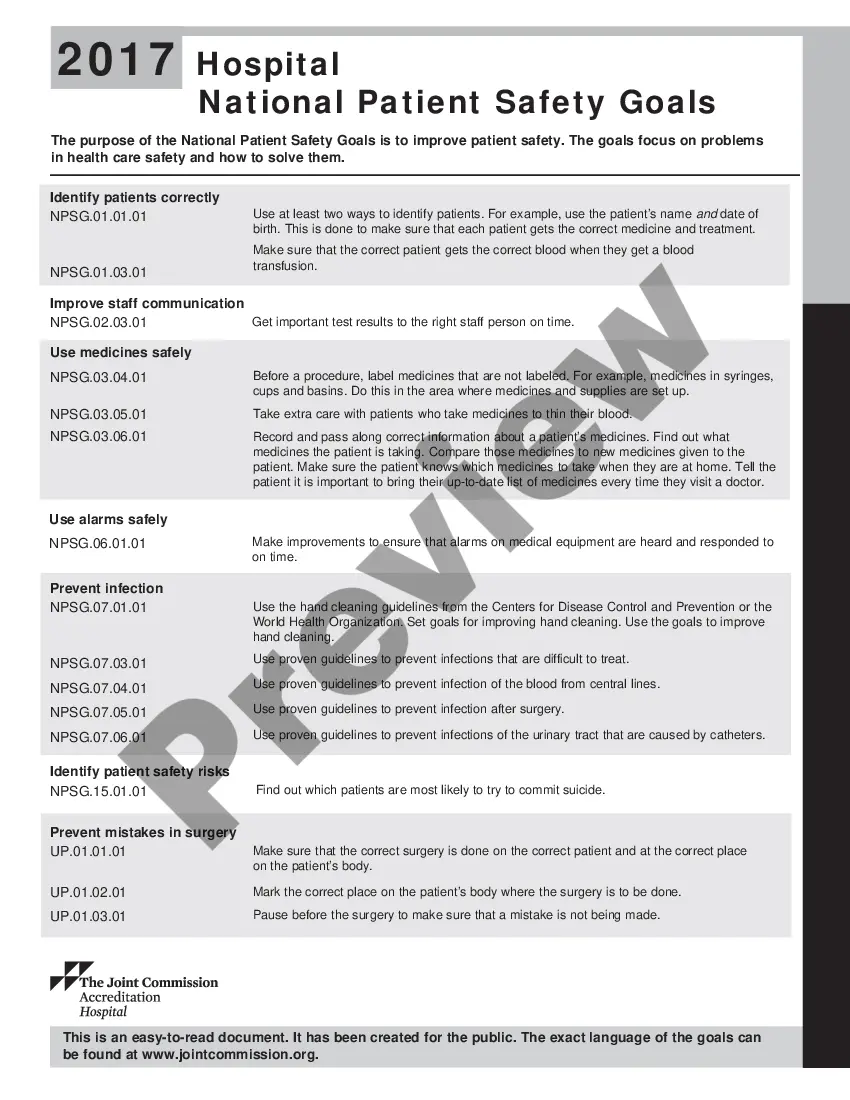
Oklahoma Hospital National Patient Safety Goals (Nests) are a set of guidelines and initiatives implemented to improve patient safety and prevent potential adverse events within hospitals and healthcare facilities across Oklahoma. These goals are established by The Joint Commission, a nonprofit organization that accredits and certifies healthcare organizations in the United States. The primary objective of the Oklahoma Hospital Nests is to provide a standardized framework and promote a culture of safety, ensuring that patients receive high-quality care while minimizing the risk of harm or errors during their hospital stay. These goals encompass several crucial areas of patient safety, including: 1. Patient identification: To prevent patient identification and ensure the correct patient receives the intended treatment, it is essential to accurately identify patients through the use of two unique patient identifiers. 2. Effective communication: Adequate communication among healthcare providers is critical to prevent errors and delays in patient care. Implementing standardized communication processes and vital information hand off protocols can significantly enhance patient safety. 3. Medication safety: Reducing medication errors is a key focus area. Hospitals need to establish systems for safely prescribing, dispensing, and administering medications. This includes utilizing barcode scanning technology, educating staff on medication safety practices, and reconciling medications during care transitions. 4. Infection prevention: Preventing healthcare-associated infections is another crucial aspect of patient safety. Healthcare facilities should have comprehensive infection control programs in place, which include proper hand hygiene, appropriate use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and adherence to isolation protocols. 5. Fall prevention: Hospitals should implement fall prevention strategies to minimize the risk of patient falls, especially among vulnerable populations such as the elderly. This may involve conducting fall risk assessments, providing appropriate assistive devices, and ensuring a safe environment. 6. Surgical site infection prevention: Specific goals focus on reducing the occurrence of surgical site infections by implementing evidence-based practices, such as proper surgical site preparation, antibiotic administration, and maintaining sterile techniques during surgery. 7. Clinical alarm management: Healthcare organizations need to develop and implement processes for managing clinical alarms effectively to avoid alarm fatigue and enhance patient safety. This involves establishing alarm systems that are appropriately set, monitored, and responded too promptly. It is important to note that these goals are regularly updated and refined by The Joint Commission based on emerging patient safety issues and best practices. Healthcare organizations in Oklahoma must proactively adopt and adhere to these goals to ensure the highest level of patient safety and quality care delivery.
Oklahoma Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Oklahoma Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
Are you inside a situation where you will need documents for sometimes company or person purposes just about every time? There are tons of legal document templates accessible on the Internet, but getting kinds you can depend on isn`t simple. US Legal Forms offers a large number of type templates, such as the Oklahoma Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, that are created to satisfy state and federal requirements.
When you are previously acquainted with US Legal Forms website and also have your account, simply log in. Next, you can down load the Oklahoma Hospital National Patient Safety Goals web template.
Unless you provide an profile and need to begin using US Legal Forms, adopt these measures:
- Get the type you require and make sure it is for the proper metropolis/state.
- Make use of the Review key to analyze the shape.
- Look at the description to actually have selected the appropriate type.
- When the type isn`t what you are looking for, use the Lookup area to obtain the type that suits you and requirements.
- If you obtain the proper type, click Buy now.
- Pick the pricing strategy you desire, submit the desired info to make your account, and buy the transaction utilizing your PayPal or bank card.
- Select a handy document formatting and down load your duplicate.
Discover all the document templates you have purchased in the My Forms food selection. You can get a extra duplicate of Oklahoma Hospital National Patient Safety Goals at any time, if possible. Just go through the necessary type to down load or print the document web template.
Use US Legal Forms, the most comprehensive assortment of legal forms, to save lots of time and avoid blunders. The assistance offers professionally created legal document templates that you can use for a variety of purposes. Generate your account on US Legal Forms and begin making your lifestyle easier.