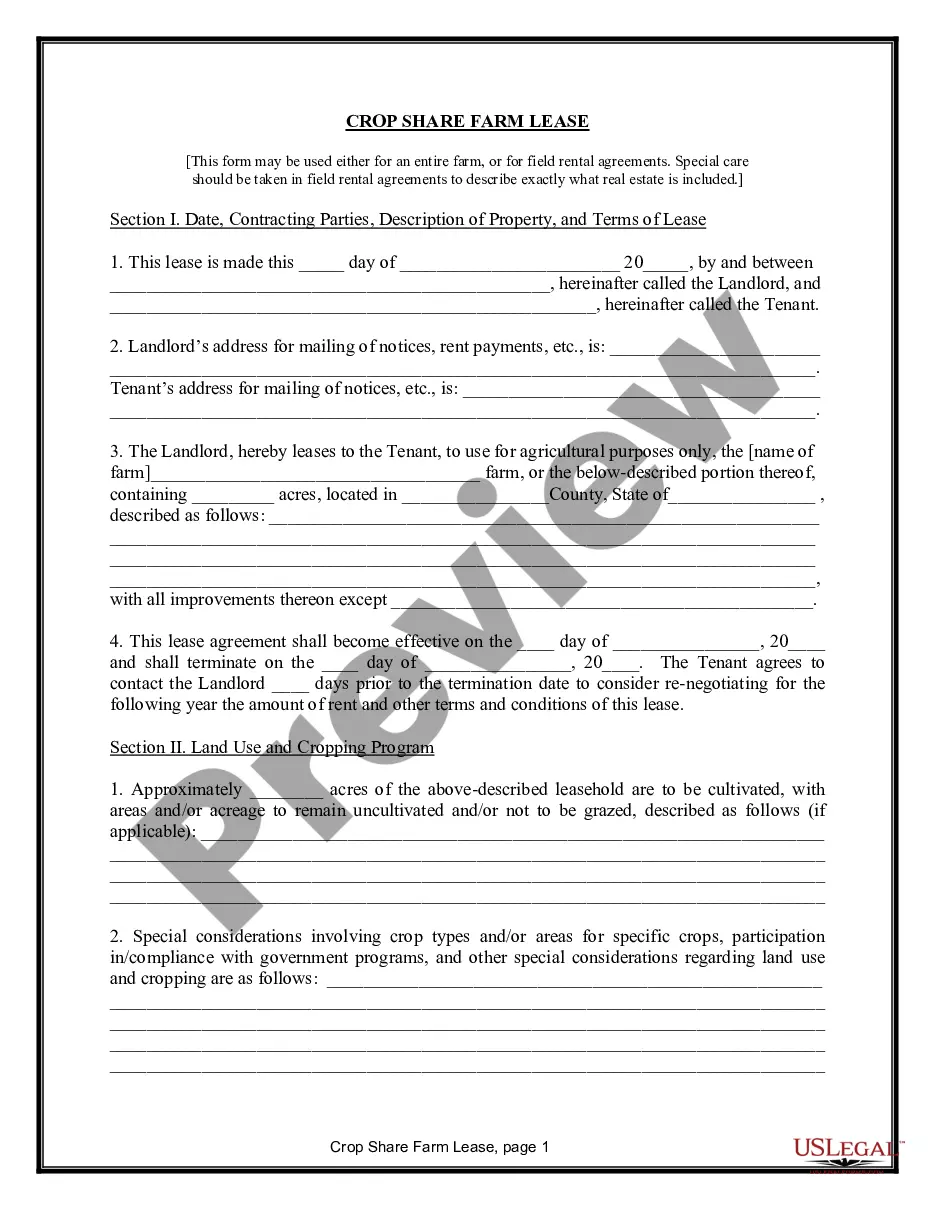
Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement
Description
How to fill out Sharecropping Contract Or Agreement?
Are you now situated in the location where you need documents for either business or personal reasons almost all the time.
There are numerous authentic document templates available online, but finding ones you can trust isn't simple.
US Legal Forms provides thousands of form templates, such as the Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement, which are designed to satisfy state and federal regulations.
Once you discover the appropriate form, click Purchase now.
Select the pricing plan you desire, fill in the necessary details to create your account, and purchase the order using your PayPal or credit card.
- If you are already aware of the US Legal Forms website and possess an account, simply Log In.
- Then, you can download the Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement template.
- If you do not have an account and wish to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps.
- Locate the form you need and ensure it is for your specific city/state.
- Use the Review option to examine the form.
- Read the description to ensure you have chosen the right form.
- If the form is not what you are searching for, use the Search area to find the form that suits your needs and requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
A sharecropping contract is a legal document outlining the arrangement between a landowner and a farmer, where the farmer is allowed to cultivate the land and share a portion of the harvest. This agreement aims to support agricultural production while providing a livelihood to those who may not own land. Understanding the elements of a Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement is crucial for anyone entering into such an arrangement, and platforms like uslegalforms can provide valuable resources.
The fairness of a sharecropping contract largely depends on the specific terms outlined within it. While some contracts provide equitable distributions of crops and responsibilities, others may favor the landowner significantly. To determine the fairness of a Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement, both parties should carefully review its clauses, ensuring mutual benefits are established before agreeing.
The sharecropper contract was an agreement between landowners and farmers where the farmers worked the land in exchange for a share of the crops produced. This arrangement was common in agricultural areas like Nevada, helping to ensure that both parties had a vested interest in the success of the crop. It's important to understand the details of a Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement to ensure fair terms for all involved.
Sharecropping is a farming arrangement where a farmer works on a landowner's property and shares the crops produced. In simple terms, the farmer gets to use the land without owning it and pays the landowner with a portion of the harvest. This system allows farmers to grow crops while providing landowners with a return on their investment. A clear Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement captures this relationship, promoting transparency and cooperation between parties.
A sharecropping contract is a legal agreement between a landowner and a farmer. In this arrangement, the farmer cultivates the land and, in return, shares a portion of the profits with the landowner. This type of contract is essential in Nevada as it defines the roles and responsibilities of each party, ensuring clarity and fairness in the farming process. Utilizing a Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement can help prevent disputes and foster a productive partnership.
Landowners provided several essential resources to sharecroppers, including land for farming and necessary tools for cultivation. These provisions often extended to financial assistance for inputs like seeds and fertilizers, creating a framework for both parties to succeed. By offering such support within a Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement, landowners aimed to ensure fruitful harvests while fostering a reliable labor system.
A sharecropping agreement in Nevada usually specifies the support provided by the landowner. This can include land access, farming equipment, and sometimes initial funding for seeds and fertilizers. By clearly laying out what is provided, the Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement fosters a cooperative relationship that benefits both the landowner and the sharecropper.
In a Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement, landowners typically provide land to sharecroppers for cultivation. They may also supply tools, seeds, and sometimes even housing or financial support. By offering these resources, landowners enable sharecroppers to work the land and produce crops, ultimately earning a share of the yield.
A sharecropping contract was a legal agreement defining the relationship between landowners and sharecroppers. It typically included provisions on how the crops would be divided and the expectations for labor and land use. This contract aimed to formalize the arrangement and protect the interests of both parties while facilitating agricultural production under the framework of a Nevada Sharecropping Contract or Agreement.
The contract between sharecroppers generally involved agreements on the distribution of crops and the obligations of each party. Sharecroppers would agree to cultivate land owned by landowners while sharing a significant portion of the harvested crops in return. These agreements were often seen as a necessity for many agricultural workers who sought to earn a living in a challenging economic environment, similar to modern Nevada Sharecropping Contracts or Agreements.