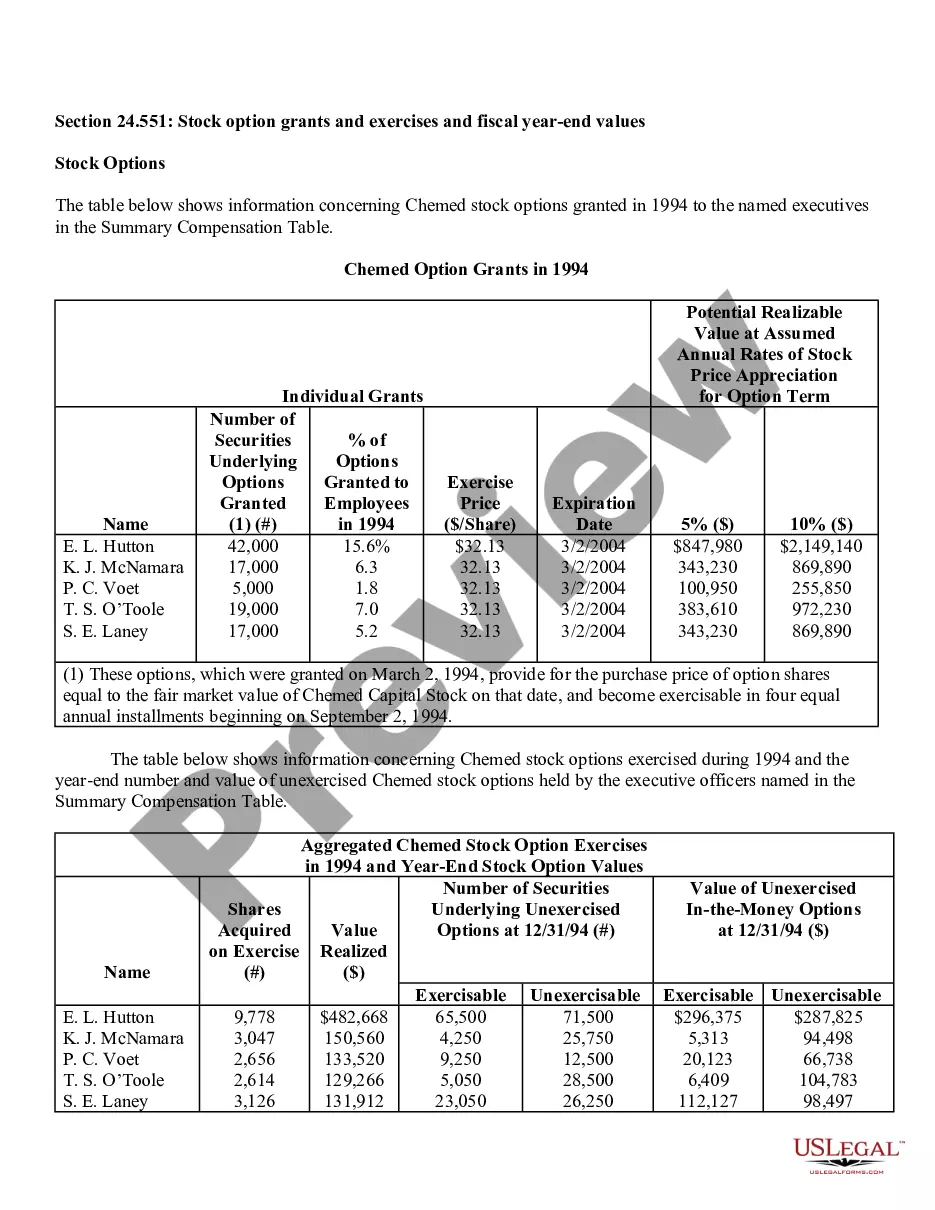
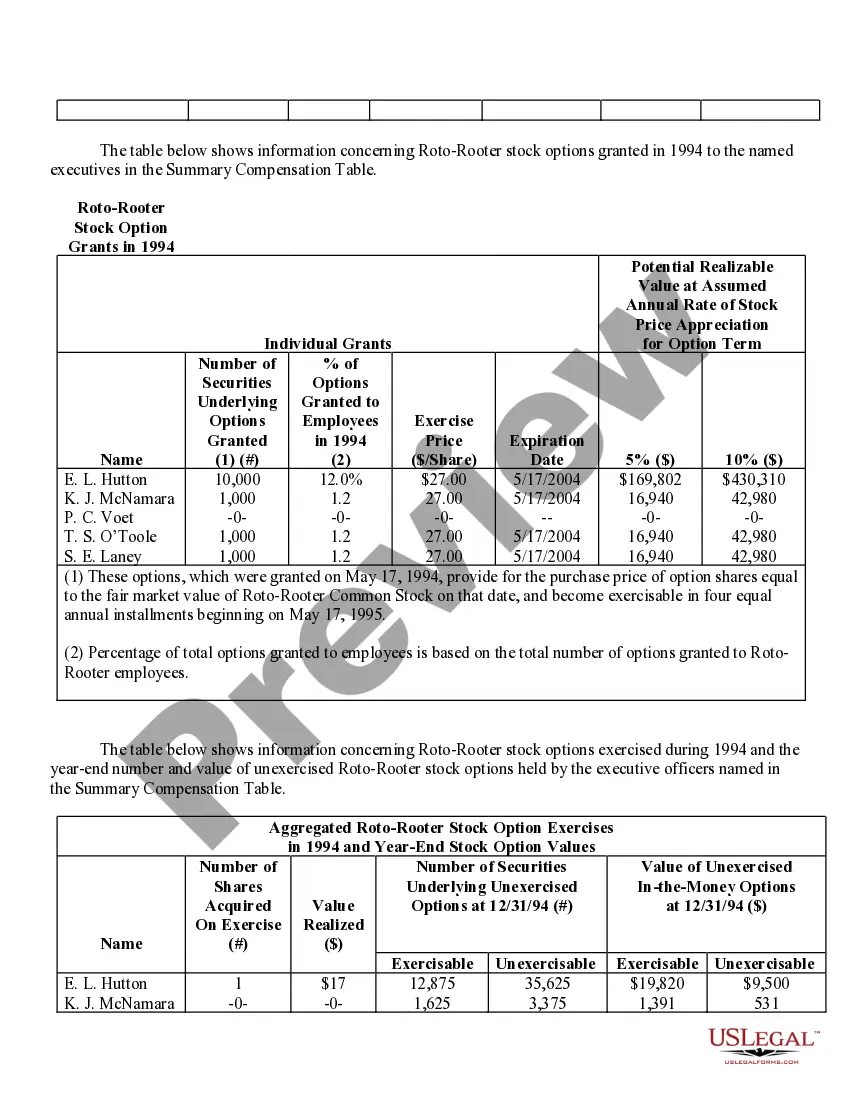
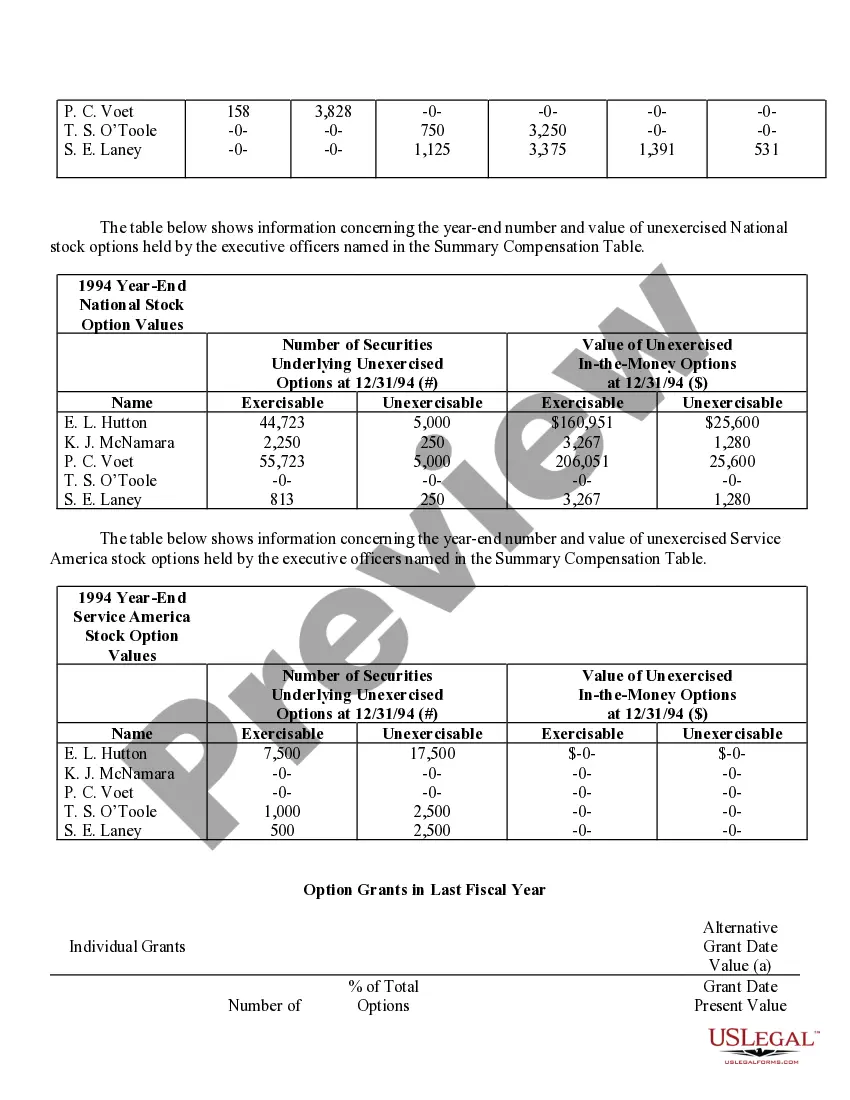
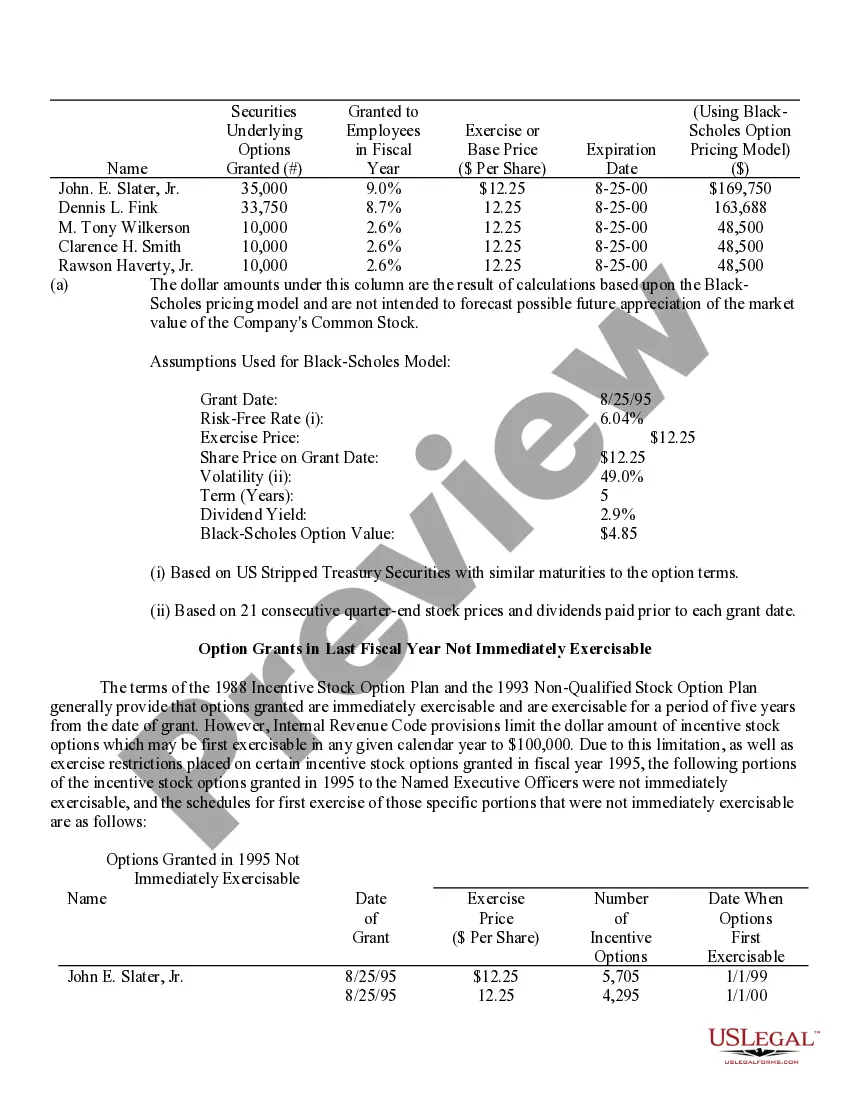
New York Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values
Description
How to fill out Stock Option Grants And Exercises And Fiscal Year-End Values?
You can spend hours on the web attempting to find the authorized record template that meets the federal and state specifications you require. US Legal Forms gives a huge number of authorized forms which are examined by specialists. It is possible to obtain or produce the New York Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values from my service.
If you already possess a US Legal Forms accounts, you may log in and click the Obtain button. Next, you may full, edit, produce, or signal the New York Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values. Each and every authorized record template you get is your own for a long time. To have yet another duplicate of the bought type, proceed to the My Forms tab and click the corresponding button.
Should you use the US Legal Forms website the very first time, adhere to the simple instructions listed below:
- Very first, be sure that you have selected the proper record template for the region/area of your choice. See the type description to make sure you have chosen the right type. If readily available, utilize the Review button to appear with the record template too.
- If you want to discover yet another variation of the type, utilize the Look for field to obtain the template that fits your needs and specifications.
- Once you have located the template you want, click Purchase now to continue.
- Pick the pricing plan you want, type your qualifications, and register for a free account on US Legal Forms.
- Full the transaction. You should use your bank card or PayPal accounts to purchase the authorized type.
- Pick the formatting of the record and obtain it for your gadget.
- Make modifications for your record if required. You can full, edit and signal and produce New York Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values.
Obtain and produce a huge number of record templates making use of the US Legal Forms site, that offers the greatest collection of authorized forms. Use professional and status-particular templates to handle your organization or person demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
Both call and put options have an exercise price. Investors also refer to the exercise price as the strike price. The difference between the exercise price and the underlying security's price determines if an option is ?in the money? or ?out of the money."
The grant price is the price at which you can purchase shares, and the grant date is the day the stock options are given to you. Vesting is the process of fulfilling the grant (promise). The vesting schedule determines the vesting date - the date when you can begin purchasing stock and using your options.
A strike price, also known as a grant price or exercise price, is the fixed cost that you'll pay per share in order to exercise your stock options so you can own them.
In the case of statutory stock options (Internal Revenue Code, sections 422 and 423), the entire amount of gain or loss recognized for Federal income tax purposes (both the compensation element and any appreciation in the value of the stock after the exercise date) is includable in New York source income.
Every stock option has an exercise price, also called the strike price, which is the price at which a share can be bought. In the US, the exercise price is typically set at the fair market value of the underlying stock as of the date the option is granted, in order to comply with certain requirements under US tax law.
You can calculate the aggregate exercise price by taking the strike price of the option and multiplying it by its contract size. In the case of a bond option, the exercise price is multiplied by the face value of the underlying bond.
Exercising a stock option means purchasing the issuer's common stock at the price set by the option (grant price), regardless of the stock's price at the time you exercise the option.
You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell the stock you bought by exercising the option. You generally treat this amount as a capital gain or loss. However, if you don't meet special holding period requirements, you'll have to treat income from the sale as ordinary income.