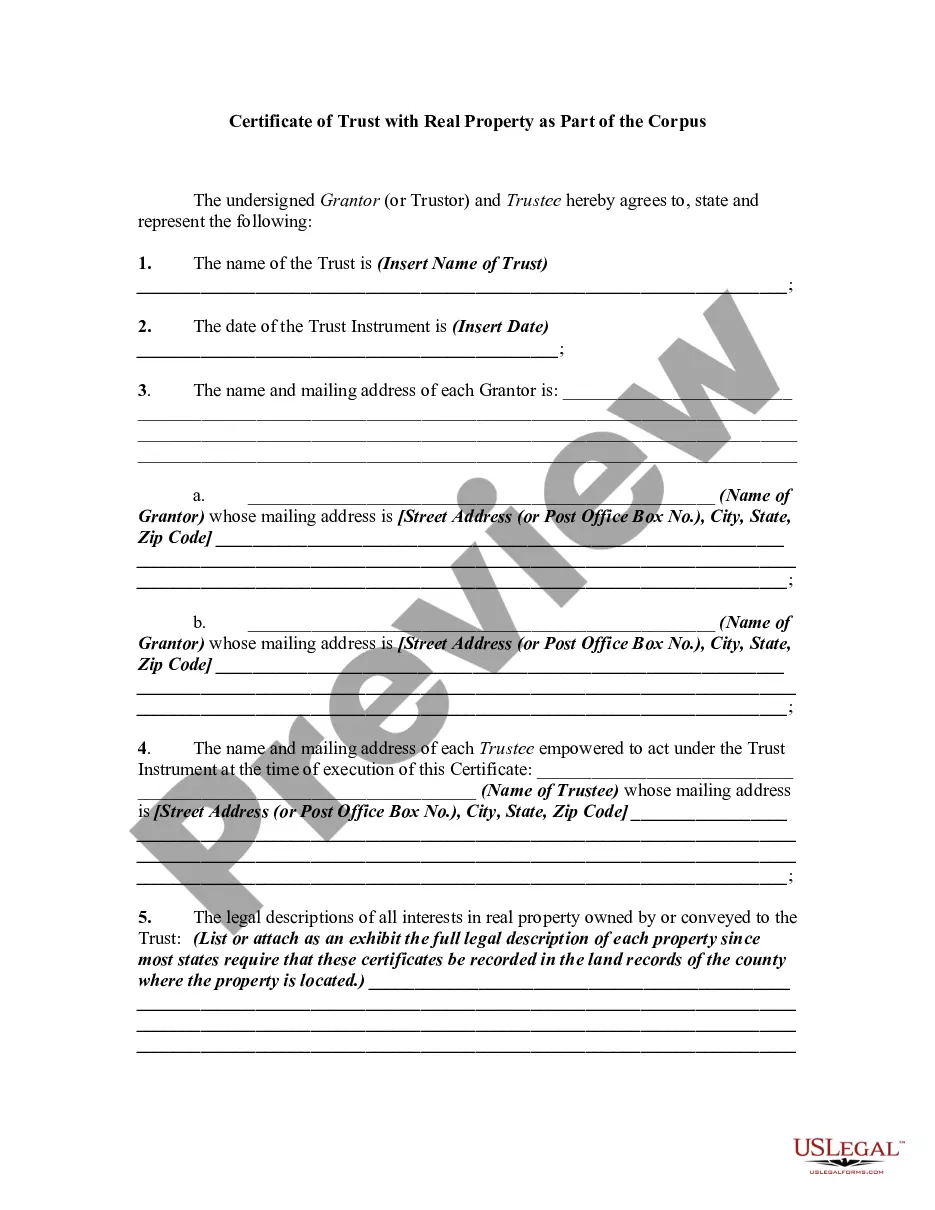
This lease rider form may be used when you are involved in a lease transaction, and have made the decision to utilize the form of Oil and Gas Lease presented to you by the Lessee, and you want to include additional provisions to that Lease form to address specific concerns you may have, or place limitations on the rights granted the Lessee in the standard lease form.
Oklahoma Fresh Water Use and Limitations: A Comprehensive Overview Freshwater resources are crucial for sustaining life, supporting ecosystems, and promoting economic growth. In the state of Oklahoma, the management and utilization of fresh water are critical due to its semi-arid climate and growing population. Understanding the various types of fresh water use and the limitations associated with it is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability of this vital resource. 1. Agricultural Water Use: Agriculture is the largest consumer of freshwater resources in Oklahoma, accounting for a significant amount of water usage. Farmers rely on irrigation systems to cultivate crops and sustain livestock, requiring vast amounts of water. However, the limitations lie in the availability of water supply and the energy-intensive nature of irrigation systems, which can strain both surface and groundwater resources. 2. Municipal Water Use: Municipalities in Oklahoma heavily rely on fresh water for meeting the demands of households, industries, and commercial establishments. This includes water for drinking, sanitation, industrial processes, and generating electricity. The primary concern associated with municipal water use is ensuring a sustainable supply to meet the growing urban population's needs, especially during droughts or periods of water scarcity. 3. Industrial Water Use: Various industries, including manufacturing, mining, and energy production, depend on freshwater resources for their operations. Industries utilize water as a coolant, solvent, and raw material, among other purposes. However, industrial water use often faces limitations due to competition with other sectors, potential pollution through discharge, and the need for advanced treatment facilities to preserve water quality. 4. Recreational Water Use: Oklahoma's abundant freshwater resources also provide significant opportunities for recreational activities such as fishing, boating, swimming, and tourism. This water use category is vital for promoting local economies, enhancing quality of life, and attracting visitors. However, limitations may arise in ensuring sustainable recreational water use due to potential pollution from various sources, such as runoff from agriculture, urban areas, or improper waste disposal practices. 5. Environmental Water Use: Maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems and supporting wildlife habitats are critical aspects of freshwater management in Oklahoma. Environmental water use refers to water reserved for protecting natural ecosystems, including rivers, lakes, and wetlands. Limitations in this sector arise when water allocations do not adequately address the ecological needs of these sensitive environments, leading to habitat degradation and loss of biodiversity. To address the limitations and ensure the sustainable use of freshwater resources in Oklahoma, various strategies are employed. These include implementing efficient irrigation techniques in agriculture, promoting water conservation and recycling in urban areas, regulating industrial discharge practices, enforcing pollution control measures, establishing protected areas for wildlife, and encouraging public awareness and participation in water resource management. In conclusion, Oklahoma's fresh water use and limitations encompass diverse sectors like agriculture, municipalities, industries, recreation, and the environment. Effective management and understanding of these sectors are vital for balancing economic development, environmental protection, and population needs. By adopting sustainable practices and ensuring proper allocation, Oklahoma can secure its freshwater resources for future generations.