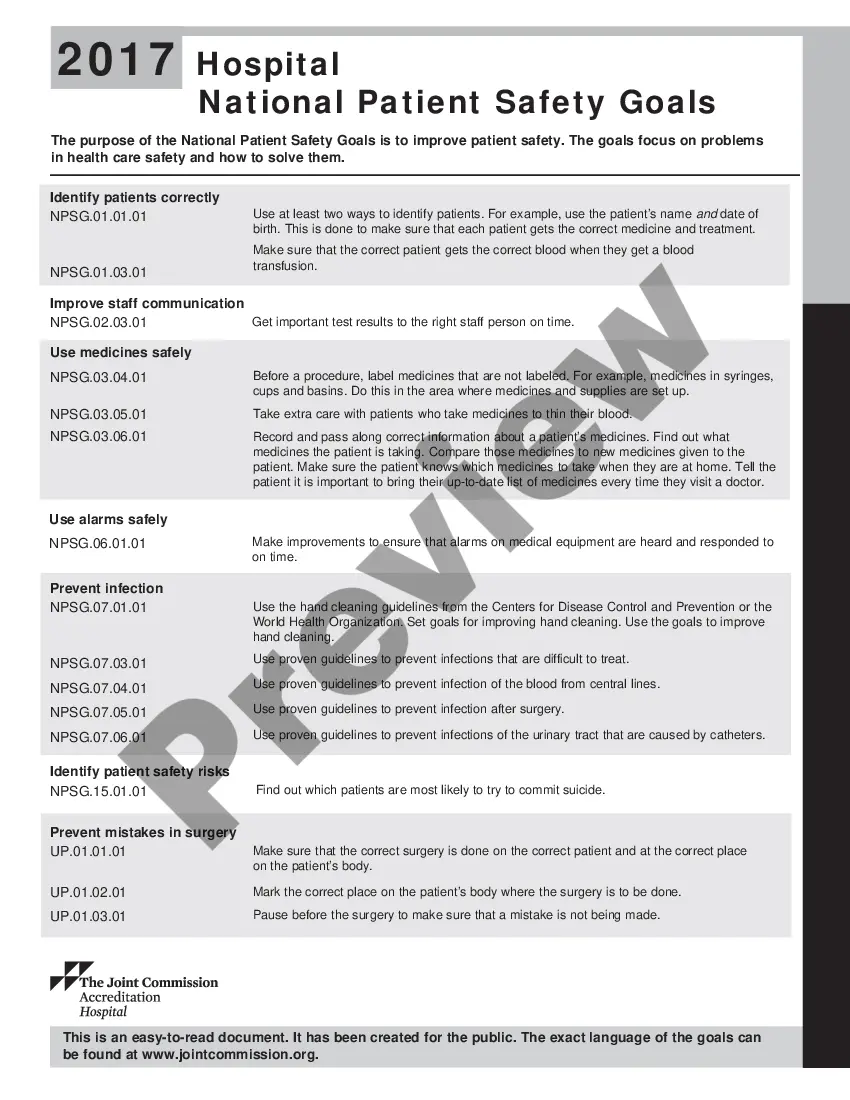
The Nevada Hospital National Patient Safety Goals are guidelines established by the Joint Commission to ensure the highest level of safety and quality of care for patients in hospitals throughout the state of Nevada. These goals are designed to address critical areas where vulnerabilities and opportunities for improvement exist within healthcare facilities. 1. Infection Control: One of the key goals is to prevent healthcare-associated infections (His). This encompasses measures to improve hand hygiene, prevent surgical site infections, minimize the spread of multi-drug resistant organisms, and reduce the risk of bloodstream infections. 2. Medication Safety: Another crucial goal focuses on medication safety to prevent errors in medication administration. This includes accurately reconciling medications during transitions of care, labeling medications appropriately, ensuring effective communication between healthcare providers, and educating patients about their medications. 3. Patient Identification: To minimize the risk of patient identification errors, hospitals are required to establish protocols for verifying patient identities using at least two patient-specific identifiers. This helps prevent the administration of treatments or procedures to the wrong patient. 4. Clinical Alarm Safety: Alarm systems play a critical role in patient monitoring; however, their constant presence can lead to alarm fatigue and reduced responsiveness. Hospitals need to develop policies and procedures to ensure that alarm signals are appropriately set, heard, attended to, and responded too promptly. 5. Fall Prevention: Hospitals must implement strategies to prevent patient falls and reduce fall-related injuries. These initiatives involve assessing patients' risk of falling, implementing appropriate interventions such as bed alarms or non-slip footwear, and educating patients on fall prevention techniques. 6. Surgical Safety: The Nevada Hospital National Patient Safety Goals also include initiatives related to surgical safety. This encompasses the completion of preoperative verification processes (ensuring the correct patient, procedure, and site), conducting a surgical timeout before starting the procedure, and effectively communicating patient information during surgical hand-offs. 7. Suicide Risk Prevention: Hospitals should identify patients at risk for suicide and establish protocols to mitigate these risks. This includes conducting psychiatric assessments, developing individualized safety plans, restricting access to potentially harmful objects, and training staff in suicide prevention strategies. Overall, these goals aim to improve patient outcomes by promoting a culture of safety within Nevada hospitals. By addressing infection control, medication safety, patient identification, clinical alarm safety, fall prevention, surgical safety, and suicide risk prevention, healthcare facilities can enhance the quality and reliability of care provided to patients throughout their stay.
Nevada Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Nevada Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
US Legal Forms - one of several biggest libraries of authorized kinds in America - gives a variety of authorized record themes you can acquire or produce. Using the site, you can get thousands of kinds for business and personal uses, categorized by groups, suggests, or key phrases.You will discover the most recent models of kinds such as the Nevada Hospital National Patient Safety Goals within minutes.
If you already possess a monthly subscription, log in and acquire Nevada Hospital National Patient Safety Goals from the US Legal Forms collection. The Down load switch can look on every develop you look at. You have accessibility to all earlier acquired kinds inside the My Forms tab of your respective profile.
If you would like use US Legal Forms initially, here are basic recommendations to help you get started off:
- Be sure to have selected the correct develop for your personal area/area. Select the Preview switch to examine the form`s articles. Browse the develop description to actually have selected the correct develop.
- If the develop does not fit your needs, utilize the Lookup discipline at the top of the display to find the one who does.
- Should you be satisfied with the form, verify your option by simply clicking the Buy now switch. Then, opt for the rates strategy you favor and offer your qualifications to register to have an profile.
- Process the transaction. Utilize your bank card or PayPal profile to complete the transaction.
- Select the file format and acquire the form on the device.
- Make adjustments. Complete, revise and produce and indication the acquired Nevada Hospital National Patient Safety Goals.
Each template you included with your account lacks an expiry time and it is the one you have for a long time. So, if you would like acquire or produce one more copy, just go to the My Forms portion and then click around the develop you require.
Obtain access to the Nevada Hospital National Patient Safety Goals with US Legal Forms, probably the most comprehensive collection of authorized record themes. Use thousands of specialist and condition-certain themes that meet your business or personal demands and needs.