A 401(k) is a type of retirement savings account in the United States, which takes its name from subsection 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code (Title 26 of the United States Code). A contributor can begin to withdraw funds after reaching the age of 59 1/2 years. 401(k)s were first widely adopted as retirement plans for American workers, beginning in the 1980s. The 401(k) emerged as an alternative to the traditional retirement pension, which was paid by employers. Employer contributions with the 401(k) can vary, but in general the 401(k) had the effect of shifting the burden for retirement savings to workers themselves. In 2011, about 60% of American households nearing retirement age have 401(k)-type accounts .
Employers can help their employees save for retirement while reducing taxable income under this provision, and workers can choose to deposit part of their earnings into a 401(k) account and not pay income tax on it until the money is later withdrawn in retirement. Interest earned on money in a 401(k) account is never taxed before funds are withdrawn. Employers may choose to, and often do, match contributions that workers make. The 401(k) account is typically administered by the employer, while in the usual "participant-directed" plan, the employee may select from different kinds of investment options. Employees choose where their savings will be invested, usually, between a selection of mutual funds that emphasize stocks, bonds, money market investments, or some mix of the above. Many companies' 401(k) plans also offer the option to purchase the company's stock. The employee can generally re-allocate money among these investment choices at any time. In the less common trustee-directed 401(k) plans, the employer appoints trustees who decide how the plan's assets will be invested.
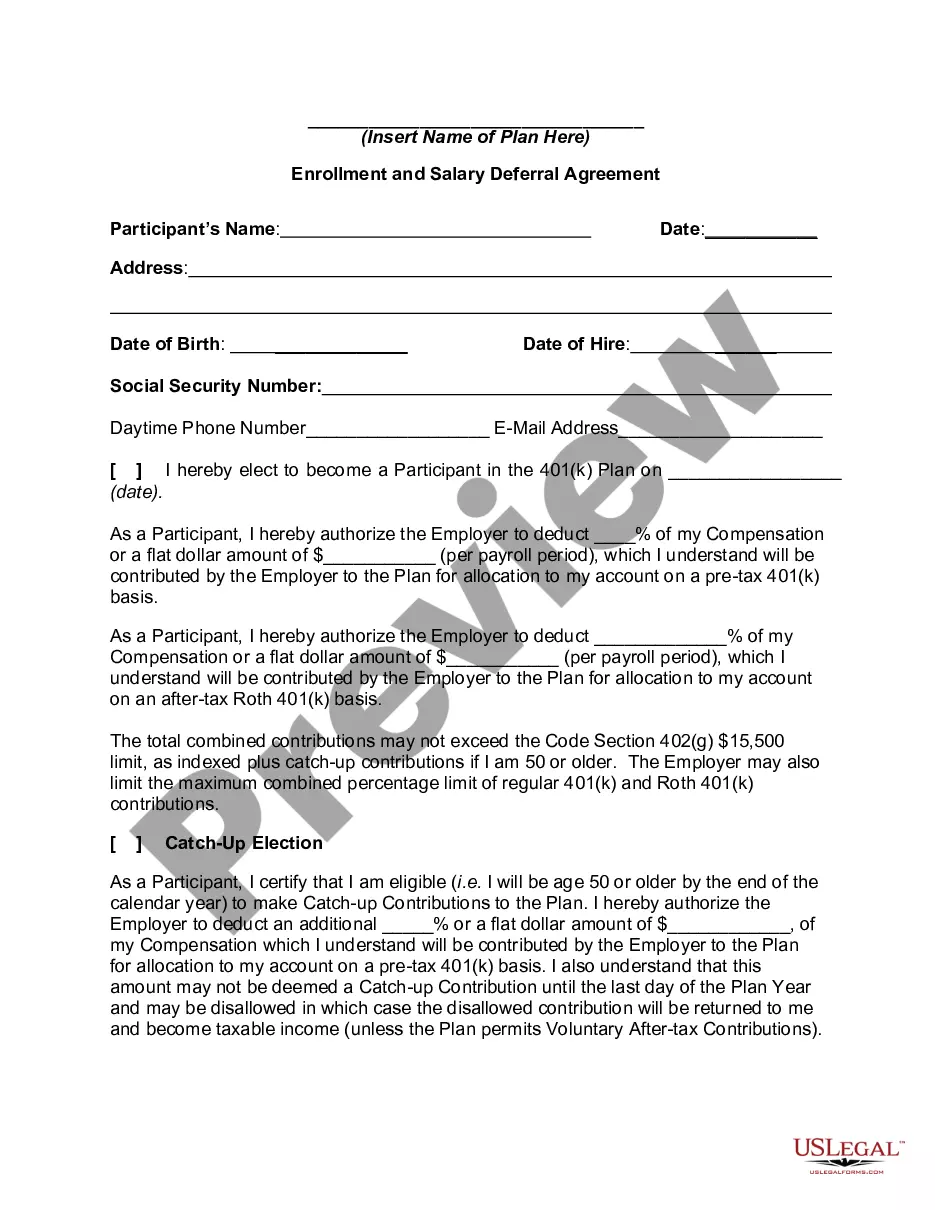
Oklahoma Enrollment and Salary Deferral Agreement is a legally binding agreement entered into by an employer and an employee in the state of Oklahoma. This agreement allows employees to defer a portion of their salary or wages for retirement savings purposes. It is designed to provide tax advantages and financial security to the employees in their future retirement years. The primary purpose of the Oklahoma Enrollment and Salary Deferral Agreement is to offer employees the opportunity to contribute a predetermined amount of their salary to a retirement plan, such as a 401(k) or 403(b) plan. These plans are set up by the employer and are usually governed by the rules and regulations established by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This agreement specifies the terms and conditions under which the employee can defer a portion of their salary. It outlines the amount or percentage of salary that can be deferred, the timeframe during which the deferral can occur, and any limitations or restrictions imposed by the employer or the retirement plan. There are different types of Oklahoma Enrollment and Salary Deferral Agreements based on the retirement plan chosen by the employer. Some common types include: 1. Traditional 401(k) Plan: In this plan, an eligible employee can defer a portion of their salary before taxes are withheld, which means the contributions are made on a pre-tax basis. These contributions are then invested and grow tax-deferred until they are withdrawn at retirement. 2. Roth 401(k) Plan: Unlike the traditional 401(k) plan, the Roth 401(k) plan allows employees to make after-tax contributions. The contributions grow tax-free, and qualified withdrawals are also tax-free during retirement. 3. 403(b) Plan: This plan is typically offered by nonprofit organizations, public schools, and certain tax-exempt entities. It allows employees to defer a portion of their salary on a pre-tax basis, similar to the traditional 401(k) plan. 4. SIMPLE IRA: This plan, suitable for small businesses, allows employees to defer a portion of their salary into an Individual Retirement Account (IRA). The contributions are made on a pre-tax basis, and the employer may also make matching contributions. The Oklahoma Enrollment and Salary Deferral Agreement ensures that both the employer and the employee comply with the applicable laws and regulations set forth by the IRS and other governing bodies. It empowers employees to take control of their retirement savings by providing them with an opportunity to accumulate funds for their post-employment years. In conclusion, the Oklahoma Enrollment and Salary Deferral Agreement is a crucial tool that facilitates retirement savings for employees in Oklahoma. By deferring a portion of their salary into a retirement plan, employees can secure a financially stable future, while enjoying the various tax advantages provided by the different types of plans available.Oklahoma Enrollment and Salary Deferral Agreement is a legally binding agreement entered into by an employer and an employee in the state of Oklahoma. This agreement allows employees to defer a portion of their salary or wages for retirement savings purposes. It is designed to provide tax advantages and financial security to the employees in their future retirement years. The primary purpose of the Oklahoma Enrollment and Salary Deferral Agreement is to offer employees the opportunity to contribute a predetermined amount of their salary to a retirement plan, such as a 401(k) or 403(b) plan. These plans are set up by the employer and are usually governed by the rules and regulations established by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This agreement specifies the terms and conditions under which the employee can defer a portion of their salary. It outlines the amount or percentage of salary that can be deferred, the timeframe during which the deferral can occur, and any limitations or restrictions imposed by the employer or the retirement plan. There are different types of Oklahoma Enrollment and Salary Deferral Agreements based on the retirement plan chosen by the employer. Some common types include: 1. Traditional 401(k) Plan: In this plan, an eligible employee can defer a portion of their salary before taxes are withheld, which means the contributions are made on a pre-tax basis. These contributions are then invested and grow tax-deferred until they are withdrawn at retirement. 2. Roth 401(k) Plan: Unlike the traditional 401(k) plan, the Roth 401(k) plan allows employees to make after-tax contributions. The contributions grow tax-free, and qualified withdrawals are also tax-free during retirement. 3. 403(b) Plan: This plan is typically offered by nonprofit organizations, public schools, and certain tax-exempt entities. It allows employees to defer a portion of their salary on a pre-tax basis, similar to the traditional 401(k) plan. 4. SIMPLE IRA: This plan, suitable for small businesses, allows employees to defer a portion of their salary into an Individual Retirement Account (IRA). The contributions are made on a pre-tax basis, and the employer may also make matching contributions. The Oklahoma Enrollment and Salary Deferral Agreement ensures that both the employer and the employee comply with the applicable laws and regulations set forth by the IRS and other governing bodies. It empowers employees to take control of their retirement savings by providing them with an opportunity to accumulate funds for their post-employment years. In conclusion, the Oklahoma Enrollment and Salary Deferral Agreement is a crucial tool that facilitates retirement savings for employees in Oklahoma. By deferring a portion of their salary into a retirement plan, employees can secure a financially stable future, while enjoying the various tax advantages provided by the different types of plans available.