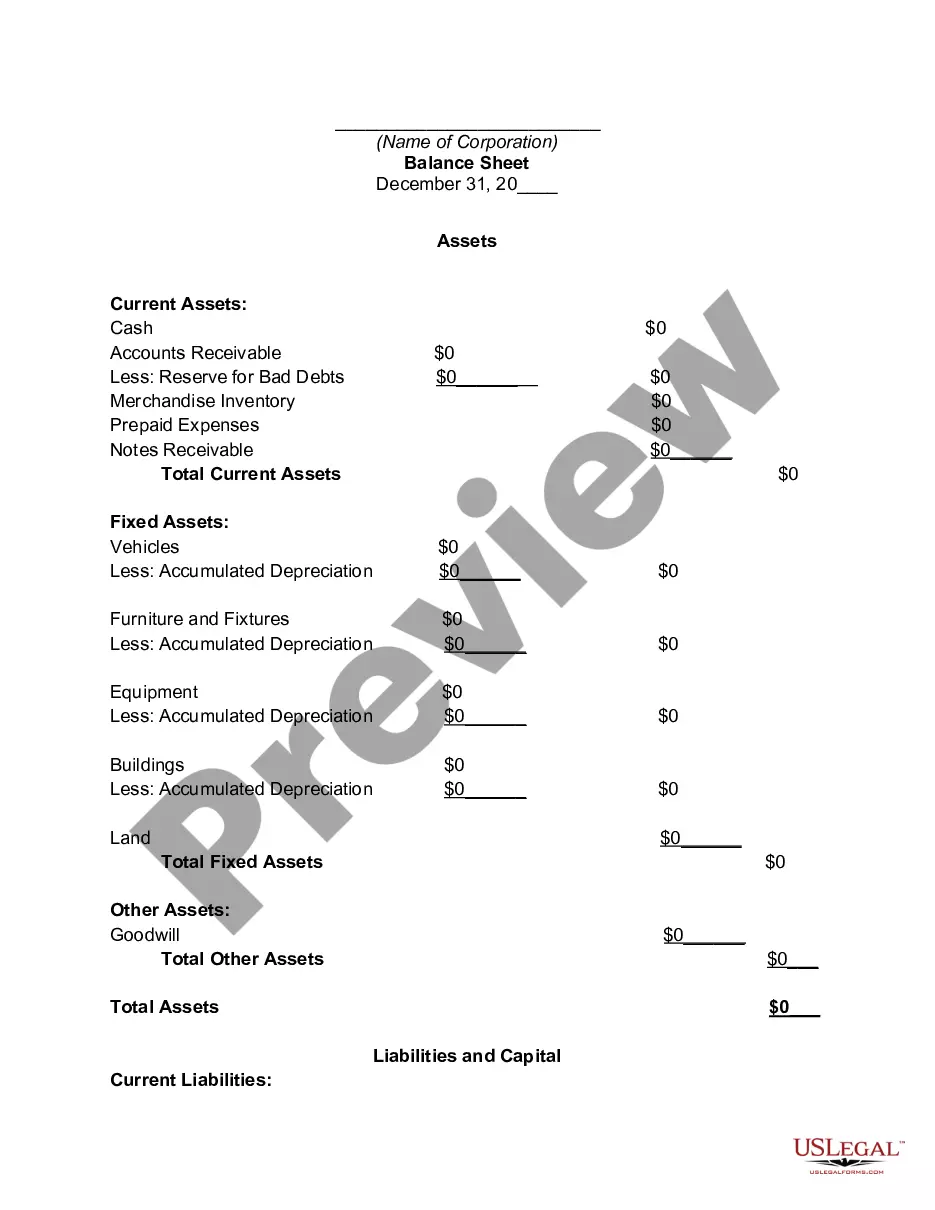
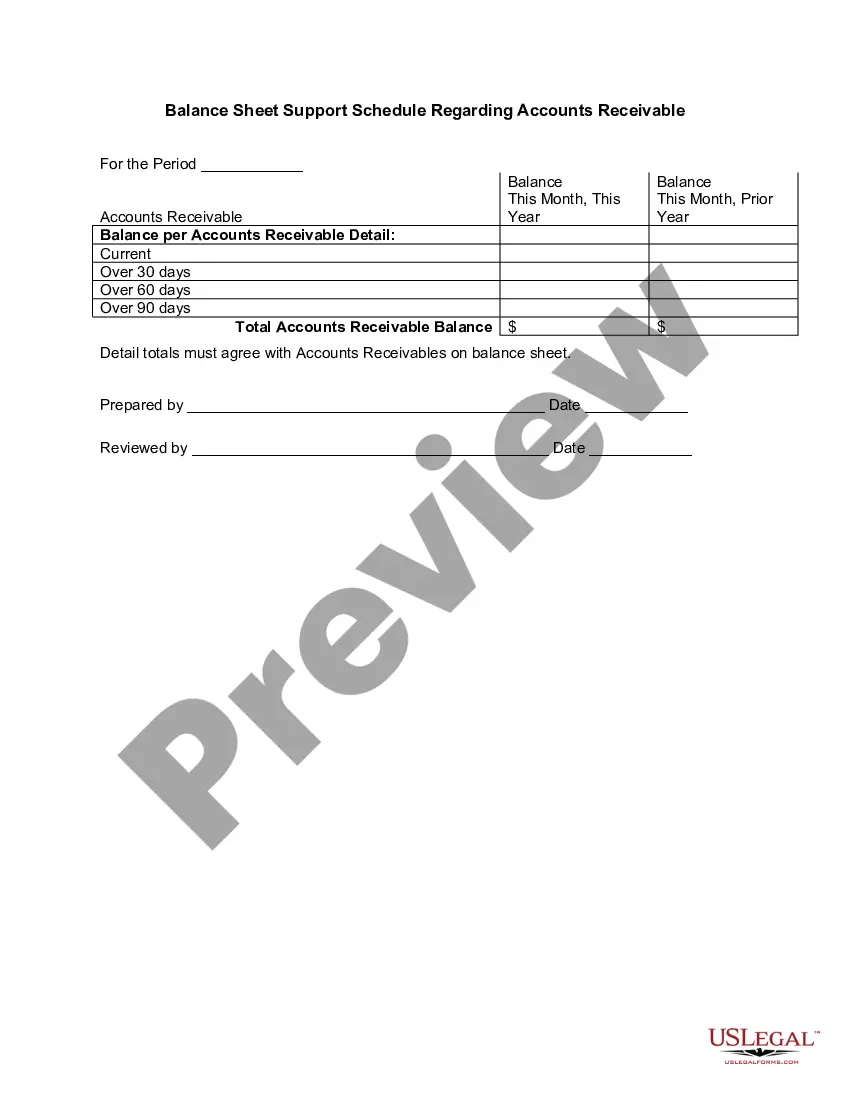
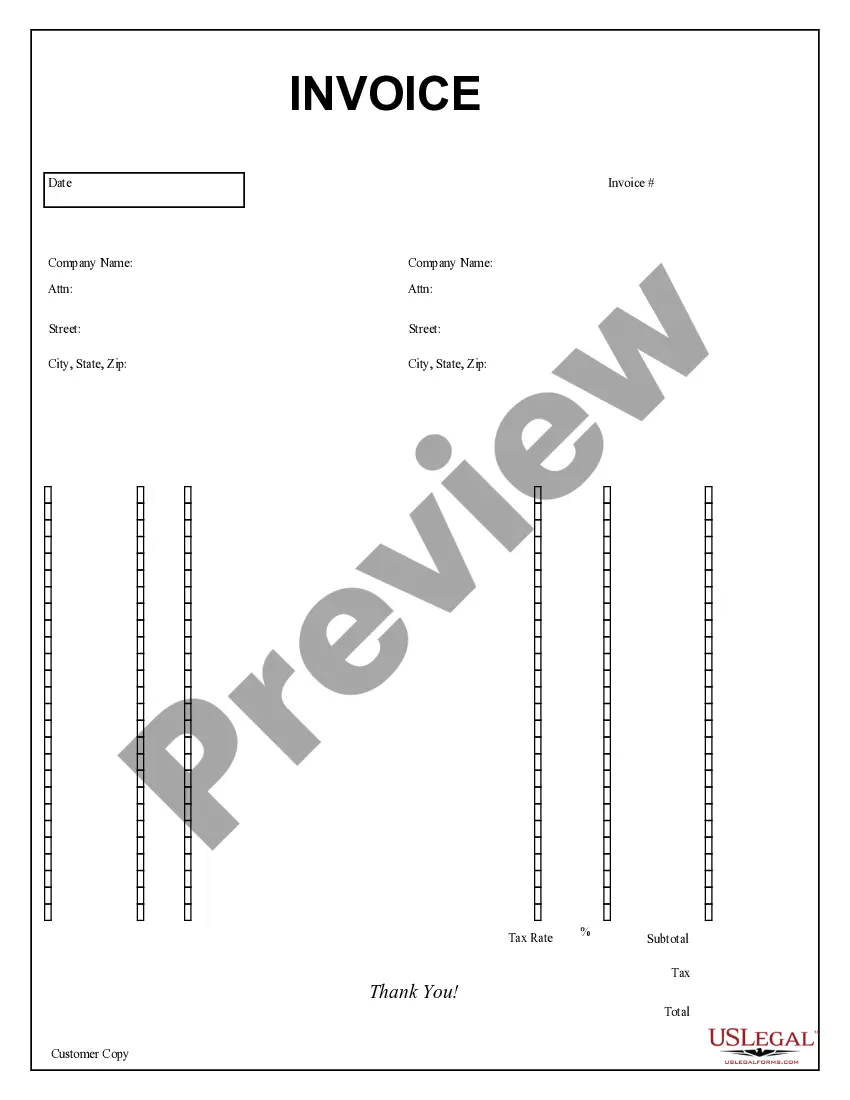
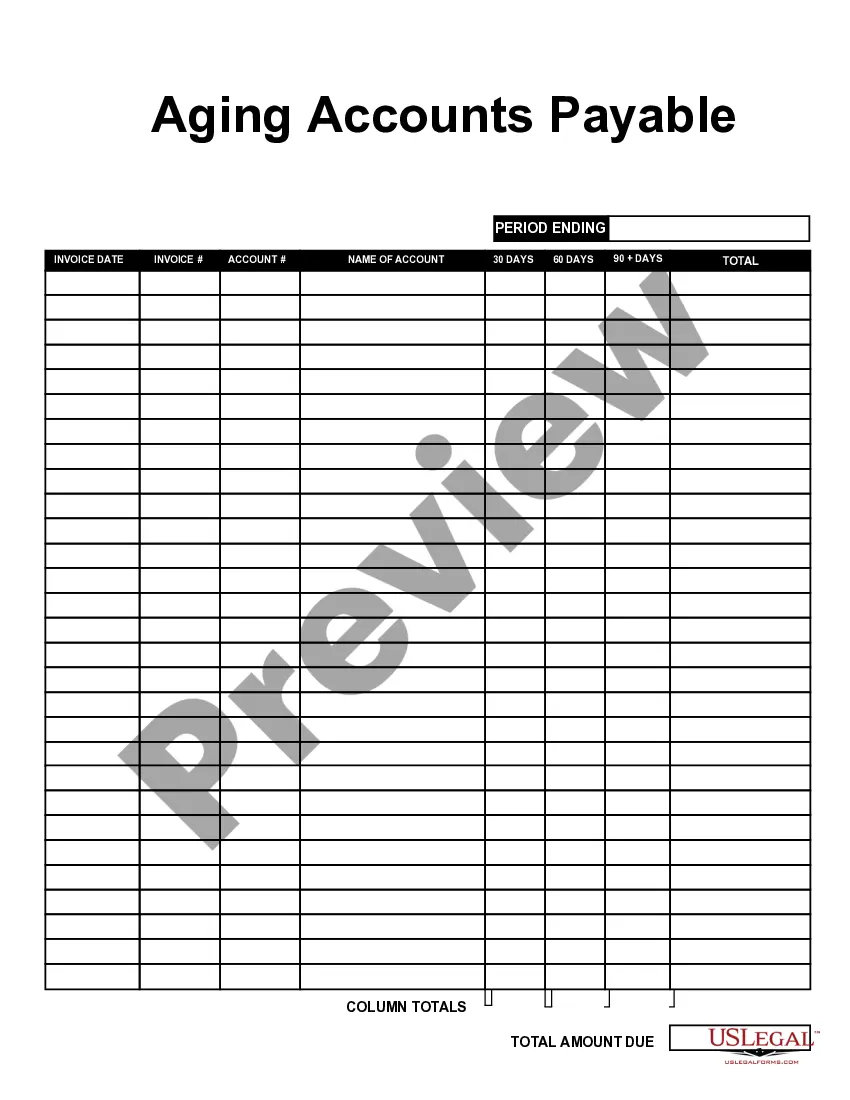
Nevada Aging Accounts Payable
Description
How to fill out Aging Accounts Payable?
Locating the appropriate valid document format can be a challenge.
Naturally, there are many templates accessible online, but how do you locate the authentic document you require.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. The platform provides thousands of templates, including the Nevada Aging Accounts Payable, which can be utilized for business and personal purposes.
You can preview the form using the Preview button and review the details to confirm it is suitable for you.
- All of the forms are reviewed by professionals and comply with federal and state regulations.
- If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click on the Obtain button to find the Nevada Aging Accounts Payable.
- Use your account to search through the legal forms you have previously purchased.
- Proceed to the My documents tab of your account and obtain another copy of the document you need.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are simple instructions that you should adhere to.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct form for your area/state.
Form popularity
FAQ
Office of the State Controller As the State's Chief Fiscal Officer, the Controller serves as an independent resource to promote accountability while protecting the financial integrity of the State.
The State Controller's FunctionsAccount for and control disbursement of all state funds. Determine legality and accuracy of every claim against the State. Issue warrants in payment of the State's bills including lottery prizes. Administer the Uniform State Payroll System.
Administration and Disbursements DivisionProduces the warrants (checks) and electronic fund transfers from the State Treasury, annually issuing about 49 million payments including state payroll, retirement rolls, Medi-Cal, personal income tax refunds, and payments to vendors.
Nevada State Controller's Office - Catherine Byrne, CPA Controller.
The State Controller's FunctionsAccount for and control disbursement of all state funds. Determine legality and accuracy of every claim against the State. Issue warrants in payment of the State's bills including lottery prizes. Administer the Uniform State Payroll System.
The Controller is the Chief Fiscal Officer (CFO) of the state and is responsible for administering the state's accounting system, registering vendors, settling all claims against the state and collecting debts owed to the state.
The State Controller's FunctionsAccount for and control disbursement of all state funds. Determine legality and accuracy of every claim against the State. Issue warrants in payment of the State's bills including lottery prizes. Administer the Uniform State Payroll System.
The Controller processes and records the state's financial transactions, conducts the final audit and ensures compliance with our Nevada Constitution, federal laws and state statutes.
Catherine Byrne (born March 27, 1964) is an American politician from the state of Nevada. She was elected Controller of Nevada on November 6, 2018, defeating Republican incumbent Ron Knecht with 50.58% of the votes. She is a certified public accountant and graduated from California Lutheran University.
Nevada State Controller's Office - Catherine Byrne, CPA Controller.