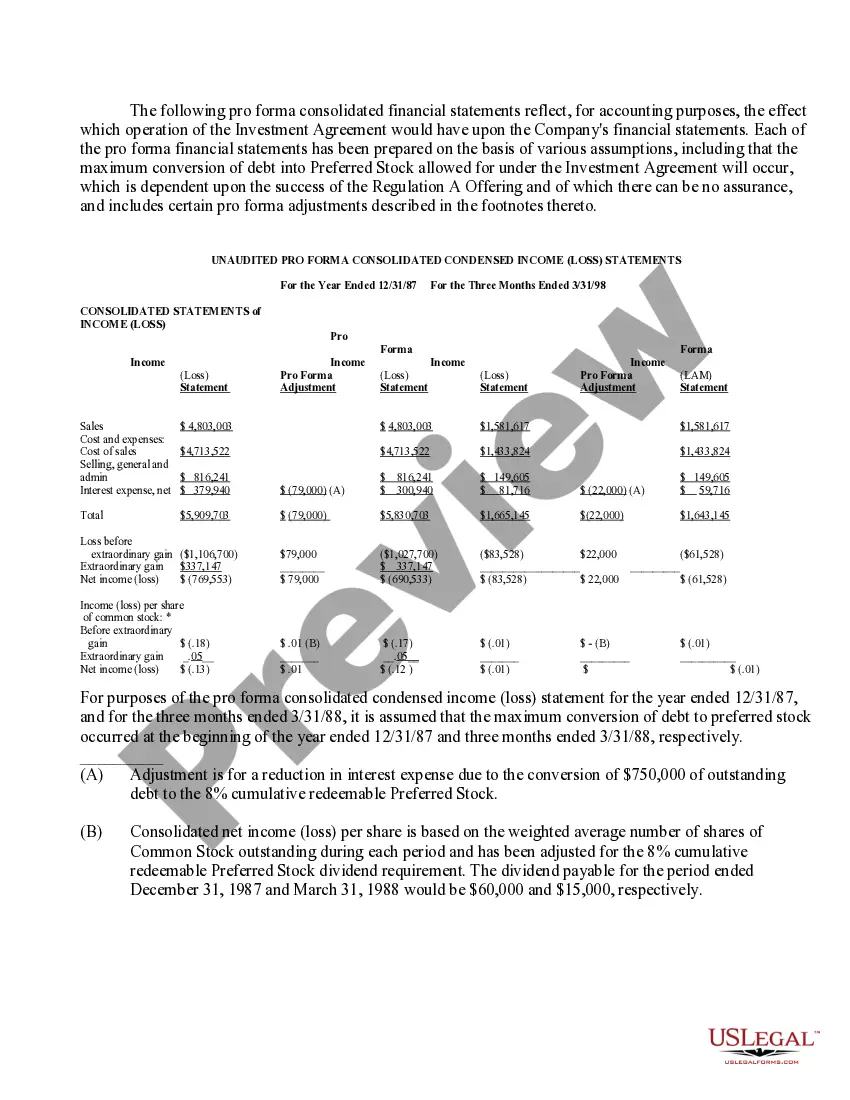
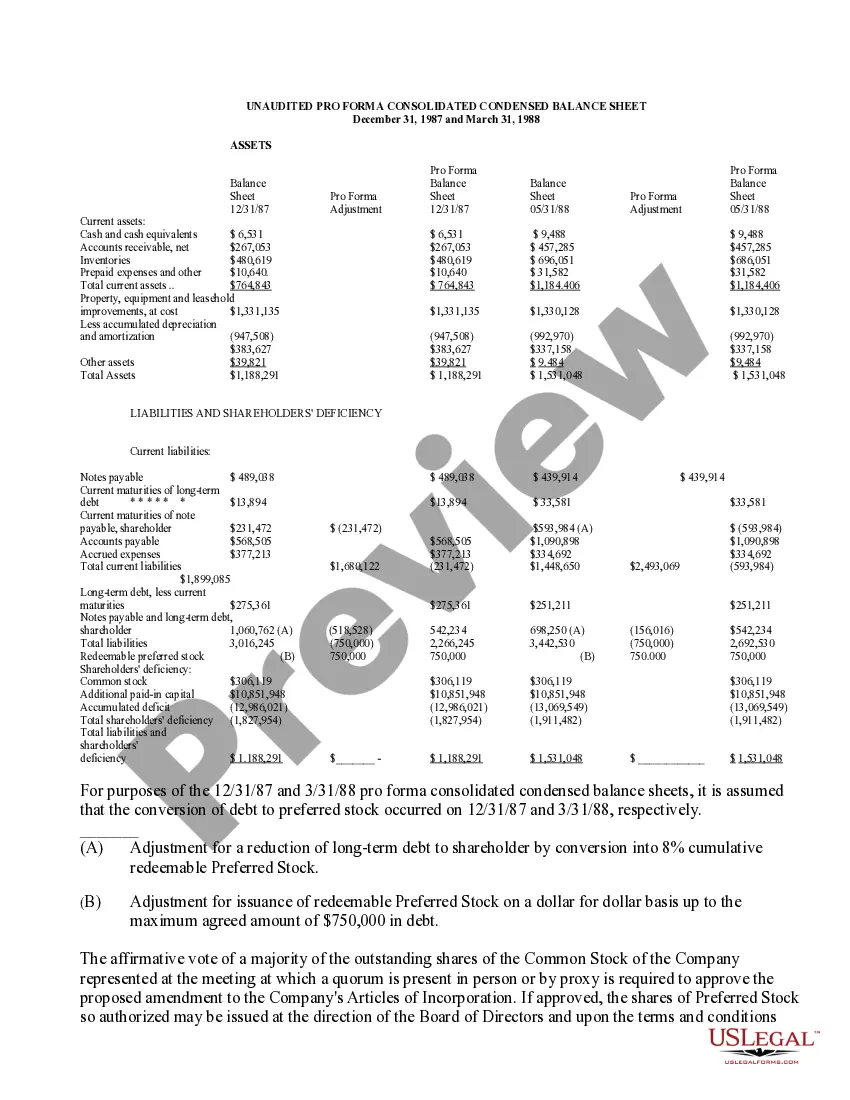
Nevada Approval of Authorization of Preferred Stock: A Comprehensive Overview In the realm of corporate finance and securities, Nevada's approval of authorization of preferred stock plays a significant role. Preferred stock represents a class of ownership shares in a corporation that offers certain privileges to shareholders, distinguishing it from common stock. This article aims to provide a detailed description of what Nevada Approval of Authorization of Preferred Stock entails, shedding light on the various types and highlighting relevant keywords. Nevada Approval Process: When a corporation in Nevada wishes to issue preferred stock, it must obtain the necessary approval from both its board of directors and shareholders. This process involves drafting and adopting a resolution, which outlines the terms and conditions of the preferred stock issuance, and submitting this resolution to seek approval from relevant stakeholders. The Nevada Approval process ensures transparency and legal compliance when a company decides to authorize and issue preferred stock. Benefits of Preferred Stock: Preferred stock offers distinct advantages to both corporations and investors. It grants shareholders a higher priority claim on company assets and earnings compared to common stockholders. Preferred stockholders enjoy preferential treatment in terms of dividends, meaning they receive fixed or adjustable dividend payments before common stockholders. Moreover, in the event of liquidation, preferred stockholders are entitled to be repaid their investment amount ahead of common shareholders, enhancing their security. Types of Preferred Stock in Nevada: Several types of preferred stock can be authorized in Nevada, each offering unique features to accommodate specific corporate needs and investor preferences. Some relevant keywords associated with various types of preferred stock include: 1. Cumulative Preferred Stock: This type of preferred stock grants shareholders the right to accumulate unpaid dividends, ensuring that if a company misses a dividend payment, it remains a liability until settled. 2. Convertible Preferred Stock: Convertible preferred stock allows shareholders to convert their preferred shares into a fixed number of common shares, offering potential capital appreciation if the company's value increases. 3. Adjustable Rate Preferred Stock: This variant enables dividends to adjust according to specified criteria, such as changes in interest rates. This flexibility ensures that shareholders' dividend payments align with prevailing market conditions. 4. Redeemable Preferred Stock: Shareholders of redeemable preferred stock have the right to redeem their shares at a specified future date or under certain predefined circumstances, as outlined by the company. 5. Participating Preferred Stock: With participating preferred stock, shareholders not only receive fixed dividends but also have the opportunity to share in additional profits with common stockholders, beyond their fixed dividend rate. 6. Non-Cumulative Preferred Stock: Non-cumulative preferred stock does not allow unpaid dividends to accumulate. If a company skips a dividend payment, it does not remain an obligation for future payments. Overall, Nevada's approval of authorization of preferred stock paves the way for corporations to leverage various types of preferred stock. These different forms of preferred stock enable tailored financial arrangements that suit the needs of both companies and investors, promoting a dynamic and flexible corporate landscape.
Nevada Approval of authorization of preferred stock
Description
How to fill out Nevada Approval Of Authorization Of Preferred Stock?
US Legal Forms - one of the greatest libraries of authorized varieties in the States - gives a variety of authorized document web templates you may obtain or printing. Making use of the web site, you can get a large number of varieties for business and specific functions, categorized by categories, claims, or key phrases.You can find the most up-to-date types of varieties like the Nevada Approval of authorization of preferred stock within minutes.
If you already have a registration, log in and obtain Nevada Approval of authorization of preferred stock through the US Legal Forms local library. The Down load option can look on each and every form you see. You get access to all formerly delivered electronically varieties within the My Forms tab of your accounts.
If you want to use US Legal Forms the first time, allow me to share simple directions to get you started:
- Ensure you have selected the right form for your personal town/region. Click on the Review option to review the form`s articles. Browse the form outline to actually have chosen the right form.
- In case the form doesn`t suit your requirements, use the Look for field on top of the monitor to discover the the one that does.
- Should you be content with the form, confirm your decision by visiting the Get now option. Then, select the prices strategy you favor and supply your references to register on an accounts.
- Method the transaction. Use your charge card or PayPal accounts to accomplish the transaction.
- Find the structure and obtain the form on your system.
- Make adjustments. Fill out, edit and printing and signal the delivered electronically Nevada Approval of authorization of preferred stock.
Every single web template you added to your money lacks an expiration date and is the one you have permanently. So, in order to obtain or printing yet another duplicate, just check out the My Forms portion and click around the form you will need.
Get access to the Nevada Approval of authorization of preferred stock with US Legal Forms, probably the most comprehensive local library of authorized document web templates. Use a large number of skilled and express-particular web templates that meet your business or specific needs and requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
Board approval, either by written consent or at a board meeting (for more about the differences between board consents and board meetings, please see our article), is required for every issuance of a security, whether that security is common stock, preferred stock, a warrant, an option or a note that is convertible ...
Issuing new shares typically requires approval from the company's shareholders. This may involve holding a vote at a shareholder meeting or obtaining written consent from a majority of shareholders. The approval process will depend on the company's bylaws and state laws governing the issuance of new shares.
NRS 78.138 - Directors and officers: Fiduciary duties; exercise of powers; presumptions and considerations; liability to corporation, stockholders and creditors. 1. The fiduciary duties of directors and officers are to exercise their respective powers in good faith and with a view to the interests of the corporation.
Blank check preferred stock facilitates the ability of the company to adopt a "white squire" defense when faced with a hostile bid, which involves sale to a friendly party (i.e., a party that is interested in making an investment in, but presumably is not seeking to gain control of, the target) of a block of the ...
Under current Section 312.03(b), shareholder approval is required when a company sells shares to a related party if the amount to be issued exceeds 1% of the number of shares or voting power outstanding before issuance.
Issuance of Preferred Stock: When a company issues preferred stock, it debits (increases) the cash account on the balance sheet for the total value received and credits (increases) the ?preferred stock? account in the equity section of the balance sheet.
Chapter 78 Private Corporations. NRS 78.315 Directors' meetings: Quorum; consent for actions taken without meeting; participation by telephone or similar method. NRS 78.315 Directors' meetings: Quorum; consent for actions taken without meeting; participation by telephone or similar method.
The most common issuers of preferred stocks are banks, insurance companies, utilities and real estate investment trusts, or REITs. Companies issuing preferreds may have more than one offering for you to vet. Often you may find several different offerings of preferreds from the same issuer but with different yields.