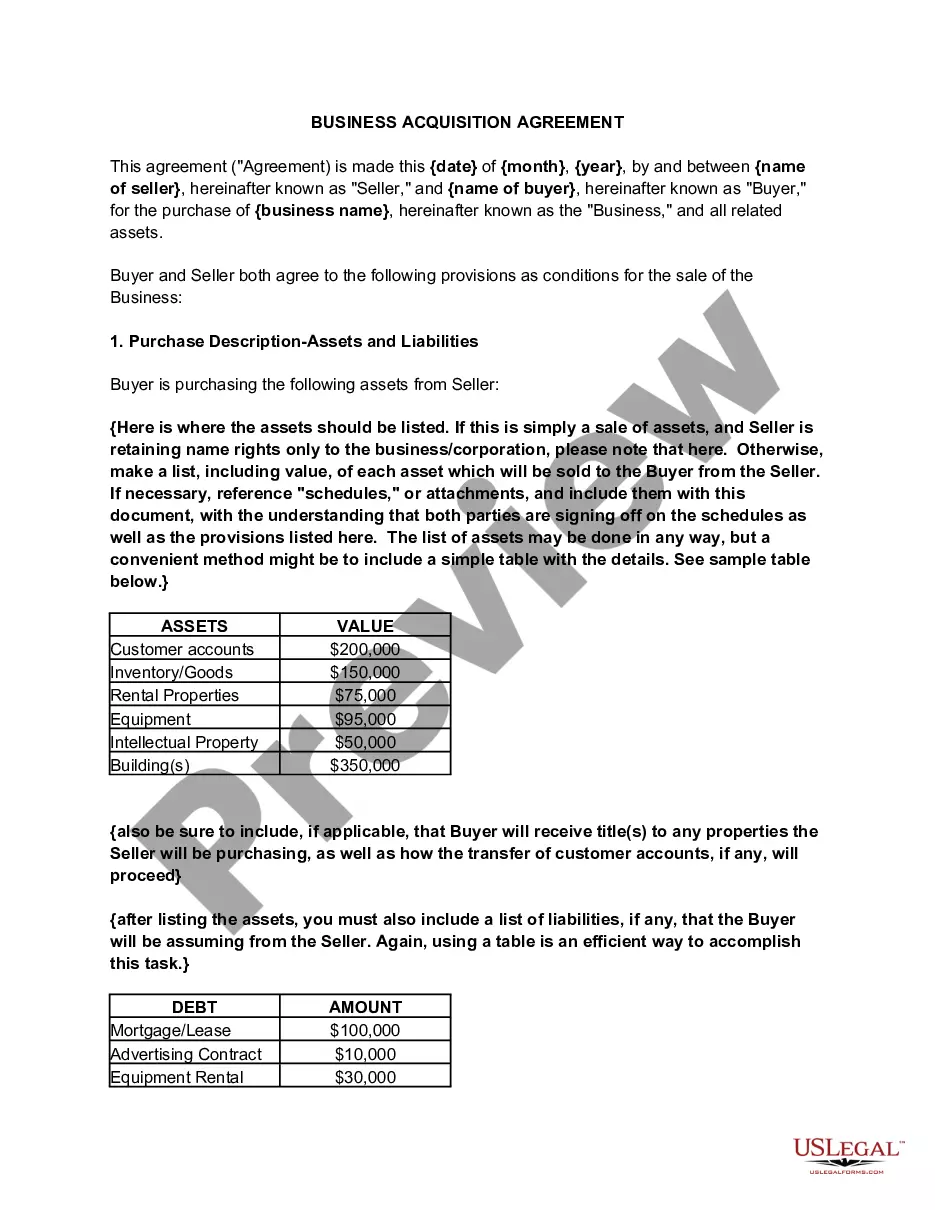
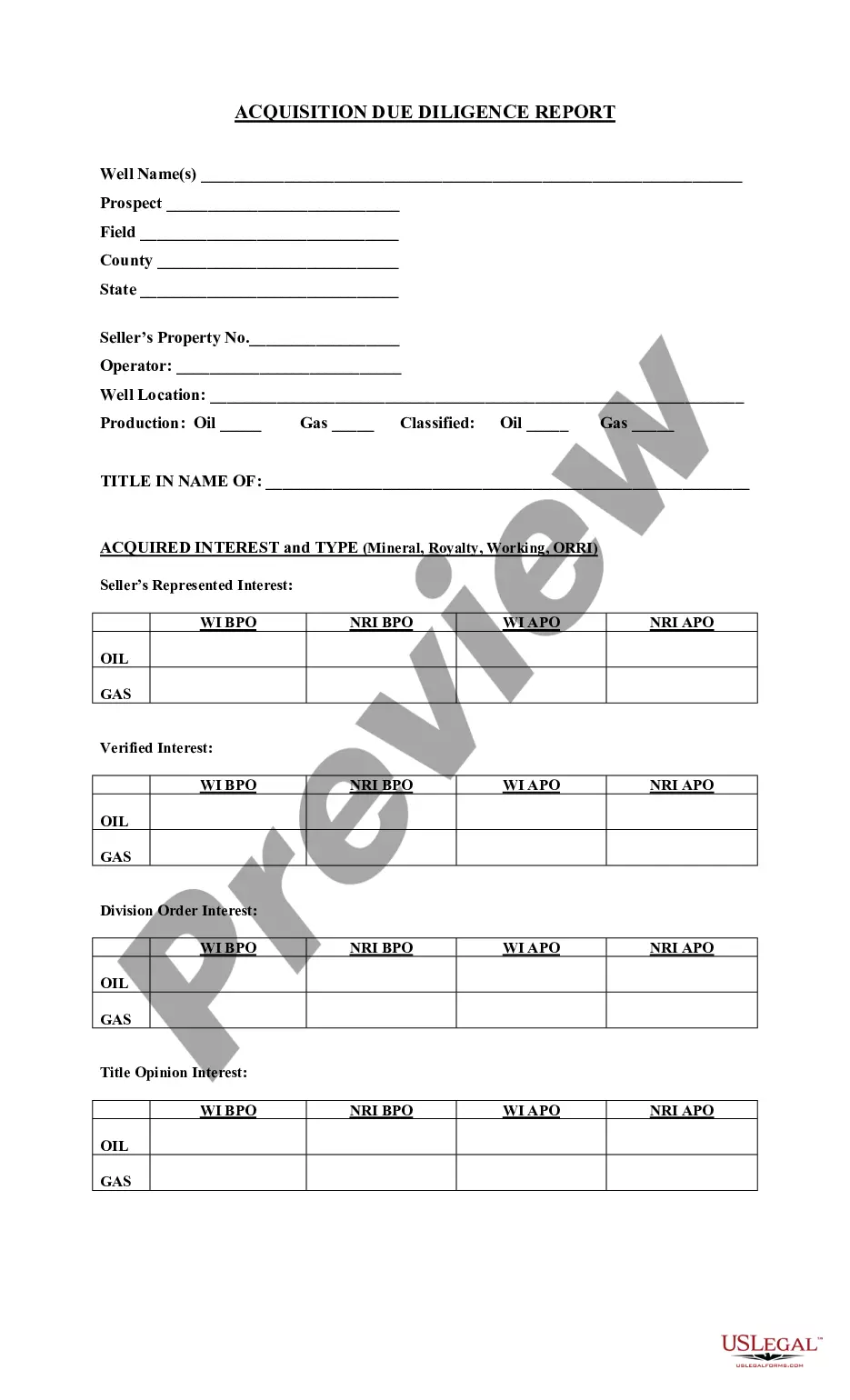
Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties, this form is is a outline of the acquisition representing the sellers and buyers in the sale of producing properties in the dealing with oil, gas or minerals.
Nevada Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties
Description
How to fill out Outline Of The Acquisition Process Representing Sellers And Buyers In The Sale Of Producing Properties?
You can commit hours on the web looking for the legitimate papers design which fits the federal and state requirements you need. US Legal Forms gives thousands of legitimate varieties that happen to be examined by experts. You can actually download or produce the Nevada Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties from my assistance.
If you currently have a US Legal Forms bank account, it is possible to log in and click the Acquire switch. Following that, it is possible to full, revise, produce, or indication the Nevada Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties. Each and every legitimate papers design you purchase is your own permanently. To have one more duplicate of the acquired kind, go to the My Forms tab and click the related switch.
If you are using the US Legal Forms web site initially, keep to the basic directions below:
- First, make certain you have selected the best papers design for that county/city of your liking. Look at the kind description to make sure you have picked out the proper kind. If accessible, utilize the Preview switch to search from the papers design as well.
- If you would like get one more variation from the kind, utilize the Search discipline to obtain the design that meets your needs and requirements.
- When you have found the design you desire, just click Get now to proceed.
- Choose the rates prepare you desire, key in your references, and sign up for a free account on US Legal Forms.
- Total the transaction. You can use your charge card or PayPal bank account to pay for the legitimate kind.
- Choose the format from the papers and download it to your device.
- Make changes to your papers if required. You can full, revise and indication and produce Nevada Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties.
Acquire and produce thousands of papers themes while using US Legal Forms website, that provides the most important selection of legitimate varieties. Use specialist and express-distinct themes to deal with your small business or individual demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
NRS 113.110 Conditions required for ?conveyance of property? and to complete service of document. NRS 113.120 Regulations prescribing format and contents of form for disclosing condition of property.
The Statutes of Nevada are a compilation of all legislation passed by the Nevada Legislature during a particular Legislative Session. The Nevada Administrative Code (NAC) is the codified, administrative regulations of the Executive Branch.
The seller's real property disclosure must be completed, signed by the seller and furnished to the purchaser or purchaser's agent no less than ten days before the property is scheduled to close.
The purpose of the disclosure is to make the buyer aware that the property is subject to a Private Transfer Fee Obligation (PTFO) which will require the buyer, upon conveyance of the property by the seller, to pay either a one-time fixed amount or a one-time percentage of the purchase price to a third party payee.
SELLER'S REAL PROPERTY DISCLOSURE FORM.
NRS: CHAPTER 119 - SALE OF SUBDIVIDED LAND: LICENSING AND REGULATION.