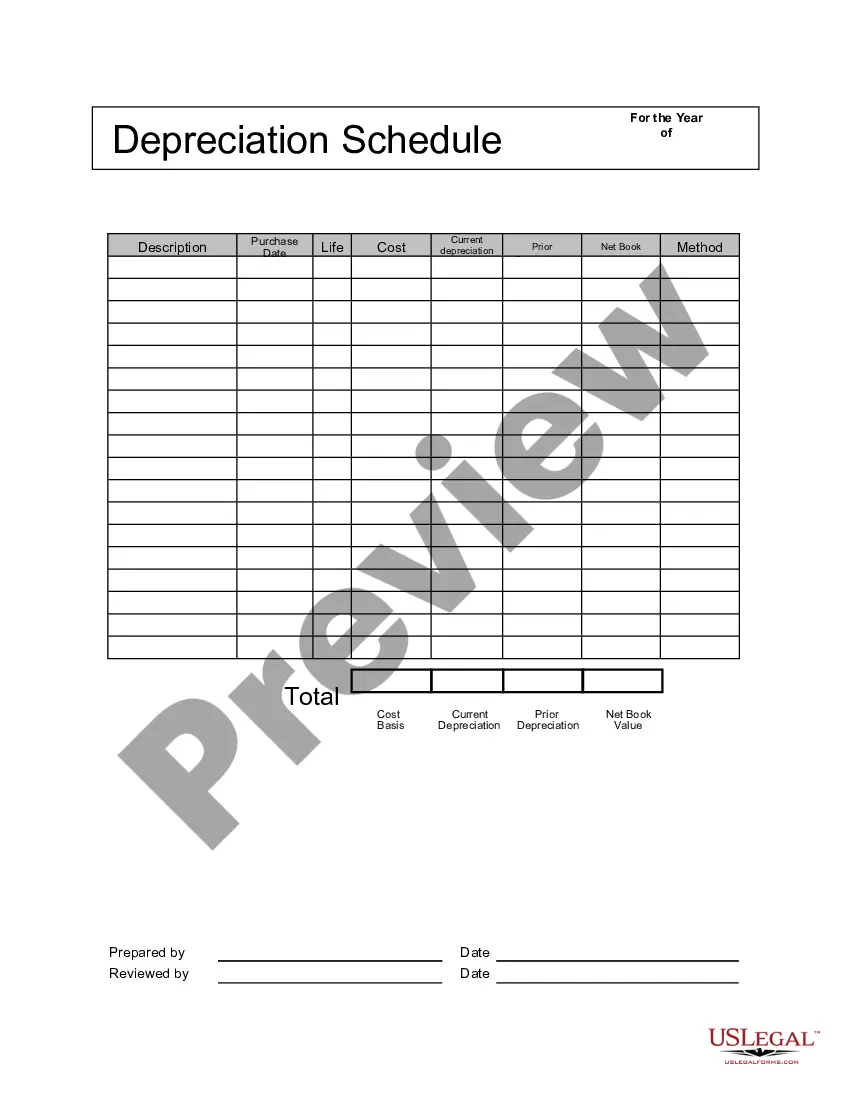
The Ohio Depreciation Schedule is a guide used to determine the depreciation rates and methods applied to various assets for tax purposes in the state of Ohio. It plays a crucial role in calculating the annual depreciation expense for businesses and individuals when reporting their taxable income. This schedule provides guidelines and formulas for determining the useful life and depreciation rates of different asset categories. It helps Ohio taxpayers understand how much of an asset's value can be expensed each year, ensuring accurate financial reporting and tax calculations. It is essential to follow the Ohio Depreciation Schedule correctly as it allows businesses and individuals to allocate the cost of an asset over its useful life rather than deducting the full cost of the asset in the year of purchase. By spreading the depreciation expense over several years, taxpayers can have a more accurate representation of an asset's value over time, reflecting its wear and tear and eventual obsolescence. The Ohio Depreciation Schedule encompasses various asset types, such as buildings, furniture, vehicles, machinery, equipment, computers, and intangible assets like patents or software. Each asset category has its own useful life and depreciation method specified in the schedule. Here are some of the different types of depreciation methods commonly used in the Ohio Depreciation Schedule: 1. Straight-line depreciation: This method spreads the cost of an asset evenly over its useful life, resulting in a steady annual deduction in value. 2. Accelerated depreciation: This method allows for higher depreciation deductions in the earlier years of an asset's useful life while gradually reducing the deductions in subsequent years. It recognizes that assets tend to lose value more rapidly in the early stages of use. 3. Declining balance depreciation: This method applies a higher depreciation rate to an asset's carrying value, resulting in larger deductions during the early years. As the asset's carrying value decreases over time, so does the depreciation deduction. 4. Sum-of-the-year's-digits (SYD) depreciation: This method also front-loads the depreciation deduction, but at a slightly different rate than declining balance. It calculates the annual depreciation expense by multiplying the depreciable base by a fraction based on the asset's remaining useful life. 5. Units-of-production depreciation: This method is used for assets whose value depends on their usage or production output. It calculates the depreciation expense based on the asset's total expected output during its useful life. The Ohio Depreciation Schedule ensures consistent and fair tax treatment of assets, promotes proper financial reporting, and allows businesses and individuals in Ohio to account for asset depreciation accurately. By following the schedule, taxpayers can optimize their tax deductions while complying with the state's regulations and guidelines.
Ohio Depreciation Schedule
Description
How to fill out Ohio Depreciation Schedule?
Choosing the right authorized document template could be a have a problem. Naturally, there are a lot of layouts available on the net, but how will you find the authorized kind you want? Take advantage of the US Legal Forms internet site. The services offers thousands of layouts, such as the Ohio Depreciation Schedule, that can be used for enterprise and personal demands. All of the forms are checked by specialists and meet federal and state demands.
Should you be already listed, log in in your profile and click on the Acquire key to get the Ohio Depreciation Schedule. Make use of your profile to check throughout the authorized forms you possess purchased formerly. Proceed to the My Forms tab of your profile and get another duplicate in the document you want.
Should you be a new customer of US Legal Forms, listed here are basic recommendations that you should stick to:
- Initially, make certain you have selected the right kind for your personal area/region. It is possible to look over the shape using the Preview key and browse the shape explanation to make sure it is the right one for you.
- In the event the kind is not going to meet your requirements, use the Seach area to obtain the proper kind.
- Once you are certain the shape would work, click on the Get now key to get the kind.
- Pick the prices program you would like and enter the required information and facts. Build your profile and buy an order making use of your PayPal profile or Visa or Mastercard.
- Select the data file formatting and down load the authorized document template in your device.
- Complete, edit and print out and sign the obtained Ohio Depreciation Schedule.
US Legal Forms may be the largest collection of authorized forms that you can discover numerous document layouts. Take advantage of the service to down load professionally-produced documents that stick to state demands.