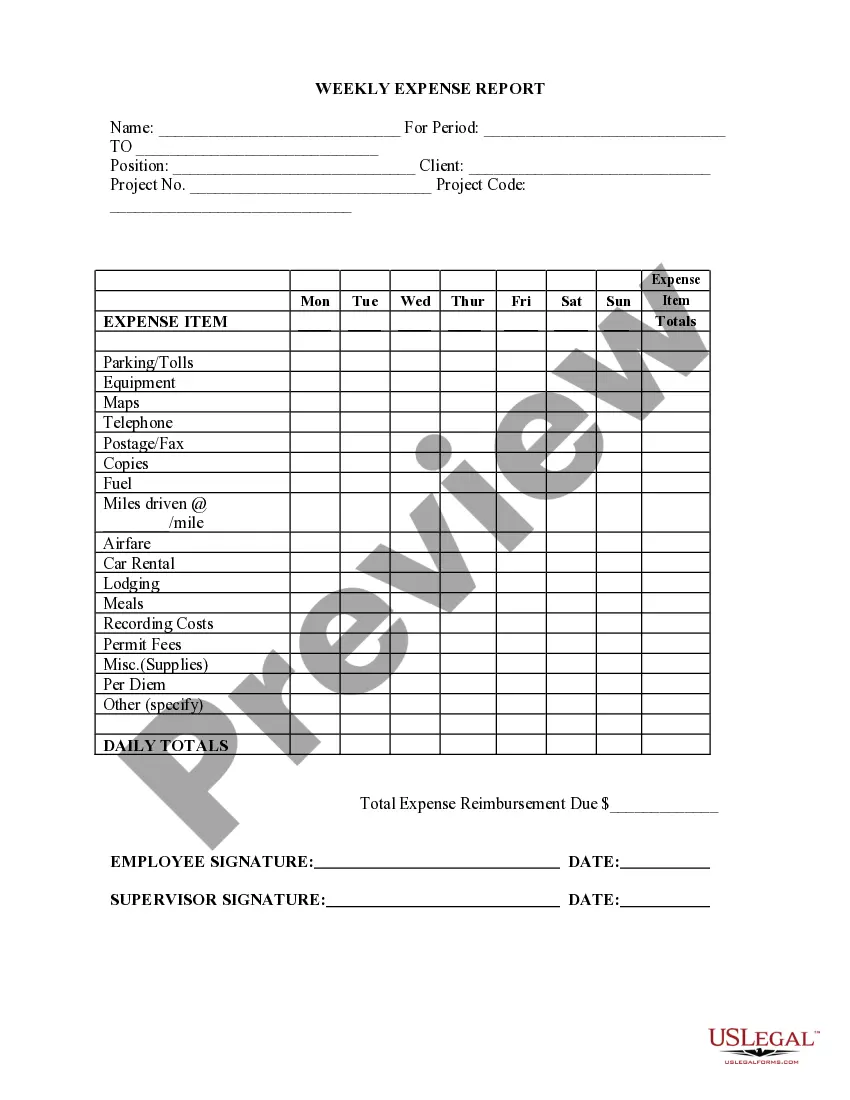
Ohio Employee Time Report (Nonexempt)
Description
How to fill out Employee Time Report (Nonexempt)?
Are you currently in a situation where you require documents for either business or personal purposes almost every day.
There are numerous legal document templates available online, but discovering reliable ones can be challenging.
US Legal Forms offers a vast array of form templates, including the Ohio Employee Time Report (Nonexempt), designed to comply with federal and state regulations.
Once you locate the appropriate form, click Buy now.
Choose the pricing plan you require, fill in the necessary information to create your account, and process the order using PayPal or a Visa or Mastercard.
- If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms site and possess an account, simply Log In.
- Then, you can download the Ohio Employee Time Report (Nonexempt) template.
- If you do not have an account and wish to start using US Legal Forms, follow these instructions.
- Obtain the form you need and ensure it is for the correct city/county.
- Utilize the Preview button to view the form.
- Review the description to confirm that you have selected the correct form.
- If the form is not what you are looking for, use the Search field to find the form that fulfills your needs and requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
To qualify as exempt your employer must pay you a guaranteed minimum salary each week, and your primary job duties must fall into a specific category (Overtime Exemptions: Executive, Administrative, Professional, Computer Related, Outside Sales)
Salary level test. Employees who are paid less than $23,600 per year ($455 per week) are nonexempt. (Employees who earn more than $100,000 per year are almost certainly exempt.)
Examples of non-exempt employees include contractors, freelancers, interns, servers, retail associates and similar jobs. Even if non-exempt employees earn more than the federal minimum wage, they still take direction from supervisors and do not have administrative or executive positions.
Executives, administrators, and other professionals earning at least $455 per week do not have to be paid overtime under Section 13(a)(1) of the Fair Labor Standards Act. External salespeople (who often set their own hours) are also exempted from OH overtime requirements, as are some types of computer-related workers.
"Yes," your employer can require you to work overtime and can fire you if you refuse, according to the Fair Labor Standards Act or FLSA (29 U.S.C. § 201 and following), the federal overtime law. The FLSA sets no limits on how many hours a day or week your employer can require you to work.
Nonexempt: An individual who is not exempt from the overtime provisions of the FLSA and is therefore entitled to overtime pay for all hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek (as well as any state overtime provisions). Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis.
Those who are covered are considered non-exempt and must be paid for all hours worked, including overtime if more than 40 hours are worked in the week. If an employee's duties and pay change, or if the regulations are updated, that person's FLSA status may change from exempt to non-exempt.
If you are a non-exempt employee, your employer must pay you at least the federal minimum wage (currently $7.25 per hour in Texas and under federal law) and must pay you overtime pay at a rate of at least one and a half times your hourly pay rate for all hours worked over 40 in each workweek.
Some employees are not included in the overtime pay rules because of their duties and annual pay. They are considered exempt. Those who are covered are considered non-exempt and must be paid for all hours worked, including overtime if more than 40 hours are worked in the week.
Exempt employees are mostly paid on a salary basis and not per hour. Unlike non-exempt employees, employers may decide whether to pay exempt employees for any extra work outside the official 40 working hours per week. As a business owner, this allows you flexibility in your payment and employee benefits policies.