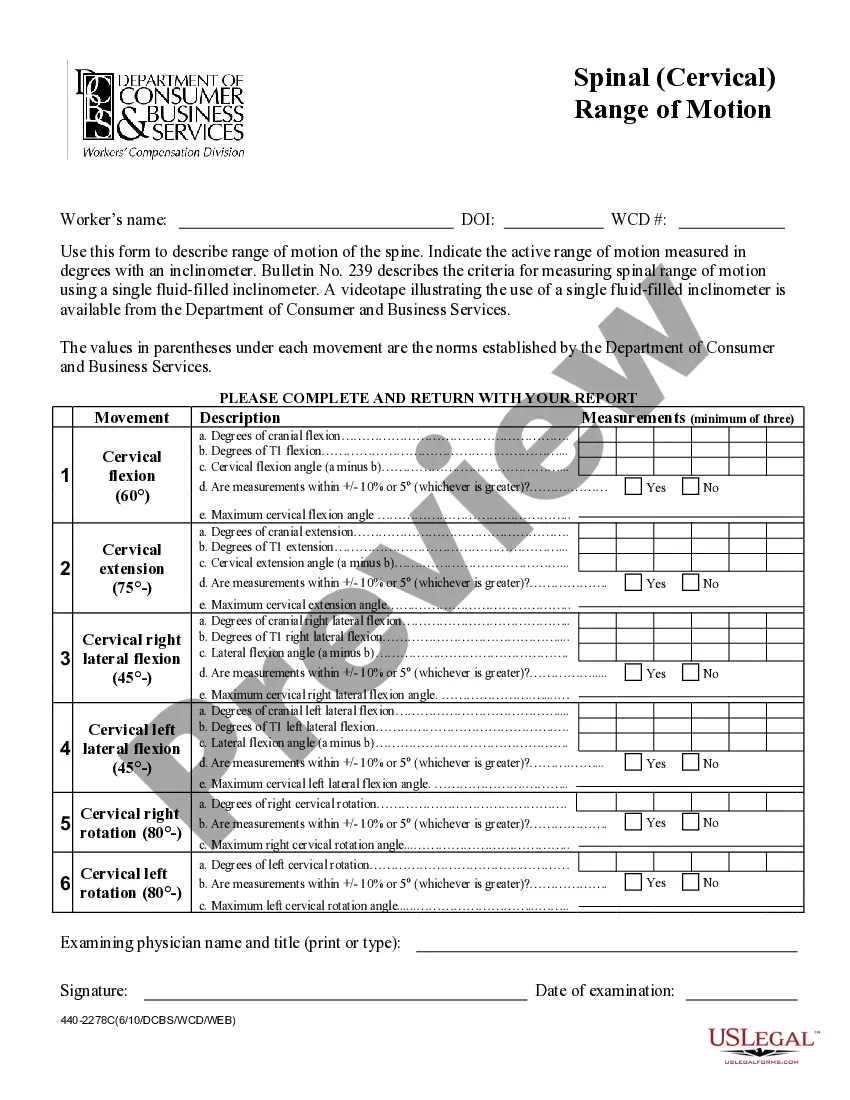
Oregon Spinal (Thoracic) Range of Motion is a physical therapy assessment and treatment procedure used to evaluate the mobility and flexibility of the thoracic spine. It involves testing the range of motion of the thoracic spine in all six directions: flexion, extension, lateral flexion, hyperextension, rotation, and side bending. This assessment can help identify restrictions in movement, weakness, and tightness in the thoracic spine, which can then be addressed with targeted exercises and manual therapy. There are two main types of Oregon Spinal (Thoracic) Range of Motion: Active and Passive. Active Range of Motion is performed by the patient with minimal assistance from the clinician, while Passive Range of Motion is performed by the clinician with the patient remaining relaxed. Both techniques are used to assess and improve thoracic spine mobility and flexibility.
Oregon Spinal (Thoracic) Range of Motion
Description
How to fill out Oregon Spinal (Thoracic) Range Of Motion?
US Legal Forms is the most easy and profitable way to locate appropriate formal templates. It’s the most extensive web-based library of business and personal legal paperwork drafted and checked by attorneys. Here, you can find printable and fillable templates that comply with national and local regulations - just like your Oregon Spinal (Thoracic) Range of Motion.
Obtaining your template requires just a few simple steps. Users that already have an account with a valid subscription only need to log in to the web service and download the form on their device. Afterwards, they can find it in their profile in the My Forms tab.
And here’s how you can get a properly drafted Oregon Spinal (Thoracic) Range of Motion if you are using US Legal Forms for the first time:
- Look at the form description or preview the document to guarantee you’ve found the one corresponding to your requirements, or locate another one utilizing the search tab above.
- Click Buy now when you’re sure of its compatibility with all the requirements, and judge the subscription plan you like most.
- Create an account with our service, log in, and purchase your subscription using PayPal or you credit card.
- Choose the preferred file format for your Oregon Spinal (Thoracic) Range of Motion and download it on your device with the appropriate button.
Once you save a template, you can reaccess it anytime - simply find it in your profile, re-download it for printing and manual completion or import it to an online editor to fill it out and sign more proficiently.
Take advantage of US Legal Forms, your trustworthy assistant in obtaining the required formal paperwork. Try it out!
Form popularity
FAQ
The normal ROM of forward flexion (forward bending) in the thoracic spine is 20° to 45°. Method 1: A difference of 2.7 cm (1.1 inch) in tape measure length (C7-T12) is considered normal.
The individual is instructed to place one hand on the posterior aspect of their neck and rotate the thoracic spine to that side while maintaining the kneeling position (Figure 4b). Once the individual reaches end range, the angle of the inclinometer is recorded. Figure 4.
To consider if a thoracic rotation movement is functional, the torso rotation range measured in seated position and lumbar locked position should be 50 degrees or greater.
Lateral flexion of the thoracic spine is said to average around 20 degrees, the same as the lumbar spine.
On average, each thoracic vertebra can rotate approximately 3 °. Therefore, the entire thoracic spine should demonstrate between 30 -35 ° of total rotation to each side (Neumann, 2010).