This Agreement is to insure that no dispute or controversy directly or indirectly concerning any matter relating to this Operating Agreement shall become the subject of court action, but that any dispute or controversy shall be presented to an Arbitration Panel, except as specifically set forth in this provision. The decision of the panel shall be final and binding as to all Parties and their privies without the right of appeal.
Ohio Arbitration
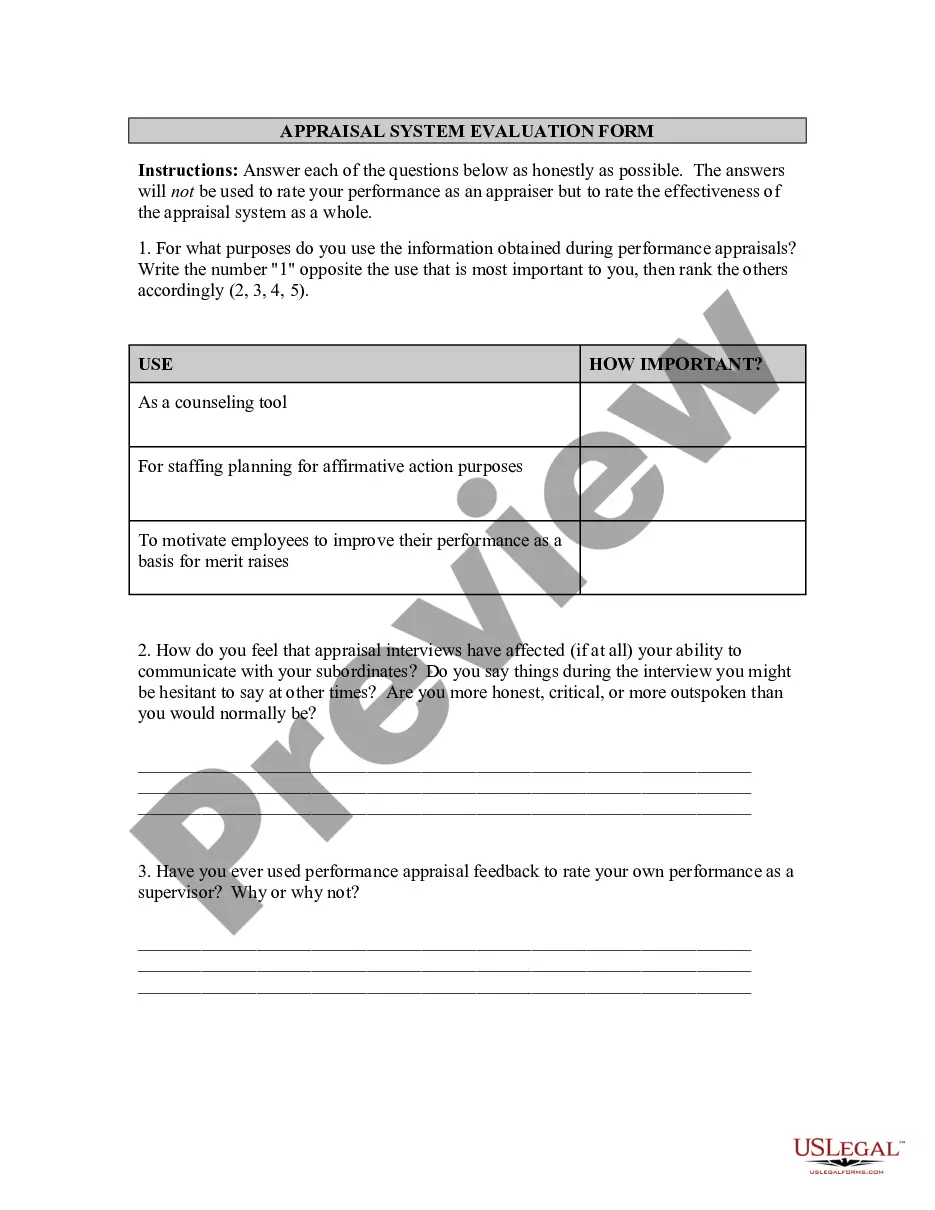
Description
How to fill out Arbitration?
You are able to spend several hours on-line searching for the authorized document web template that suits the state and federal requirements you require. US Legal Forms offers thousands of authorized forms that happen to be examined by specialists. You can actually acquire or printing the Ohio Arbitration from our assistance.
If you already have a US Legal Forms bank account, it is possible to log in and then click the Down load option. Afterward, it is possible to total, revise, printing, or indicator the Ohio Arbitration. Every authorized document web template you purchase is your own property for a long time. To acquire an additional version of any purchased develop, visit the My Forms tab and then click the corresponding option.
If you use the US Legal Forms website for the first time, stick to the easy directions beneath:
- Very first, make certain you have chosen the correct document web template to the county/area of your choice. Look at the develop explanation to ensure you have selected the correct develop. If accessible, make use of the Preview option to look from the document web template too.
- If you wish to get an additional variation from the develop, make use of the Look for discipline to obtain the web template that fits your needs and requirements.
- When you have located the web template you want, just click Acquire now to proceed.
- Find the rates strategy you want, type your qualifications, and sign up for your account on US Legal Forms.
- Full the financial transaction. You may use your credit card or PayPal bank account to pay for the authorized develop.
- Find the format from the document and acquire it for your system.
- Make modifications for your document if required. You are able to total, revise and indicator and printing Ohio Arbitration.
Down load and printing thousands of document templates using the US Legal Forms web site, which offers the greatest variety of authorized forms. Use specialist and express-certain templates to deal with your small business or specific needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
Mediators and arbitrators do not always lead to settlement. If this is true for you, choosing to go to court may be the best option for your case. Mediators and arbitrators can help reach settlement. But if they fail, going to court may be your best option.
Arbitration is a voluntary process in which a third party neutral, the arbitrator, hears the facts of the case and renders a decision that may be binding upon the parties. Parties may agree to arbitration in a contract or after the dispute arises. Court-ordered arbitration in Ohio is mandatory and non-binding.
The parties and arbitrators meet in person to conduct the hearing in which the parties present arguments and evidence in support of their respective cases. After the conclusion of the hearing, the arbitrators deliberate the facts of the case and render a written decision called an award.
Usually less expensive Most of the time, but not always the case, arbitration is a lot less expensive than litigation. Arbitration is often resolved much more quickly than court proceedings, so attorney fees are reduced.
You will likely have to take your workplace dispute to arbitration if, in your employment agreement or application for employment, you signed an ?arbitration clause.? An arbitration clause is typically found in an employment agreement, application, or employee handbook.
Arbitrations are very similar to trials in that each party gets to present their side of the case. Although the procedures are much less formal, arbitrations are structured similarly to mini-trials. Each side presents an opening statement in which they clarify their version of the matters at stake.
Ohio has a public policy favoring the enforcement of arbitration provisions in contracts and ORC 2711.01(A) provides that such provisions will be enforced unless grounds exist in law or equity for revocation of the contract.
Judicial Arbitration is like a trial. But it is less formal and there is no jury. Each side presents its case to a ?neutral? person, also called ?arbitrator.? The arbitrator is either a lawyer or a retired judge, and does not take sides or give advice.