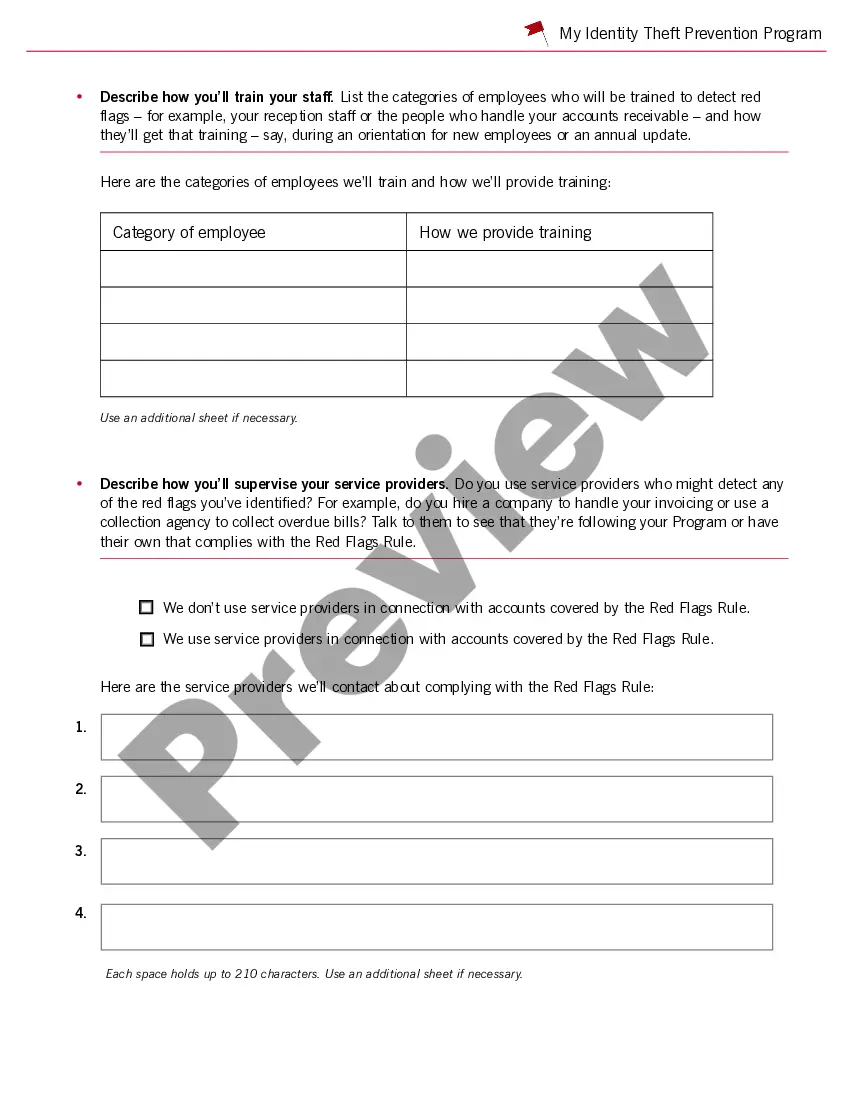
This guide has two parts: Part A to help you determine whether your business or organization is at low risk, and Part B to help you design your written Identity Theft Prevention Program if your business is in the low risk category.
Note: The preview only shows the 1st page of the document.
The Oklahoma Guide to Complying with the Red Flags Rule under the FCRA (Fair Credit Reporting Act) and FACT (Fair and Accurate Credit Transactions Act) is a comprehensive resource designed to assist businesses and organizations in Oklahoma to understand and adhere to the requirements of these federal regulations. The Red Flags Rule aims to protect consumers from identity theft by requiring businesses and organizations that offer or maintain "covered accounts" to implement a program that detects, prevents, and mitigates identity theft. The FACT, on the other hand, enhances the accuracy and privacy of consumer information held by creditors and provides individuals with the right to access their credit reports. This guide is essential for any entity in Oklahoma that considers itself a creditor or routinely extends credit to customers, including banks, credit unions, mortgage lenders, auto dealerships, telecommunications companies, and healthcare providers. It provides detailed instructions on how to develop and implement a compliant Identity Theft Prevention Program (ITP) tailored to each organization's unique circumstances. Key topics covered in the Oklahoma Guide to Complying with the Red Flags Rule include: 1. Definition of covered accounts: The guide clearly outlines what types of accounts fall under the Red Flags Rule, including credit card accounts, mortgage loans, student loans, and other types of consumer accounts. 2. Identifying red flags: It provides an extensive list of red flags that may indicate possible identity theft, such as suspicious documents, unusual account activities, and alerts from credit reporting agencies. 3. Risk assessment: The guide highlights the importance of conducting a risk assessment to identify specific red flags that are relevant to the organization's operations and customer base. 4. Designing an Identity Theft Prevention Program: It provides step-by-step instructions on how to develop an effective ITP, including the appointment of a program administrator, employee training requirements, and methods for detecting, preventing, and responding to identity theft incidents. 5. Ongoing program updates: The guide emphasizes the need for regular evaluation and updates to the ITP to ensure its effectiveness as new risks and technologies emerge. Different types of Oklahoma Guides to Complying with the Red Flags Rule may exist, depending on the industry or sector. For example, there might be specific guides tailored for financial institutions, healthcare providers, or educational institutions in Oklahoma, addressing industry-specific considerations and compliance requirements. By adhering to the Oklahoma Guide to Complying with the Red Flags Rule under the FCRA and FACT, businesses and organizations can safeguard their customers' personal information, prevent identity theft, and mitigate potential losses. Compliance with these regulations not only protects consumers but also helps establish trust and credibility in the marketplace.The Oklahoma Guide to Complying with the Red Flags Rule under the FCRA (Fair Credit Reporting Act) and FACT (Fair and Accurate Credit Transactions Act) is a comprehensive resource designed to assist businesses and organizations in Oklahoma to understand and adhere to the requirements of these federal regulations. The Red Flags Rule aims to protect consumers from identity theft by requiring businesses and organizations that offer or maintain "covered accounts" to implement a program that detects, prevents, and mitigates identity theft. The FACT, on the other hand, enhances the accuracy and privacy of consumer information held by creditors and provides individuals with the right to access their credit reports. This guide is essential for any entity in Oklahoma that considers itself a creditor or routinely extends credit to customers, including banks, credit unions, mortgage lenders, auto dealerships, telecommunications companies, and healthcare providers. It provides detailed instructions on how to develop and implement a compliant Identity Theft Prevention Program (ITP) tailored to each organization's unique circumstances. Key topics covered in the Oklahoma Guide to Complying with the Red Flags Rule include: 1. Definition of covered accounts: The guide clearly outlines what types of accounts fall under the Red Flags Rule, including credit card accounts, mortgage loans, student loans, and other types of consumer accounts. 2. Identifying red flags: It provides an extensive list of red flags that may indicate possible identity theft, such as suspicious documents, unusual account activities, and alerts from credit reporting agencies. 3. Risk assessment: The guide highlights the importance of conducting a risk assessment to identify specific red flags that are relevant to the organization's operations and customer base. 4. Designing an Identity Theft Prevention Program: It provides step-by-step instructions on how to develop an effective ITP, including the appointment of a program administrator, employee training requirements, and methods for detecting, preventing, and responding to identity theft incidents. 5. Ongoing program updates: The guide emphasizes the need for regular evaluation and updates to the ITP to ensure its effectiveness as new risks and technologies emerge. Different types of Oklahoma Guides to Complying with the Red Flags Rule may exist, depending on the industry or sector. For example, there might be specific guides tailored for financial institutions, healthcare providers, or educational institutions in Oklahoma, addressing industry-specific considerations and compliance requirements. By adhering to the Oklahoma Guide to Complying with the Red Flags Rule under the FCRA and FACT, businesses and organizations can safeguard their customers' personal information, prevent identity theft, and mitigate potential losses. Compliance with these regulations not only protects consumers but also helps establish trust and credibility in the marketplace.