The New York Hospital National Patient Safety Goals aim to enhance patient safety and quality of care within healthcare facilities. These goals are a set of guidelines established by the New York Hospital Association (NYH) and align with the national patient safety goals set by The Joint Commission. They serve as a blueprint for healthcare organizations in New York, ensuring that they prioritize patient safety and implement necessary measures to prevent errors, infections, and other adverse events. The following are some key areas covered under the New York Hospital National Patient Safety Goals: 1. Patient identification: Hospitals are required to use at least two patient identifiers, such as name and date of birth, to accurately identify patients before any treatment or procedure. This helps prevent errors related to identification. 2. Medication safety: This goal focuses on reducing medication errors by implementing various strategies, including labeling medications, reconciling medications at each transition of care, and involving patients in their medication management. 3. Infection prevention: Preventing healthcare-associated infections is vital. Hospitals are responsible for implementing evidence-based practices minimizing the risk of infections, such as hand hygiene protocols, proper sterilization techniques, and infection control education for healthcare staff. 4. Falls prevention: Hospitals must develop and implement a falls' reduction program to minimize the risk of patient falls. This includes assessing patient fall risk, implementing preventive measures like bed alarms and nonslip surfaces, and educating patients and their families about fall prevention strategies. 5. Surgical safety: This goal emphasizes the importance of preventing surgical errors and complications. It involves measures like performing preoperative verification processes, marking the surgical site, conducting a "timeout" before surgery to ensure correct procedures, and implementing infection control protocols during surgical procedures. 6. Communication among healthcare team: Effective communication is crucial to ensure patient safety. Hospitals must establish standardized processes for hand off communication during care transitions, provide timely follow-up on critical test results, and encourage open and clear communication among healthcare providers. 7. Patient and family engagement: This goal emphasizes the involvement of patients and their families in their healthcare decisions and encourages healthcare providers to promote patient education and involvement in their care planning. It also focuses on enhancing patient satisfaction and overall experience. These are some National Patient Safety Goals that New York hospitals strive to achieve. By aligning with these goals, healthcare organizations in New York ensure a safe environment, minimize errors, and improve patient outcomes.
New York Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out New York Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
You can commit several hours online looking for the lawful document web template which fits the federal and state needs you need. US Legal Forms gives a large number of lawful types that are analyzed by professionals. You can easily acquire or produce the New York Hospital National Patient Safety Goals from my service.
If you currently have a US Legal Forms bank account, it is possible to log in and then click the Down load switch. Afterward, it is possible to full, change, produce, or indication the New York Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. Each and every lawful document web template you get is yours forever. To obtain one more duplicate for any purchased develop, check out the My Forms tab and then click the corresponding switch.
If you use the US Legal Forms web site for the first time, follow the straightforward instructions under:
- First, ensure that you have chosen the best document web template for that area/city of your choosing. Browse the develop description to ensure you have selected the proper develop. If readily available, take advantage of the Preview switch to appear from the document web template as well.
- In order to locate one more edition from the develop, take advantage of the Look for discipline to obtain the web template that meets your needs and needs.
- After you have discovered the web template you would like, simply click Purchase now to move forward.
- Choose the prices prepare you would like, enter your qualifications, and sign up for a merchant account on US Legal Forms.
- Total the purchase. You can use your bank card or PayPal bank account to pay for the lawful develop.
- Choose the formatting from the document and acquire it to your gadget.
- Make modifications to your document if possible. You can full, change and indication and produce New York Hospital National Patient Safety Goals.
Down load and produce a large number of document themes utilizing the US Legal Forms site, that provides the greatest assortment of lawful types. Use specialist and condition-specific themes to tackle your company or personal requires.
Form popularity
FAQ
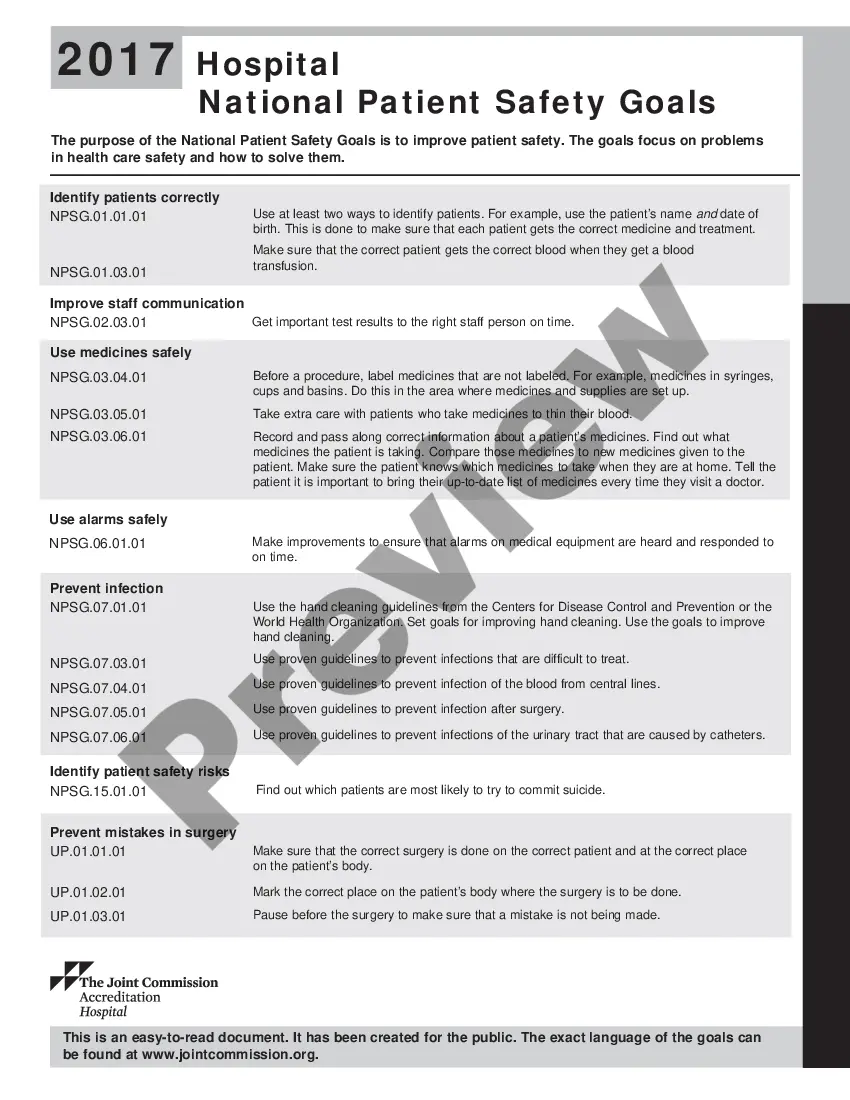
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
20172021 versionsGoal 1: Identify patients correctly.Goal 2: Improve effective communication.Goal 3: Improve the safety of high-alert medications.Goal 4: Ensure safe surgery.Goal 5: Reduce the risk of health care-associated infections.Goal 6: Reduce the risk of patient harm resulting from falls.
What Are the 7 National Patient Safety Goals for Hospitals in 2021?Identify patients correctly.Improve staff communication.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.Prevent infection.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
2022 Joint Commission National Patient Safety Goals1 Identify Patients Correctly.2 Improve Staff Communication.3 Use Medicines Safely.4 Use Alarms Safely.5 Prevent Infection.6 Surgery Verification.
Goal 6: Reduce patient harm associated with clinical alarm systems.
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...
The initiative recommends that care providers make sure that all drugs are labeled clearly. The Hospital National Patient Safety Goals also call for increased caution when treating individuals with different diagnosis. An example of this would be for someone who requires medication to thin their blood.
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...