Oregon Opinion of Lehman Brothers
Description
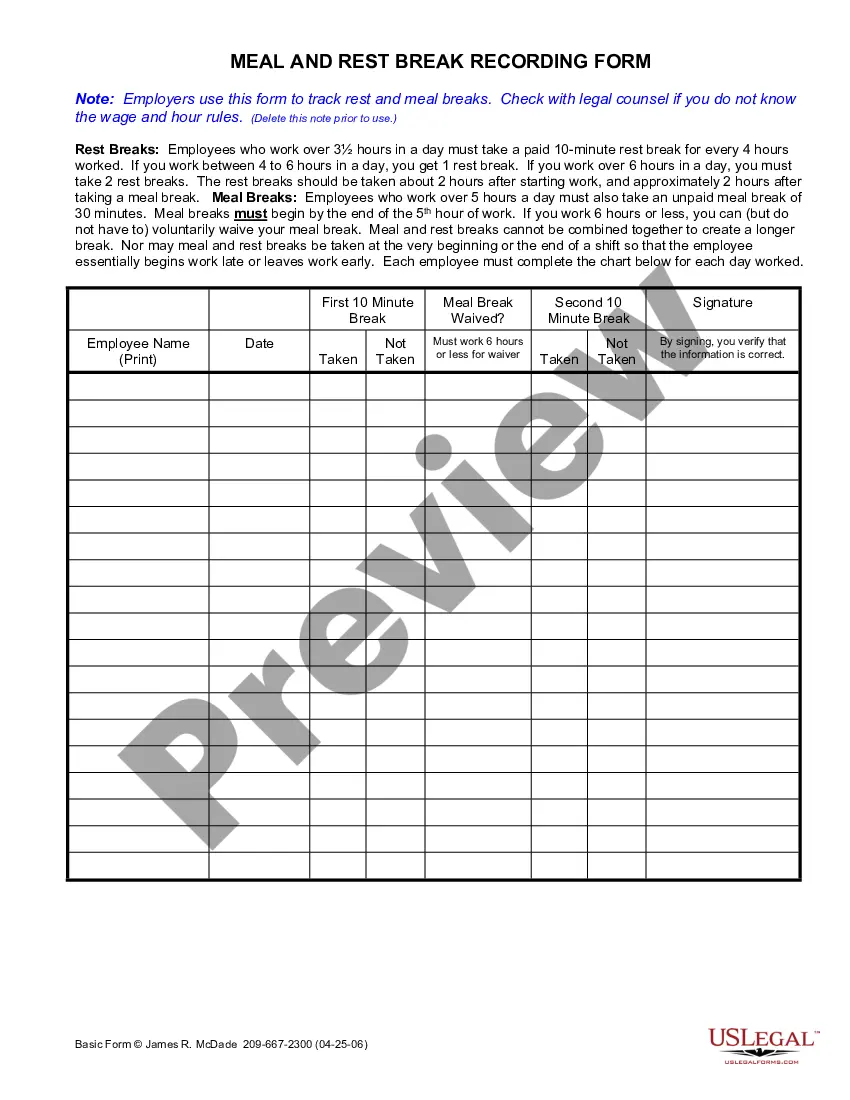
How to fill out Opinion Of Lehman Brothers?
Are you in the situation the place you will need documents for sometimes organization or specific uses just about every day? There are tons of lawful record themes available on the net, but locating types you can trust is not easy. US Legal Forms delivers a huge number of develop themes, like the Oregon Opinion of Lehman Brothers, which are created to fulfill state and federal needs.
In case you are already informed about US Legal Forms web site and also have your account, just log in. Following that, you can obtain the Oregon Opinion of Lehman Brothers design.
Should you not have an account and need to begin using US Legal Forms, abide by these steps:
- Find the develop you need and make sure it is for that proper metropolis/county.
- Make use of the Preview switch to check the form.
- Look at the description to actually have selected the appropriate develop.
- In case the develop is not what you are searching for, make use of the Lookup discipline to discover the develop that suits you and needs.
- If you discover the proper develop, click on Buy now.
- Opt for the rates prepare you would like, fill out the required info to make your bank account, and pay money for your order making use of your PayPal or credit card.
- Choose a hassle-free data file format and obtain your duplicate.
Find each of the record themes you may have bought in the My Forms food selection. You can aquire a further duplicate of Oregon Opinion of Lehman Brothers anytime, if required. Just click the needed develop to obtain or printing the record design.
Use US Legal Forms, by far the most extensive selection of lawful forms, in order to save some time and steer clear of faults. The support delivers expertly produced lawful record themes which can be used for an array of uses. Create your account on US Legal Forms and commence making your way of life easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
Instead, Lehman's fate was determined by officials' views of the political and economic consequences of a Lehman rescue or a Lehman bankruptcy. The deciding factor was politics: the decision-makers, especially Paulson, were unwilling to endure the intense criticism that would have followed a Lehman rescue.
Lehman Brothers world headquarters is shown in New York on Sept. 15, 2008, the day the 158-year-old investment bank, choked by the credit crisis and falling real estate values, filed for bankruptcy. Fifteen years ago, the world witnessed the largest commercial collapse in history.
The catalysts for the GFC were falling US house prices and a rising number of borrowers unable to repay their loans. House prices in the United States peaked around mid 2006, coinciding with a rapidly rising supply of newly built houses in some areas.
Regulators claimed they could not have rescued Lehman because it did not have adequate collateral to support a bailout loan under the Federal Reserve's emergency lending powers. 14 Furthermore, the financial system was by then more fragile compared to when the Fed saved Bear Stearns.
Exposure to the mortgage market Lehman borrowed significant amounts to fund its investing in the years leading to its bankruptcy in 2008, an intricate process known as leveraging or gearing. A significant portion of this investment was in housing-related assets, making it vulnerable to a downturn in that market.
Ethical malpractices were core in the fall of the Lehman Brothers' investment company. The firm invested without a proper analysis as required by ethics. Failure to conduct useful marketing research led to excess leveraging of mortgage firms.
Regulators claimed they could not have rescued Lehman because it did not have adequate collateral to support a bailout loan under the Federal Reserve's emergency lending powers. 14 Furthermore, the financial system was by then more fragile compared to when the Fed saved Bear Stearns.
In the most dramatic moment of the Great Recession, the Federal Reserve (the Fed) withheld an emergency bailout from Lehman Brothers, a peer investment bank among other firms infamously deemed ?too big to fail.? In light of Lehman's banefully consequential bankruptcy, the Fed's decision remains a most controversial one ...