New York Accredited Investor Qualification and Verification Requirements for Reg D, Rule 506(c) Offerings
Description
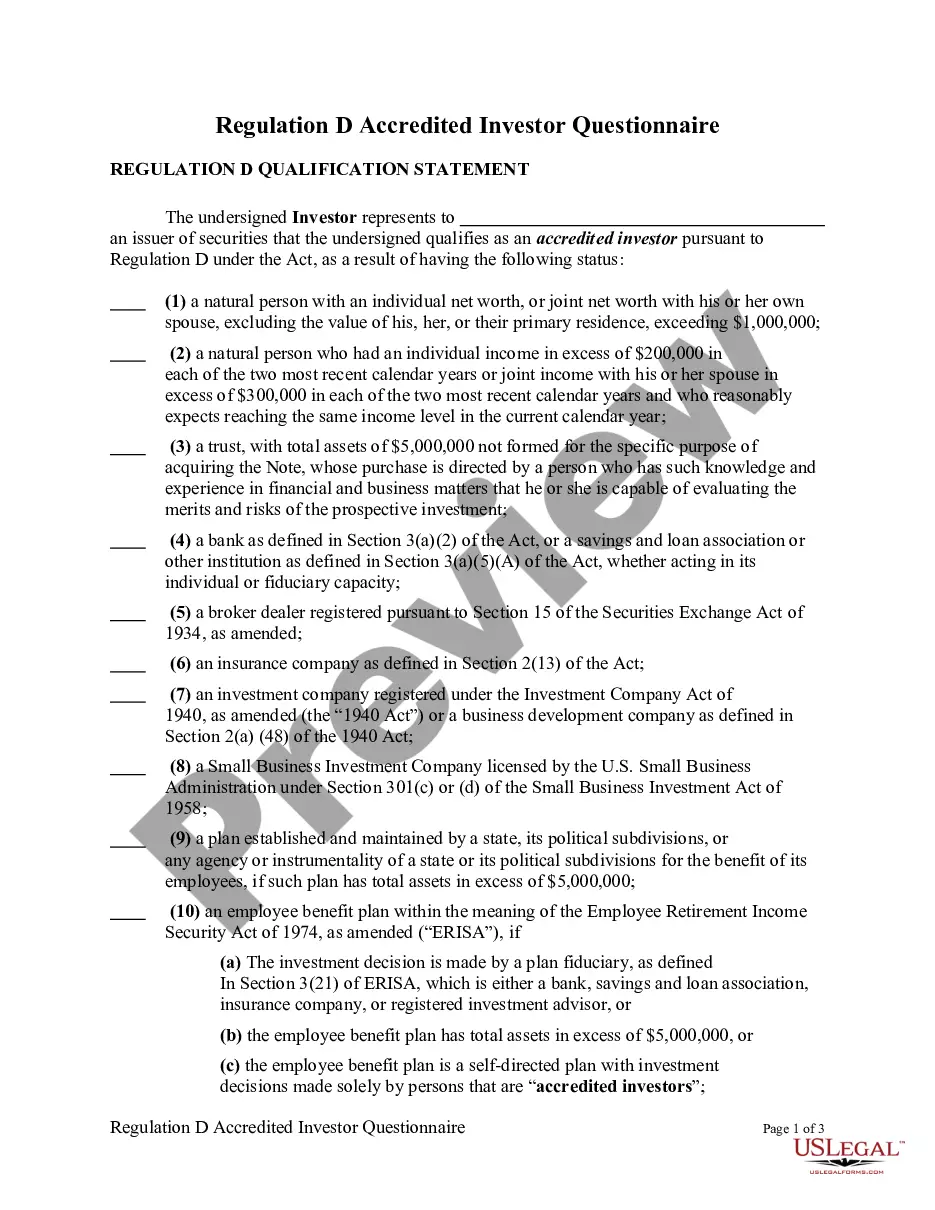
To become an accredited investor the (SEC) requires certain wealth, income or knowledge requirements. The investor must fall into one of three categories. Firms selling unregistered securities must put investors through their own screening process to determine if investors can be considered an accredited investor.
The Verifying Individual or Entity should take reasonable steps to verify and determined that an Investor is an "accredited investor" as such term is defined in Rule 501 of the Securities Act, and hereby provides written confirmation. This letter serves to help the Entity determine status, take Investor statements regarding information, and waiver of claims."
How to fill out Accredited Investor Qualification And Verification Requirements For Reg D, Rule 506(c) Offerings?
Choosing the right legitimate papers format could be a have difficulties. Naturally, there are a variety of templates accessible on the Internet, but how do you find the legitimate form you require? Make use of the US Legal Forms website. The assistance delivers thousands of templates, for example the New York Accredited Investor Qualification and Verification Requirements for Reg D, Rule 506(c) Offerings, that you can use for organization and personal requirements. All of the varieties are checked by professionals and satisfy state and federal demands.
In case you are currently registered, log in to the profile and click on the Obtain button to obtain the New York Accredited Investor Qualification and Verification Requirements for Reg D, Rule 506(c) Offerings. Make use of your profile to search through the legitimate varieties you may have ordered earlier. Check out the My Forms tab of the profile and acquire another copy of your papers you require.
In case you are a new user of US Legal Forms, listed below are easy guidelines that you can follow:
- First, ensure you have chosen the appropriate form to your city/state. You can look through the form while using Review button and look at the form description to guarantee this is the right one for you.
- In the event the form will not satisfy your needs, make use of the Seach industry to obtain the correct form.
- When you are sure that the form is acceptable, click the Purchase now button to obtain the form.
- Choose the prices prepare you want and enter the required details. Build your profile and pay money for your order utilizing your PayPal profile or bank card.
- Select the file file format and acquire the legitimate papers format to the system.
- Full, modify and print out and signal the obtained New York Accredited Investor Qualification and Verification Requirements for Reg D, Rule 506(c) Offerings.
US Legal Forms is the largest local library of legitimate varieties where you can see a variety of papers templates. Make use of the service to acquire professionally-manufactured papers that follow state demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
The two most common exemptions provided for in the Securities Act are Section 4(a)(2) and Regulation D. Regulation D is a set of rules and safe harbor exemptions that allow companies to raise capital through sales of securities without the need for a full-scale registration process with the SEC.
Key Takeaways. Form D, also known as the Notice of Sale of Securities, is required by the SEC for companies selling securities in a Regulation (Reg) D exemption or with Section 4(6) exemption provisions. Form D details basic information or essential facts about the company for investors.
To confirm their status as an accredited investor, an investor can submit official documents for net worth and income verification, including: Tax returns. Pay stubs. Financial statements. IRS forms. Credit report. Brokerage statements. Tax assessments. How Does the Accredited Investor Verification Process Work? montague.law ? blog ? accredited-investor-verific... montague.law ? blog ? accredited-investor-verific...
A company selling securities under Regulation D must still comply with all applicable state securities laws. U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. "Exemption For Limited Offerings Not Exceeding $10 Million?Rule 504 of Regulation D."
This means that any information a company provides to investors must be free from false or misleading statements. Similarly, a company should not exclude any information if the omission makes what is provided to investors false or misleading. Regulation D Offerings - Investor.gov investor.gov ? investing-basics ? glossary investor.gov ? investing-basics ? glossary
The company cannot use general solicitation or advertising to market the securities. The company may sell its securities to an unlimited number of "accredited investors" and up to 35 other purchasers. Rule 506 of Regulation D | Investor.gov investor.gov ? investing-basics ? glossary investor.gov ? investing-basics ? glossary
Rule 506b of Reg D allows for an unlimited amount of capital to be raised from an unlimited number of accredited investors and non-accredited investors, but they may not sponsors may not generally solicit funds.
Rule 506(c) sets out a principles-based method for accredited investor verification, requiring an objective determination by the issuer as to whether the steps taken in verification were ?reasonable? in context of the particular facts and circumstances of each purchaser and transaction. SEC Amends 506(c) Accredited Investor Verification - Vela Wood velawood.com ? sec-amends-506c-accredited-inve... velawood.com ? sec-amends-506c-accredited-inve...