Restrictive covenants in employment agreements can be very useful to companies on the leading edge of technology and business innovation. This document is a general checklist of factors employers should consider with respect to the use of such covenants.
Ohio Employee Restrictive Covenants
Description
How to fill out Employee Restrictive Covenants?
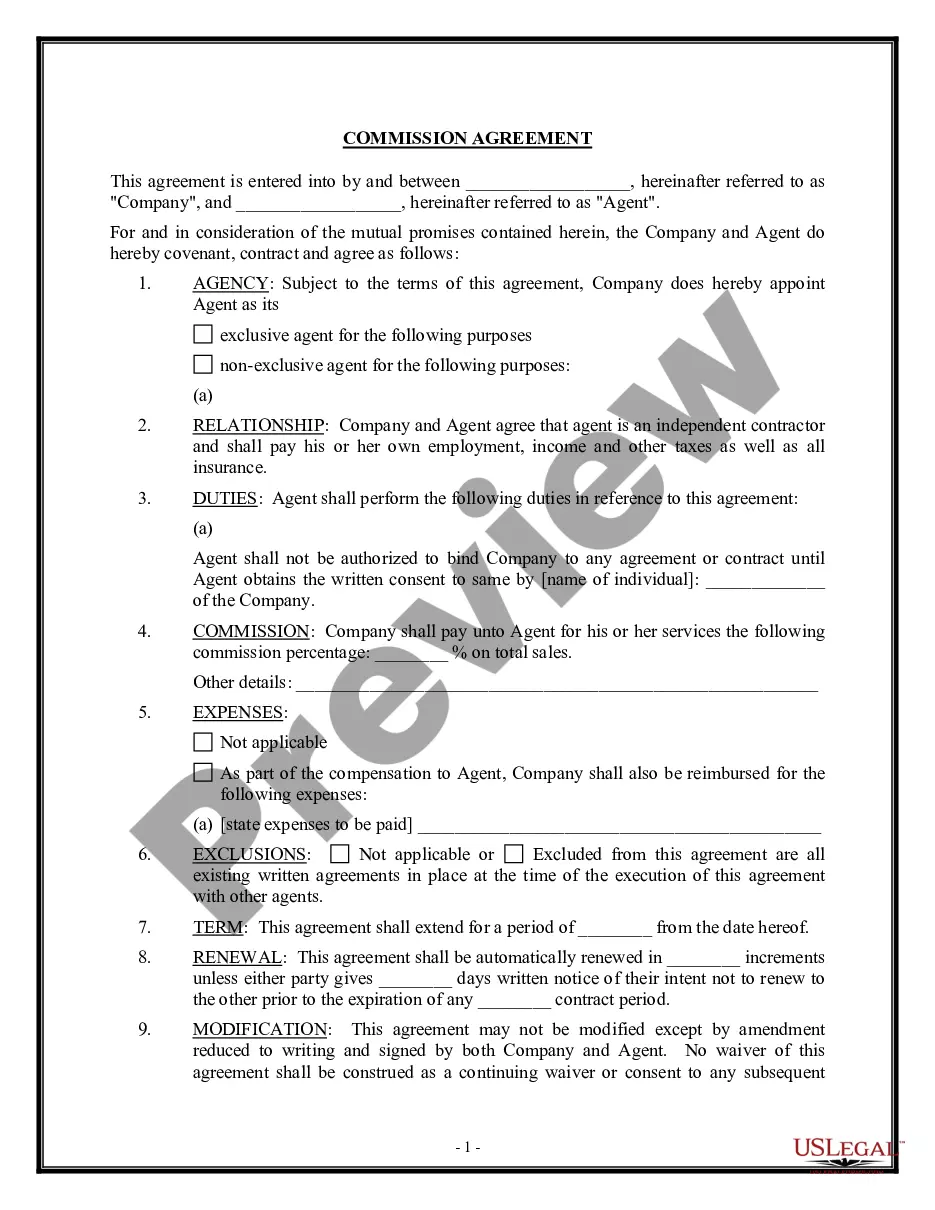
You are able to spend several hours on the web trying to find the legitimate document design that suits the state and federal needs you need. US Legal Forms gives a huge number of legitimate varieties which can be reviewed by experts. You can easily acquire or print the Ohio Employee Restrictive Covenants from the support.
If you have a US Legal Forms profile, it is possible to log in and then click the Down load switch. After that, it is possible to comprehensive, change, print, or signal the Ohio Employee Restrictive Covenants. Every legitimate document design you get is your own property eternally. To acquire one more backup associated with a obtained form, visit the My Forms tab and then click the related switch.
If you are using the US Legal Forms site the first time, adhere to the easy recommendations listed below:
- First, ensure that you have chosen the best document design for your region/city of your liking. Read the form explanation to ensure you have picked out the proper form. If offered, use the Review switch to search from the document design also.
- If you wish to locate one more edition of the form, use the Look for area to find the design that meets your needs and needs.
- After you have found the design you would like, just click Purchase now to move forward.
- Choose the pricing program you would like, type in your qualifications, and sign up for an account on US Legal Forms.
- Comprehensive the financial transaction. You may use your Visa or Mastercard or PayPal profile to purchase the legitimate form.
- Choose the structure of the document and acquire it to the device.
- Make changes to the document if possible. You are able to comprehensive, change and signal and print Ohio Employee Restrictive Covenants.
Down load and print a huge number of document templates making use of the US Legal Forms Internet site, that offers the largest assortment of legitimate varieties. Use specialist and status-specific templates to take on your small business or personal demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
North Carolina This state adheres to the strict blue pencil doctrine, such that courts may not rewrite the covenant, but sever overbroad provisions and enforce the remainder. Ohio This state follows the ?reasonable alteration? approach, in which courts have discretion to modify an overbroad covenant.
Under Ohio law, noncompetition contracts are generally enforceable if they are reasonable.
While non-competition agreements are legal in Ohio, they are scrutinized carefully by the courts. Such restrictive covenants are lawful if the restraints are reasonably necessary to protect the employer's legitimate business interests.
An Ohio Standard Clause limiting an employee's solicitation of employees and customers during the term of the employee's employment and for a specified period of time after the employment relationship ends.
Finally, while your HOA can't place restrictive covenants that violate state or federal laws, they can still limit your rights within reason.
The most common types of post-employment restrictive covenants include non-competition clauses and restrictions prohibiting the solicitation of customers/ clients and employees, each of which are in effect both during the employment relationship and for defined period thereafter (e.g. six months).
Restrictive covenants may contain 4 different types of promises: (1) a promise not to compete with one's former employer; (2) a promise not to solicit or accept business from customers of the former employer; (3) a promise not to recruit or hire away employees of the former employer; and (4) the promise not to use or ...
Under Ohio law, noncompetition contracts are generally enforceable if they are reasonable. The question of what's reasonable is a very fact-specific one though. It depends on the particular circumstances of a given situation, and the Ohio Supreme Court has set out a legal test for courts to apply.