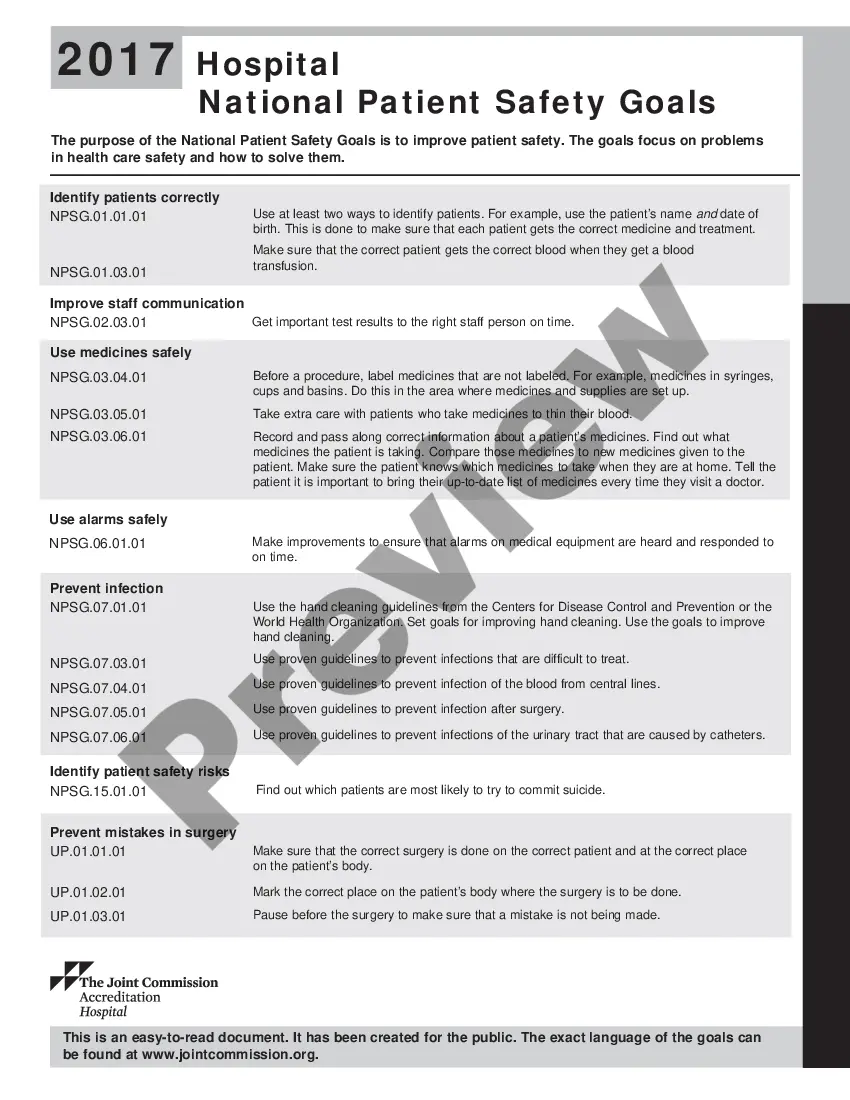
The Oregon Hospital National Patient Safety Goals (OH-NPSGs) are a set of guidelines established by the Oregon Hospital Association (OHA) to improve patient safety and reduce medical errors in healthcare facilities across the state. These goals are designed to ensure that patients receive high-quality care and are protected from harm during their hospital stay. By implementing these goals, hospitals aim to enhance patient outcomes and promote a culture of safety within their organizations. The OH-NPSGs cover various areas of patient safety and address specific focus points to enhance the quality of care provided by hospitals. These goals are regularly reviewed and updated by the OHA in alignment with the national standards set by The Joint Commission, a renowned healthcare accreditation organization. Key elements of the Oregon Hospital National Patient Safety Goals include: 1. Medication Safety: Hospitals must maintain accurate medication lists for patients, reduce the risk of medication errors, and ensure proper labeling and storage of medications. 2. Fall Prevention: Hospitals should assess patients' risk of falls, implement measures to minimize fall hazards, and educate both patients and staff on fall prevention strategies. 3. Infection Control: This goal emphasizes the importance of following established infection control practices preventing hospital-acquired infections. Compliance with hand hygiene protocols, proper cleaning and disinfection procedures, and adherence to isolation precautions are crucial aspects of this goal. 4. Patient Identification: Hospitals must utilize standardized protocols to accurately identify patients, preventing errors in medication administration, specimen collection, and other procedures. 5. Surgical Site Verification: The goal requires hospitals to implement preoperative verification processes to ensure correct patient, procedure, and surgical site, reducing the risk of wrong-site surgeries. 6. Patient and Family Engagement: Encourages hospitals to actively involve patients and their families in care decisions, provide necessary information, and promote open communication to enhance patient satisfaction and safety. 7. Care Transition: This goal focuses on ensuring smooth transitions between healthcare settings, such as coordinating the transfer of care from hospital to home or another facility. It emphasizes clear communication, accurate patient information transfer, and appropriate education during transitions. It is important to note that the Oregon Hospital National Patient Safety Goals may evolve over time, and hospitals are required to stay updated with the latest guidelines and recommendations to maintain compliance. The implementation of these goals aims to foster a patient-centered approach to healthcare delivery and create a safer environment for patients in Oregon hospitals.
Oregon Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Oregon Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
Finding the right legitimate record format might be a have difficulties. Of course, there are tons of layouts accessible on the Internet, but how can you get the legitimate develop you want? Use the US Legal Forms internet site. The assistance provides a huge number of layouts, including the Oregon Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, that you can use for business and personal needs. Each of the forms are checked by experts and meet state and federal specifications.
If you are presently authorized, log in to the bank account and then click the Down load button to obtain the Oregon Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. Use your bank account to appear through the legitimate forms you might have purchased previously. Check out the My Forms tab of your bank account and obtain another copy in the record you want.
If you are a brand new consumer of US Legal Forms, listed below are simple recommendations that you can comply with:
- First, be sure you have selected the proper develop for your personal area/region. You are able to examine the form making use of the Review button and look at the form outline to guarantee it will be the best for you.
- If the develop fails to meet your preferences, utilize the Seach industry to obtain the correct develop.
- When you are positive that the form is proper, click the Buy now button to obtain the develop.
- Pick the pricing prepare you would like and enter the essential details. Make your bank account and purchase the order utilizing your PayPal bank account or bank card.
- Opt for the data file format and acquire the legitimate record format to the device.
- Full, revise and printing and indicator the obtained Oregon Hospital National Patient Safety Goals.
US Legal Forms may be the greatest library of legitimate forms that you will find various record layouts. Use the company to acquire skillfully-produced paperwork that comply with express specifications.