Statutes have been enacted in various jurisdictions setting forth requirements as to the form and manner of execution of the constitution or articles of association, and the bylaws, of an association or club. If the drafter does not comply with such formalities, the documents may not be accepted for filing by the designated public officer, and the existence of the association or club as a legal entity will not be recognized. In some jurisdictions, the constitution or articles of association, and the bylaws, must be executed properly. Execution generally implies the signing of the instruments by the proper officers or other parties, in conformity to the requirements of the governing statute.
Statutes in some jurisdictions require that the constitution or articles of association, and the bylaws, be acknowledged or verified. In some jurisdictions, it is required by statute that the constitution or articles of association be recorded, particularly where the association or club owns real property or any interest in real property.
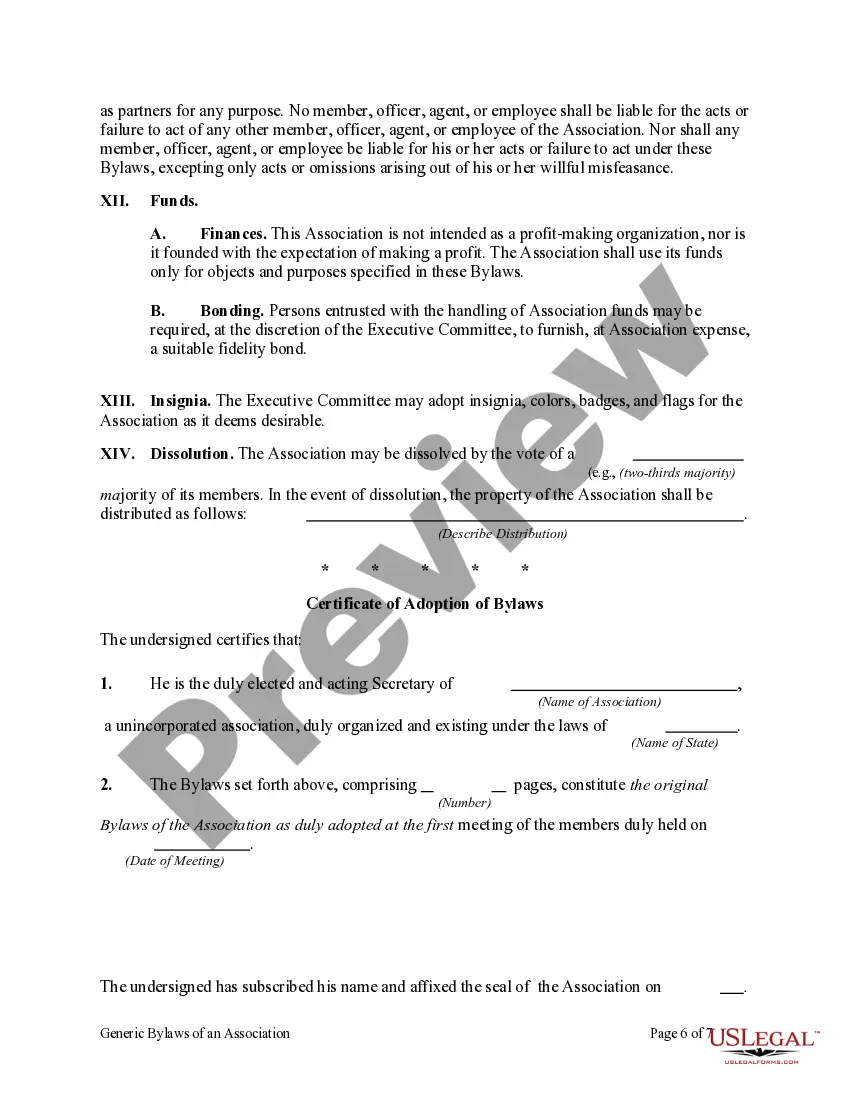
Oregon Generic Bylaws of an Association are a set of rules and regulations that an association must follow to govern its operation and ensure its members are treated fairly. These bylaws serve as a blueprint for conducting association affairs, managing finances, holding meetings, electing officers, and addressing other important matters. The Oregon Generic Bylaws of an Association are designed to be flexible and can be customized based on the specific needs and goals of the association. However, they typically contain several key provisions that are common among all associations: 1. Purpose: This section outlines the purpose and goals of the association, defining its reason for existence and the objectives it aims to achieve. 2. Membership: These bylaws specify the qualifications for membership, the process of joining or leaving the association, and the rights and responsibilities of members. 3. Board of Directors: This section describes the composition, roles, responsibilities, and powers of the board of directors. It outlines how directors are elected or appointed and how they conduct meetings and make decisions on behalf of the association. 4. Meetings: These bylaws address the frequency and notice requirements for association meetings, including board meetings, annual general meetings, and special meetings. They also dictate the procedures for voting, quorum requirements, and minutes keeping. 5. Finances: This section provides guidelines for managing the association's finances, including budgeting, dues, assessments, financial reporting, and the establishment of financial controls. 6. Committees: The Oregon Generic Bylaws often include provisions for creating committees or task forces aiding in the association's operations. It specifies the formation, responsibilities, and powers of these committees. 7. Amendments: This section outlines the process for making changes to the bylaws, including the requirements for notice, voting, and approval of amendments. While the Oregon Generic Bylaws of an Association provide a general framework applicable to most associations, there may also be specific bylaws tailored to different types of organizations, such as: 1. Homeowners' Association (HOA) Bylaws: These bylaws govern the operation of residential communities, outlining rules related to property management, common area maintenance, architectural guidelines, and enforcement provisions. 2. Nonprofit Organization Bylaws: Nonprofit associations have additional considerations, such as requirements for tax-exempt status, fundraising activities, board composition, conflict of interest policies, and the distribution of remaining assets in the event of dissolution. 3. Professional Association Bylaws: Professional associations typically have specific regulations regarding membership criteria, certifications, continuing education requirements, code of ethics, and disciplinary procedures. In conclusion, the Oregon Generic Bylaws of an Association provide a comprehensive framework for governing associations, and they can be adapted to suit the unique needs of different types of organizations, such as homeowners' associations, nonprofit organizations, and professional associations.Oregon Generic Bylaws of an Association are a set of rules and regulations that an association must follow to govern its operation and ensure its members are treated fairly. These bylaws serve as a blueprint for conducting association affairs, managing finances, holding meetings, electing officers, and addressing other important matters. The Oregon Generic Bylaws of an Association are designed to be flexible and can be customized based on the specific needs and goals of the association. However, they typically contain several key provisions that are common among all associations: 1. Purpose: This section outlines the purpose and goals of the association, defining its reason for existence and the objectives it aims to achieve. 2. Membership: These bylaws specify the qualifications for membership, the process of joining or leaving the association, and the rights and responsibilities of members. 3. Board of Directors: This section describes the composition, roles, responsibilities, and powers of the board of directors. It outlines how directors are elected or appointed and how they conduct meetings and make decisions on behalf of the association. 4. Meetings: These bylaws address the frequency and notice requirements for association meetings, including board meetings, annual general meetings, and special meetings. They also dictate the procedures for voting, quorum requirements, and minutes keeping. 5. Finances: This section provides guidelines for managing the association's finances, including budgeting, dues, assessments, financial reporting, and the establishment of financial controls. 6. Committees: The Oregon Generic Bylaws often include provisions for creating committees or task forces aiding in the association's operations. It specifies the formation, responsibilities, and powers of these committees. 7. Amendments: This section outlines the process for making changes to the bylaws, including the requirements for notice, voting, and approval of amendments. While the Oregon Generic Bylaws of an Association provide a general framework applicable to most associations, there may also be specific bylaws tailored to different types of organizations, such as: 1. Homeowners' Association (HOA) Bylaws: These bylaws govern the operation of residential communities, outlining rules related to property management, common area maintenance, architectural guidelines, and enforcement provisions. 2. Nonprofit Organization Bylaws: Nonprofit associations have additional considerations, such as requirements for tax-exempt status, fundraising activities, board composition, conflict of interest policies, and the distribution of remaining assets in the event of dissolution. 3. Professional Association Bylaws: Professional associations typically have specific regulations regarding membership criteria, certifications, continuing education requirements, code of ethics, and disciplinary procedures. In conclusion, the Oregon Generic Bylaws of an Association provide a comprehensive framework for governing associations, and they can be adapted to suit the unique needs of different types of organizations, such as homeowners' associations, nonprofit organizations, and professional associations.