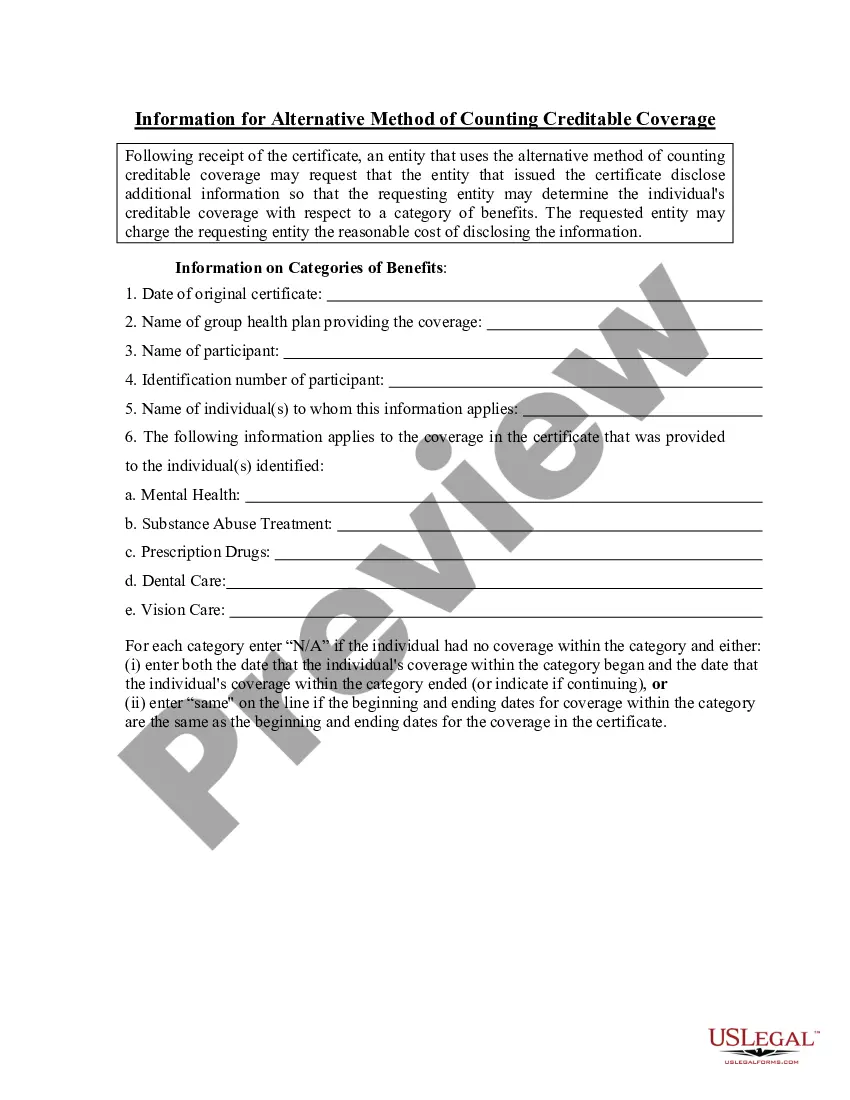
Ohio Information for Alternative Method of Counting Creditable Coverage
Description
How to fill out Information For Alternative Method Of Counting Creditable Coverage?
Selecting the finest legal document format can be a challenge.
Of course, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how do you obtain the legal document you require.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. The service offers a vast selection of templates, such as the Ohio Information for Alternative Method of Counting Creditable Coverage, which you can utilize for business and personal purposes.
You can explore the template using the Review option and examine the template details to confirm it is suitable for you.
- All forms are verified by professionals and meet state and federal regulations.
- If you are currently registered, Log In to your account and click the Download option to obtain the Ohio Information for Alternative Method of Counting Creditable Coverage.
- Use your account to browse the legal forms you have purchased previously.
- Go to the My documents section of your account and retrieve another copy of the document you need.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are simple instructions for you to follow.
- First, ensure that you have selected the correct form for your city/region.
Form popularity
FAQ
You should receive a notice from your employer or plan around September of each year, informing you if your drug coverage is creditable. If you have not received this notice, contact your human resources department, drug plan, or benefits manager.
COBRA is not normally considered to be creditable coverage for Medicare major medical benefits, so people who are enrolled in COBRA and do not enroll in Medicare Part B within 8 months of turning 65 face substantial financial penalties for the rest of their lives, even if they have months or years left on their COBRA
The Notice of Creditable Coverage works as proof of your coverage when you first become eligible for Medicare. Those who have creditable coverage through an employer or union receive a Notice of Creditable Coverage in the mail each year. This notice informs you that your current coverage is creditable.
Group health plan sponsors are required to disclose to CMS whether their prescription drug coverage is creditable or non-creditable. This disclosure is required regardless of whether the health plan's coverage is primary or secondary to Medicare.
In order to be considered creditable, the coverage plan's prescription drug coverage must meet or exceed the value of Medicare Part D. Most companies offering prescription drug coverage are required to disclose their status as creditable or non-creditable coverage programs.
Non-creditable coverage: A health plan's prescription drug coverage is non-creditable when the amount the plan expects to pay, on average, for prescription drugs for individuals covered by the plan in the coming year is less than that which standard Medicare prescription drug coverage would be expected to pay.
Creditable coverage is a health insurance, prescription drug, or other health benefit plan that meets a minimum set of qualifications. Types of creditable coverage plans include group and individual health plans, and student health plans, as well as a variety of government-sponsored or government-provided plans.
Non-creditable coverage: A health plan's prescription drug coverage is non-creditable when the amount the plan expects to pay, on average, for prescription drugs for individuals covered by the plan in the coming year is less than that which standard Medicare prescription drug coverage would be expected to pay.
The Notice of Creditable Coverage works as proof of your coverage when you first become eligible for Medicare. Those who have creditable coverage through an employer or union receive a Notice of Creditable Coverage in the mail each year. This notice informs you that your current coverage is creditable.
Prescription drug coverage is creditable if the actuarial value of the coverage equals or exceeds the actuarial value of standard prescription drug coverage under Medicare Part D, as demonstrated through the use of generally accepted actuarial principles and in accordance with Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services