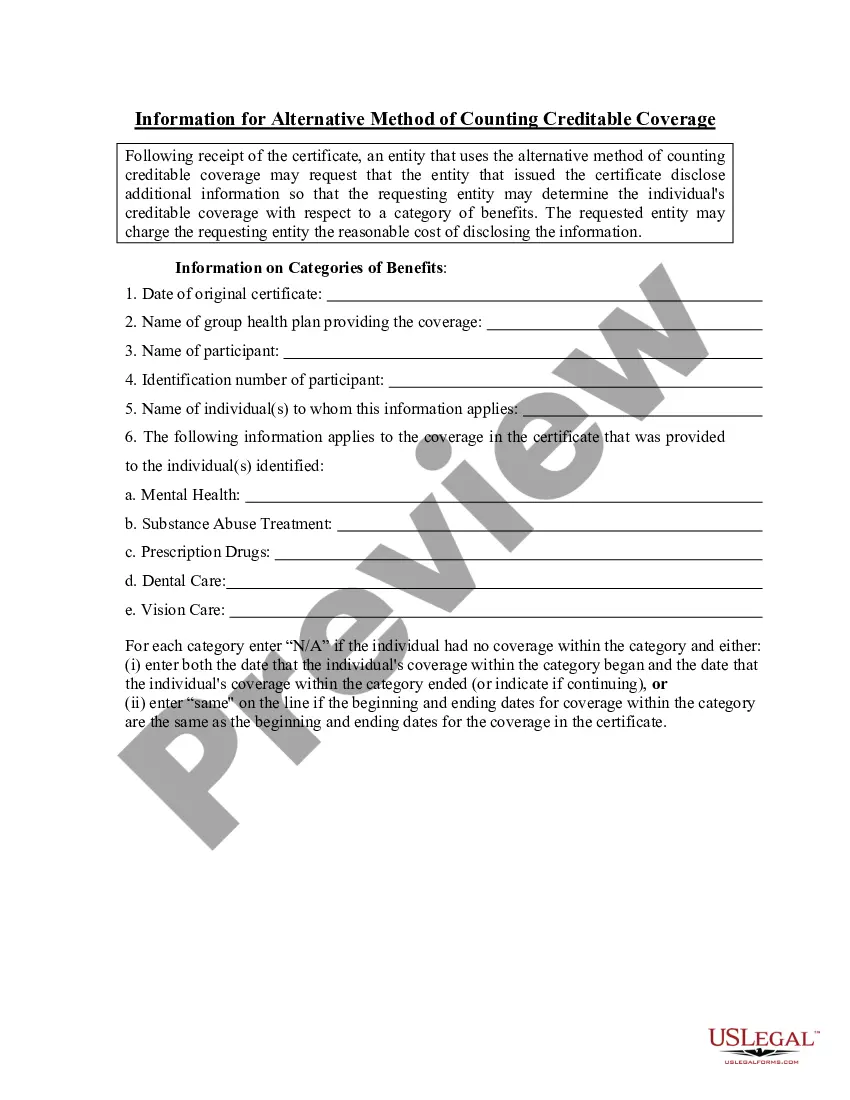
New Jersey Information for Alternative Method of Counting Creditable Coverage
Description
How to fill out Information For Alternative Method Of Counting Creditable Coverage?
Finding the appropriate official document template can be quite a challenge.
Of course, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how can you obtain the official form you require.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. This service provides thousands of templates, including the New Jersey Information for Alternative Method of Counting Creditable Coverage, which can be utilized for both business and personal needs.
Firstly, ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/state. You can view the form using the Preview button and read the form description to verify it's the right one for you.
- All the documents are vetted by experts and comply with state and federal regulations.
- If you are already registered, Log Into your account and hit the Download button to acquire the New Jersey Information for Alternative Method of Counting Creditable Coverage.
- Use your account to search for the official forms you have purchased before.
- Go to the My documents section of your account to obtain another version of the document you need.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are straightforward steps for you to follow.
Form popularity
FAQ
The PAAD program income limits are now $38,769 if single and $45,270 for a couple. The Senior Gold Prescription Discount program limits are now $48,769 if single and $55,270 if married. Assets are not an eligibility consideration for either program.
A certificate of Creditable Coverage (COCC) is a document provided by your previous insurance carrier that proves that your insurance has ended. This includes the name of the member to whom it applies as well as the coverage effective date and cancelation date.
Creditable coverage is a health insurance or health benefit plan that meets a minimum set of qualifications. Some examples include group and individual health plans, student health plans, and government-provided plans.
Do NOT include wages and self-employment income, interest income, public assistance, Social Security Benefits, dividends, medical reimbursements or foster care payments here.
Non-creditable coverage: A health plan's prescription drug coverage is non-creditable when the amount the plan expects to pay, on average, for prescription drugs for individuals covered by the plan in the coming year is less than that which standard Medicare prescription drug coverage would be expected to pay.
The Notice of Creditable Coverage works as proof of your coverage when you first become eligible for Medicare. Those who have creditable coverage through an employer or union receive a Notice of Creditable Coverage in the mail each year. This notice informs you that your current coverage is creditable.
PAAD recipients won't pay more than $5 for generic drugs and $7 for brand name drugs. Senior Gold gives a discounts on any medication with a copay higher than $15 and lowers the out of pocket amount you need to pay before qualifying for the catestrophic phase of Part D prescription coverage.
In addition to helping the elderly with the cost of their medications, PAAD provides assistance with co-payments and monthly premiums for Medicare Part D, which is prescription drug coverage through Medicare. Both programs are designed to work collaboratively with a Medicare Part D plan.
The Pharmaceutical Assistance to the Aged and Disabled (PAAD) program is a state-funded program that helps eligible seniors and individuals with disabilities save money on their prescription drug costs.
You may be eligible for PAAD if you meet the following requirements: You are a New Jersey resident; You are age 65 or older or between ages 18 and 64 and receiving Social Security Title II Disability benefits; and. Your income for 2022 is less than $38,769 if single or less than $45,270 if married.