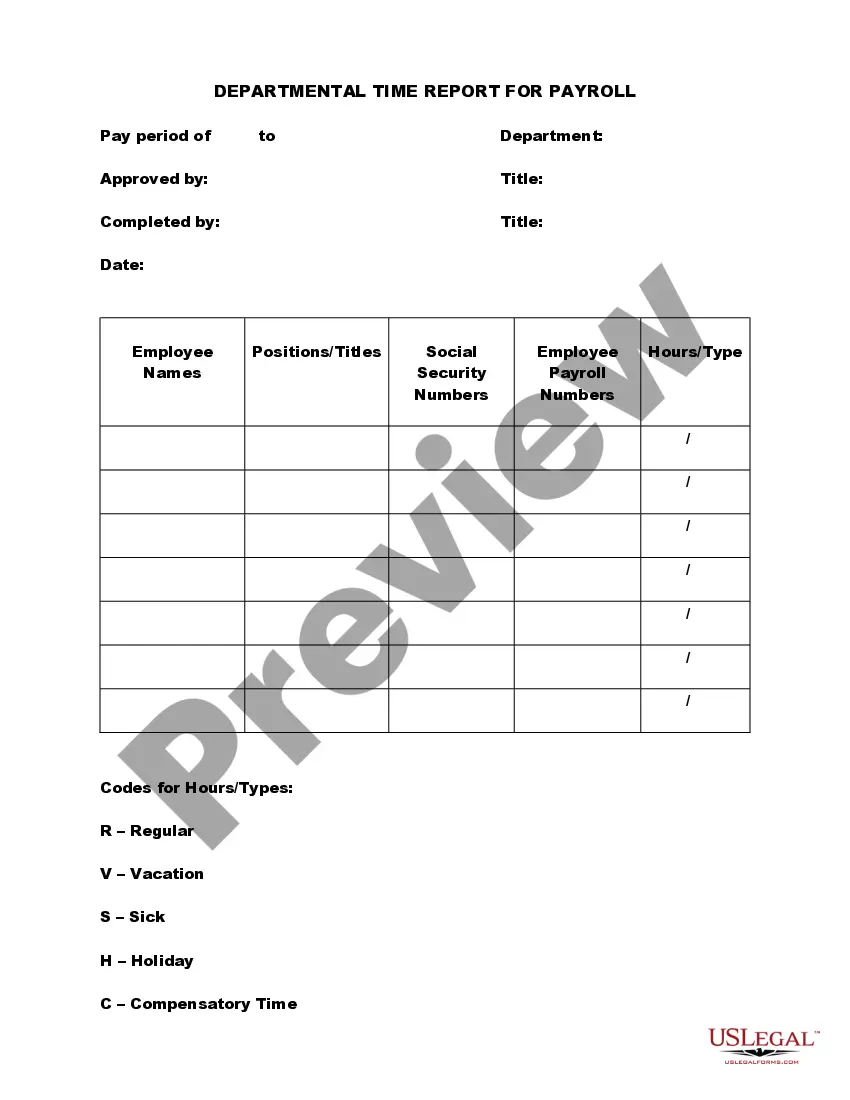
Oregon Overtime Report
Description
How to fill out Overtime Report?
You can dedicate time online exploring for the legal document template that satisfies the federal and state requirements you will require.
US Legal Forms offers thousands of legal forms that are vetted by professionals.
You can conveniently download or print the Oregon Overtime Report from our platform.
If available, utilize the Review button to browse the document template as well.
- If you currently maintain a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and click on the Download button.
- Subsequently, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the Oregon Overtime Report.
- Each legal document template you purchase is yours indefinitely.
- To obtain another copy of any purchased form, visit the My documents tab and click on the corresponding button.
- If this is your first time using the US Legal Forms website, follow the simple directions below.
- First, ensure that you have selected the correct document template for the area/city of your choice.
- Review the form details to confirm that you have chosen the right form.
Form popularity
FAQ
Oregon labor laws require an employer to pay overtime, unless otherwise exempt, at the rate of one and a half times the employee's regular rate of pay for all hours worked in excess of 40 hours in a workweek.
If your job is eligible for overtime protection under Oregon and Federal overtime law as described above, your employer is required by law to pay you an overtime premium for all qualifying overtime hours worked.
The required overtime pay is 1.5 times the hourly rate for hours worked in excess of 40 in a workweek. Overtime is calculated based on hours actually worked, and your employee worked only 35 hours during the workweek.
As a general rule under federal law and Oregon labor laws, overtime refers to hours worked beyond 40 hours in a workweek and must be paid at 1.5 times the regular hourly rate.
The federal overtime provisions are contained in the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Unless exempt, employees covered by the Act must receive overtime pay for hours worked over 40 in a workweek at a rate not less than time and one-half their regular rates of pay.
While some states have daily overtime limit which entitles any employee who works for more then a certain number of hours in a single day to be paid overtime, Oregon does not specify a daily overtime limit.
Legally, your employer can't make you work more than 48 hours a week, including overtime. If they want you to work more than that, your employer has to ask you to opt out of the 48-hour limit. Find out more about the maximum weekly working time limit.
Although there is no daily limit to the number of hours employees may work in canneries, driers and packing plants, employees may not work more than 55 hours in one workweek unless the employee requests or consents in writing, in which case the employee may be permitted to work up to 60 hours in one workweek.
For most adult workers, there are no limits on daily work hours. Theoretically, employers may schedule employees to work seven days a week, 24 hours per day, so long as minimum wage and overtime laws are observed. Manufacturing employees are limited to 13 hours of work in a 24-hour period.
The required overtime pay is 1.5 times the hourly rate for hours worked in excess of 40 in a workweek. Overtime is calculated based on hours actually worked, and your employee worked only 35 hours during the workweek.