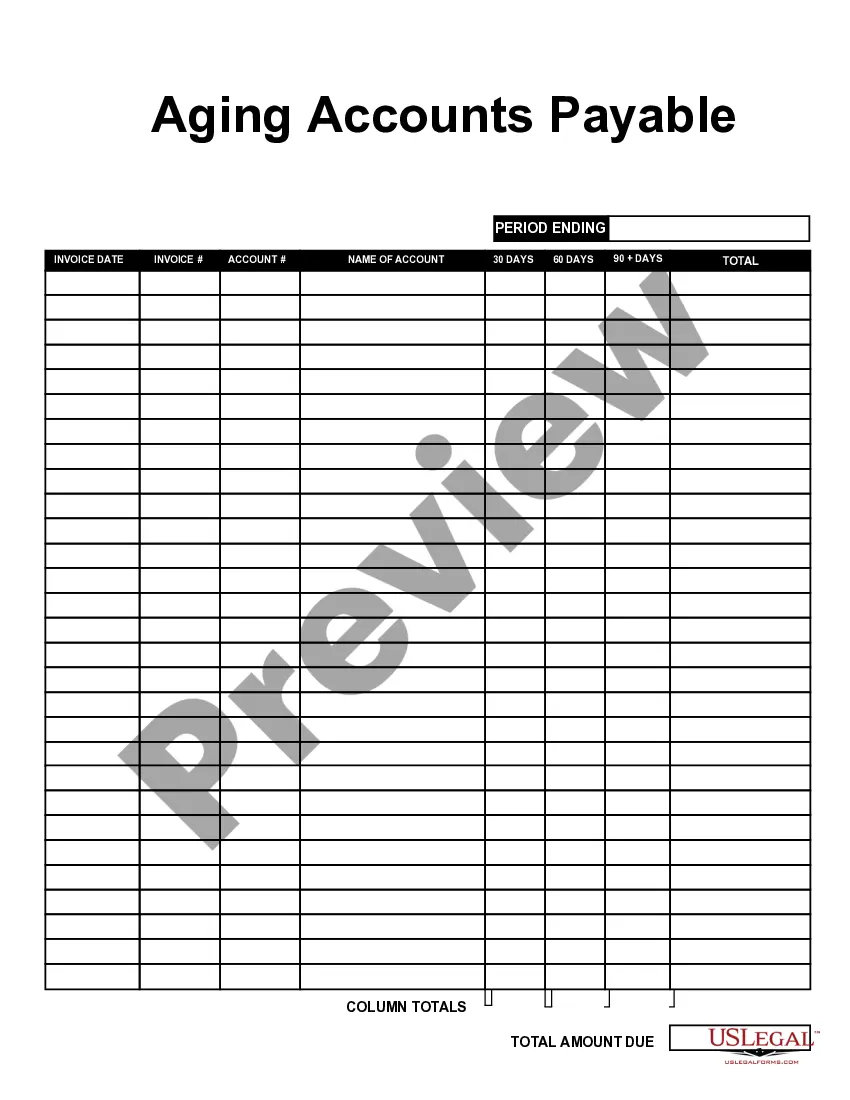
Nevada Aging of Accounts Payable
Description
How to fill out Aging Of Accounts Payable?
You can devote time online seeking the valid document format that satisfies the federal and state requirements you need.
US Legal Forms provides a vast array of valid templates that are evaluated by professionals.
You can effortlessly acquire or print the Nevada Aging of Accounts Payable from our service.
If available, use the Preview button to take a look at the document format as well.
- If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you can sign in and click the Download button.
- After that, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the Nevada Aging of Accounts Payable.
- Every valid document template you purchase is yours forever.
- To obtain an additional copy of the acquired form, visit the My documents tab and click the appropriate button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the basic instructions below.
- First, make sure you have selected the correct template for the state/city that you choose.
- Review the template details to ensure you have chosen the correct form.
Form popularity
FAQ
Filing state taxes in Nevada involves submitting the appropriate forms to the Nevada Department of Taxation. You can file online for convenience or send your forms by mail. Using tools like USLegalForms can help you prepare and organize the necessary documents, ensuring that your Nevada Aging of Accounts Payable does not hinder your filing process.
The Nevada commerce tax rate varies depending on your business type and gross revenue. Rates can range from 0.051 percent to 0.331 percent based on your revenue bracket. By staying informed about your expenses, especially through effective management of the Nevada Aging of Accounts Payable, you can predict and manage your tax liabilities.
If your business has gross revenues over $4 million, you are required to file a Nevada commerce tax return. Even if your total revenue fluctuates, it's wise to evaluate your finances regularly. Utilizing the Nevada Aging of Accounts Payable can help you manage your finances better and prepare for any potential tax filings.
To close your Nevada modified business tax account, you need to complete the appropriate forms available from the Nevada Department of Taxation. Ensure that all tax liabilities are settled before closing the account. If you have been using an organized financial approach, such as the Nevada Aging of Accounts Payable, this process will be much smoother.
Any business with gross revenue exceeding $4 million must file a Nevada commerce tax return. Even if your business operates below this threshold, it's wise to keep track of revenues to avoid potential issues. Understanding the Nevada Aging of Accounts Payable will also help you make informed decisions about your financial responsibilities.
To file the Nevada modified business tax, you can submit your return online via the Nevada Department of Taxation website. You may also file by mail, but online submission is more efficient and typically faster. If you manage your accounts payable effectively using tools like USLegalForms, it can streamline your filing process and help you stay organized.
Yes, you generally need to file a Nevada tax return if you meet certain income thresholds. It's crucial to understand the specifics of your situation, especially if you are involved in business operations. The Nevada Aging of Accounts Payable can impact your tax obligations, so consider consulting with an expert to ensure compliance.
The difference between AP and AR aging lies in their focus: AP aging centers on what your business owes, whereas AR aging looks at what is owed to your business. Understanding this distinction is crucial for effective financial management, especially when implementing the Nevada aging of accounts payable framework. This approach helps businesses prioritize payments and collect debts efficiently.
Accelerated aging focuses on older accounts that are more urgent, while real-time aging provides a current overview of all outstanding invoices. The Nevada aging of accounts payable typically utilizes both methods to ensure companies address immediate financial obligations while also keeping track of overall debts. Utilizing these approaches aids in proactive financial management.
To prepare the Nevada aging of accounts payable report, you will collect data from your accounting records and bookkeeping software. This includes details of all outstanding invoices and payment terms, which provide insights into your current obligations. Accurate data collection is crucial for creating a reliable aging report.