The Oregon Approval of Stock Option Plan refers to the process of obtaining authorization from the state of Oregon for a company to implement a stock option plan. A stock option plan is a financial incentive program offered by companies to their employees, granting them the right to purchase company stocks at a predetermined price within a specified period. When establishing a stock option plan in Oregon, companies must comply with applicable state laws and regulations. The process involves submitting an application to the Oregon office responsible for overseeing securities offerings, typically the Oregon Division of Financial Regulation. The approval ensures that the company's stock option plan aligns with the state's requirements and protects the interests of the plan participants. To successfully obtain Oregon approval for a stock option plan, companies need to adhere to certain guidelines. These guidelines may include providing comprehensive information about the plan, such as the terms and conditions, eligibility criteria, exercise price, vesting schedule, and any limitations associated with the plan. Furthermore, the Oregon Approval of Stock Option Plan may encompass different types of plans based on their objectives and structures. Some common variations include: 1. Incentive Stock Option (ISO) Plans: These plans are typically offered to key employees and provide certain tax advantages. ISO plans must comply with specific criteria set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to qualify for favorable tax treatment. 2. Non-Qualified Stock Option (NO) Plans: NO plans are more flexible than ISO plans and are usually offered to a broader group of employees. They do not adhere to the IRS's strict qualification standards and may have different tax implications. 3. Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPN): ESPN enable employees to purchase company stocks at a discounted price through regular payroll deductions. These plans often aim to promote employee ownership and provide benefits to a wide range of eligible employees. 4. Restricted Stock Unit (RSU) Plans: RSU plans grant employees the right to receive company shares or their cash equivalent at a future date, subject to certain vesting conditions. Unlike stock options, RSS do not require employees to purchase shares but rather offer them as a form of compensation. It is crucial for companies to consult with legal and financial professionals familiar with Oregon securities laws when creating and seeking approval for a stock option plan. This ensures compliance with state regulations and maximizes the benefits of the program for both the company and its employees.
Oregon Approval of Stock Option Plan
Description
How to fill out Oregon Approval Of Stock Option Plan?
US Legal Forms - one of the most significant libraries of legitimate varieties in the USA - offers an array of legitimate file web templates you are able to download or print out. Utilizing the site, you may get 1000s of varieties for company and individual reasons, categorized by categories, claims, or key phrases.You can get the latest versions of varieties like the Oregon Approval of Stock Option Plan in seconds.
If you have a monthly subscription, log in and download Oregon Approval of Stock Option Plan in the US Legal Forms library. The Obtain switch can look on each type you perspective. You have access to all formerly saved varieties inside the My Forms tab of your own accounts.
In order to use US Legal Forms the very first time, listed here are straightforward guidelines to help you started out:
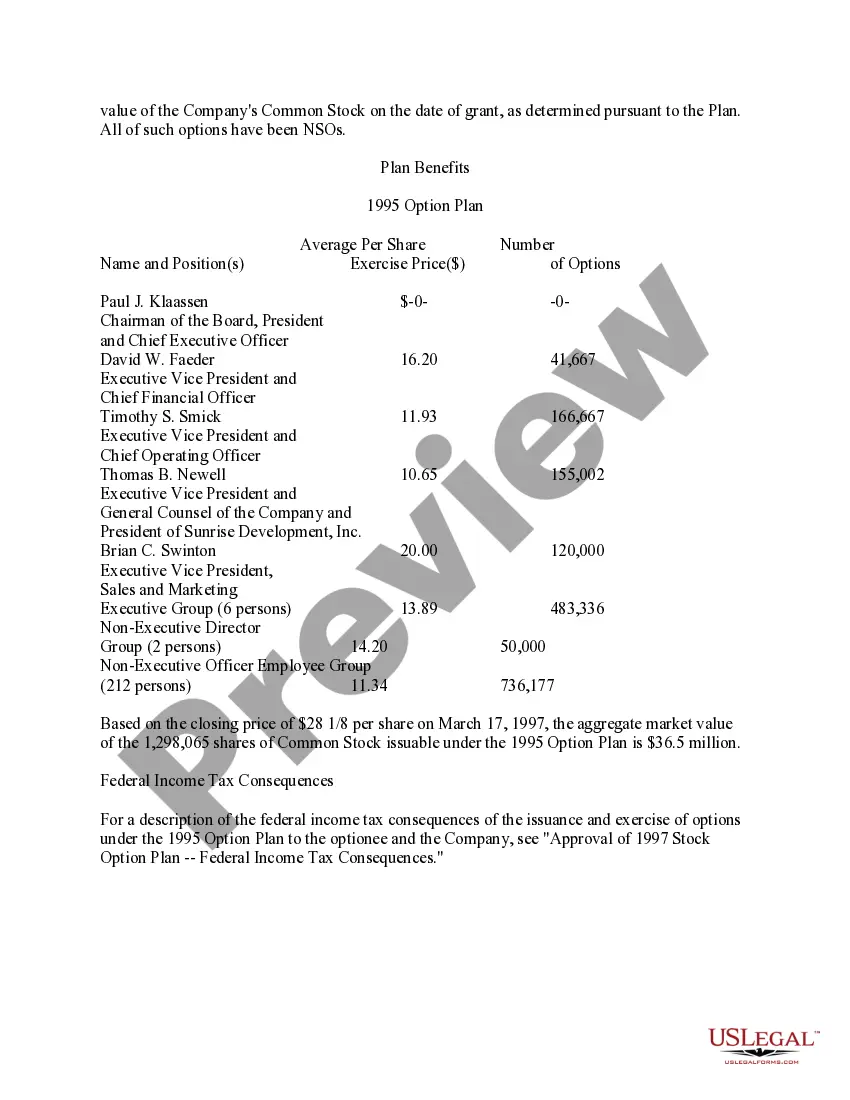
- Make sure you have chosen the right type to your city/region. Go through the Preview switch to examine the form`s content material. See the type outline to actually have selected the appropriate type.
- In the event the type doesn`t fit your specifications, use the Look for field towards the top of the display screen to obtain the the one that does.
- In case you are pleased with the shape, confirm your decision by simply clicking the Purchase now switch. Then, pick the prices program you want and supply your qualifications to register for an accounts.
- Procedure the financial transaction. Utilize your charge card or PayPal accounts to complete the financial transaction.
- Select the format and download the shape on your own system.
- Make adjustments. Complete, edit and print out and sign the saved Oregon Approval of Stock Option Plan.
Each format you added to your account does not have an expiration date and it is your own forever. So, if you wish to download or print out another backup, just go to the My Forms portion and then click about the type you need.
Gain access to the Oregon Approval of Stock Option Plan with US Legal Forms, the most considerable library of legitimate file web templates. Use 1000s of professional and express-specific web templates that meet your business or individual requirements and specifications.