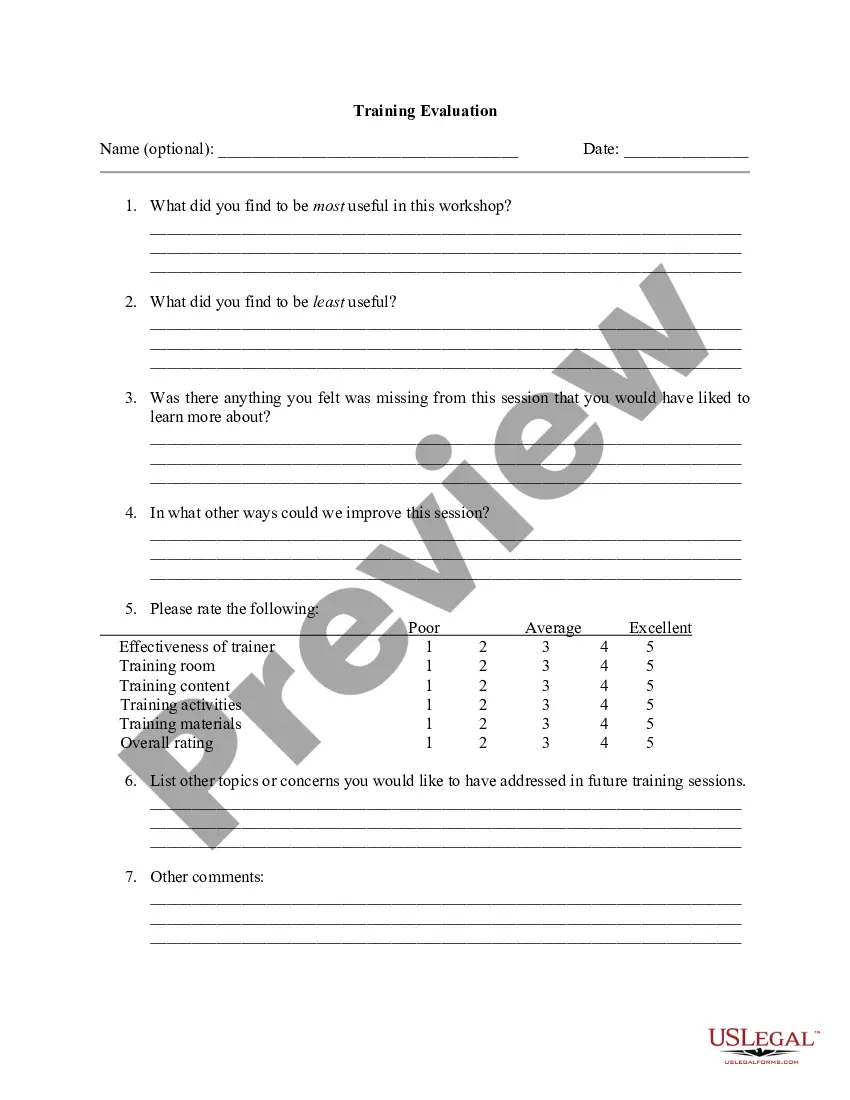
A Pennsylvania Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Trust is a legal document filed by a beneficiary of a trust in Pennsylvania seeking damages for a breach of fiduciary duty by a trustee. Keywords: Pennsylvania, complaint, breach of fiduciary duty, trust, damages, beneficiary, trustee. In Pennsylvania, there are several types of complaints for breach of fiduciary duty specifically related to trusts, including: 1. Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Trust Administration: This type of complaint is filed when a trustee fails to properly administer the trust, such as mismanaging assets, failing to exercise reasonable care, or engaging in self-dealing. 2. Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Investment of Trust Assets: This complaint is relevant when a trustee makes imprudent investments with trust assets, fails to diversify the investments, or acts negligently in managing the investments, resulting in financial losses for the trust and its beneficiaries. 3. Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Accounting and Reporting: This type of complaint is filed when a trustee fails to provide accurate and timely accounting statements to the beneficiaries, hides or misrepresents financial information, or fails to provide necessary information regarding the trust's administration. 4. Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Self-Dealing: This complaint focuses on situations where a trustee acts in their own interest, rather than in the best interest of the trust and its beneficiaries. Self-dealing may include transactions where the trustee personally benefits, such as selling trust assets to themselves or their family members at below-market prices. When filing a Pennsylvania Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Trust, the complainant must provide a detailed account of the breach of duty, supporting evidence, and the damages suffered as a result. It is essential to consult with an experienced attorney familiar with Pennsylvania trust laws to navigate the legal complexities involved in such cases.
A Pennsylvania Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Trust is a legal document filed by a beneficiary of a trust in Pennsylvania seeking damages for a breach of fiduciary duty by a trustee. Keywords: Pennsylvania, complaint, breach of fiduciary duty, trust, damages, beneficiary, trustee. In Pennsylvania, there are several types of complaints for breach of fiduciary duty specifically related to trusts, including: 1. Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Trust Administration: This type of complaint is filed when a trustee fails to properly administer the trust, such as mismanaging assets, failing to exercise reasonable care, or engaging in self-dealing. 2. Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Investment of Trust Assets: This complaint is relevant when a trustee makes imprudent investments with trust assets, fails to diversify the investments, or acts negligently in managing the investments, resulting in financial losses for the trust and its beneficiaries. 3. Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Accounting and Reporting: This type of complaint is filed when a trustee fails to provide accurate and timely accounting statements to the beneficiaries, hides or misrepresents financial information, or fails to provide necessary information regarding the trust's administration. 4. Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Self-Dealing: This complaint focuses on situations where a trustee acts in their own interest, rather than in the best interest of the trust and its beneficiaries. Self-dealing may include transactions where the trustee personally benefits, such as selling trust assets to themselves or their family members at below-market prices. When filing a Pennsylvania Complaint for Breach of Fiduciary Duty — Trust, the complainant must provide a detailed account of the breach of duty, supporting evidence, and the damages suffered as a result. It is essential to consult with an experienced attorney familiar with Pennsylvania trust laws to navigate the legal complexities involved in such cases.