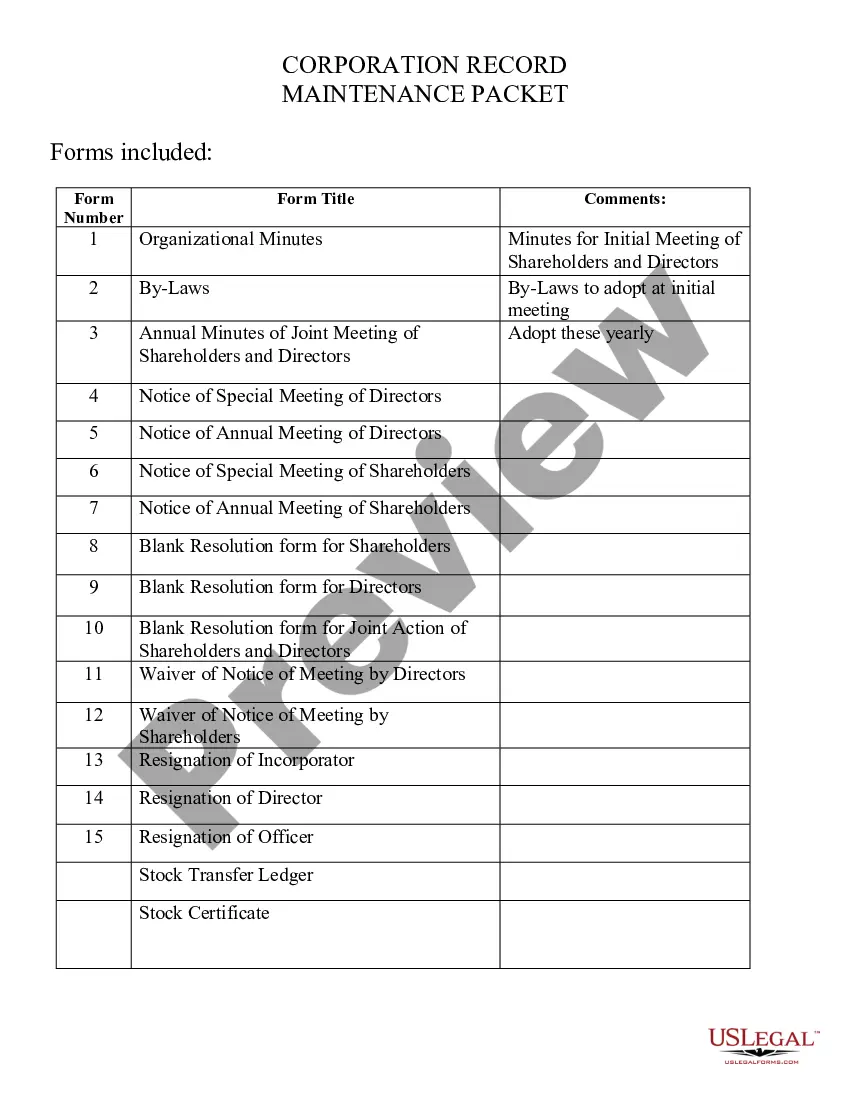
Ohio Warranty Agreement as to Website Software is a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions of the warranty for website software products in the state of Ohio. This agreement is put in place to protect both parties involved in the transaction and provide guidelines for the use and support of the software. In Ohio, there are mainly two types of Warranty Agreements as to Website Software: 1. Limited Warranty Agreement: This type of agreement defines the specific warranties provided by the software developer or vendor. It outlines the extent and duration of the warranty, stating what the developer/vendor is responsible for in case of defects or failures. The limited warranty agreement may mention coverage for a predetermined period, such as 90 days, or it may vary depending on the terms agreed upon. 2. Extended Warranty Agreement: In some cases, a website software developer or vendor may offer an extended warranty agreement. This agreement extends the coverage period beyond the initial limited warranty. It usually comes at an additional cost and provides more comprehensive coverage and support to the buyer. The Ohio Warranty Agreement as to Website Software contains distinct sections that cover various aspects: 1. Definitions: This section defines the key terms used throughout the agreement, such as "software," "developer/vendor," "user," and "defect." 2. Scope of Warranty: Here, the agreement specifies what the warranty covers regarding the website software, including functionalities, performance, and any specific features. It may also outline any exclusions to the warranty coverage. 3. Duration and Limitations: This section details the length of the warranty period, whether it is limited or extended. It also identifies any limitations or conditions under which the warranty may become void, such as improper use, modifications, or unauthorized alterations to the software. 4. Remedies: The agreement describes the available remedies in the event of a software defect or failure. These remedies can include repair, replacement, or a full refund of the purchase cost, depending on the developer/vendor's discretion. 5. Support and Maintenance: This section outlines the support services and maintenance agreements, if any, offered by the developer/vendor. It may specify response times, updates, bug fixes, and ongoing support options. 6. Indemnification: This clause explains the responsibilities of the parties regarding liabilities and indemnification. It may outline the user's obligations to use the software legally and to indemnify the developer/vendor against any claims arising from misuse. 7. Governing Law: The agreement states that it is governed by the laws of the state of Ohio and provides provisions for dispute resolution, such as arbitration or mediation. It is crucial that individuals reading and signing an Ohio Warranty Agreement as to Website Software carefully review all terms and conditions before accepting them. Consulting with legal professionals is recommended to ensure compliance and protection.
Ohio Warranty Agreement as to Web Site Software
Description
How to fill out Ohio Warranty Agreement As To Web Site Software?
US Legal Forms - one of the greatest libraries of lawful kinds in the States - delivers a wide range of lawful record themes you can down load or print. Using the website, you may get thousands of kinds for business and person reasons, sorted by classes, states, or key phrases.You can find the most recent types of kinds like the Ohio Warranty Agreement as to Web Site Software in seconds.
If you currently have a registration, log in and down load Ohio Warranty Agreement as to Web Site Software from your US Legal Forms catalogue. The Download switch will show up on each type you perspective. You have accessibility to all formerly downloaded kinds from the My Forms tab of your respective account.
If you wish to use US Legal Forms initially, listed here are straightforward instructions to obtain began:
- Ensure you have picked out the correct type for the area/region. Click the Preview switch to review the form`s information. Browse the type outline to ensure that you have chosen the right type.
- In case the type does not fit your specifications, take advantage of the Research industry on top of the display screen to discover the one who does.
- When you are happy with the shape, verify your decision by simply clicking the Acquire now switch. Then, opt for the pricing strategy you prefer and supply your accreditations to sign up to have an account.
- Procedure the financial transaction. Make use of bank card or PayPal account to perform the financial transaction.
- Choose the format and down load the shape in your device.
- Make alterations. Fill up, change and print and indicator the downloaded Ohio Warranty Agreement as to Web Site Software.
Each and every format you included in your account lacks an expiration particular date which is yours permanently. So, if you would like down load or print another duplicate, just go to the My Forms section and click on around the type you need.
Obtain access to the Ohio Warranty Agreement as to Web Site Software with US Legal Forms, the most extensive catalogue of lawful record themes. Use thousands of specialist and express-distinct themes that meet up with your small business or person requirements and specifications.