A patent is a grant of a property right by the Government to an inventor. The United States Constitution gives Congress the right to provide for patent protection in legislation in order to encourage useful inventions. The patent itself provides a detailed description of the invention, and how it is used or how to make it. Thus, if you obtain a patent you cannot keep the matter secret, which is the province of Trade Secret Law. A patent enables the owner to exclude others from making, using or selling the invention for the life of the patent.
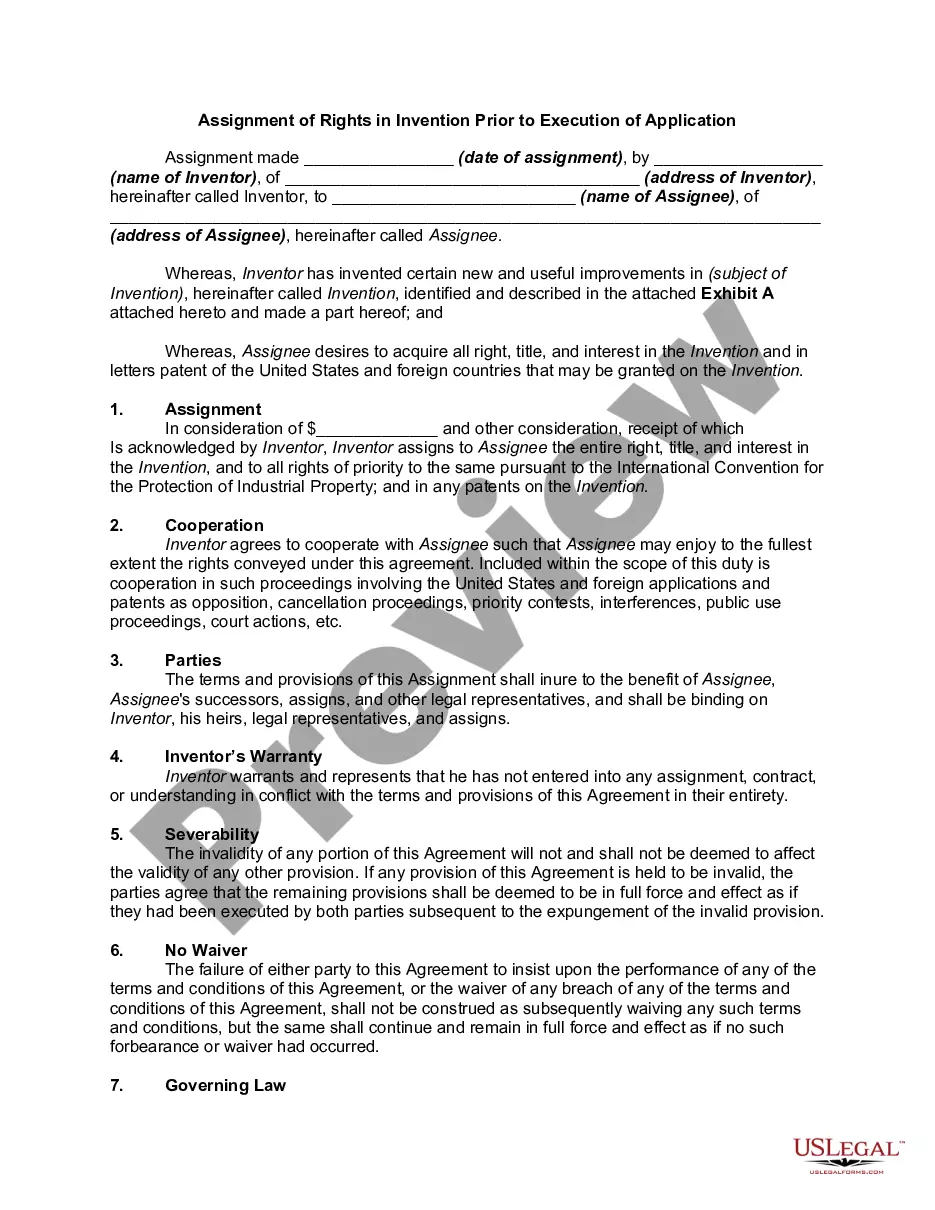
Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application
Description
How to fill out Assignment Of Rights In Invention Prior To Execution Of Application?
Are you currently at the location where you need documents for either business or personal purposes each day.
There are numerous legitimate document templates available online, but finding ones you can trust isn't simple.
US Legal Forms provides thousands of form templates, including the Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, which are drafted to fulfill state and federal requirements.
If you locate the appropriate template, click on Buy now.
Select the pricing plan you prefer, enter the required information to create your account, and complete your order using your PayPal account or credit card.
- If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and have an account, simply Log In.
- Once logged in, you can download the Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application template.
- If you do not possess an account and wish to start using US Legal Forms, follow these instructions.
- Obtain the template you need and ensure it is for the correct city/state.
- Use the Preview button to examine the form.
- Read the description to verify that you have chosen the correct template.
- If the form isn't what you're looking for, utilize the Search field to find the template that fits your needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
A list of prior inventions compiles previously developed inventions by an inventor that are not covered by current assignment agreements. This list helps to ensure transparency and protect the inventor’s rights when entering into new agreements. When dealing with Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, such a list can prevent disputes related to ownership of inventions.
An invention assignment agreement is a legal contract that specifies the conditions under which an inventor transfers their rights to their invention to another party, often an employer. This agreement should clearly outline the obligations of both parties. In Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, such agreements serve as essential documentation to establish ownership.
When you have executed a confidentiality and invention assignment agreement, it means you have formally agreed to the terms that protect confidential information while assigning rights to any inventions to the relevant party. This execution signifies your understanding and acceptance of the responsibilities and rights outlined in the agreement. This is especially important in the context of Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application.
The invention assignment policy outlines the rules and procedures regarding the ownership of inventions created by employees. This policy is critical for companies, ensuring that the rights to inventions are clearly defined. Understanding this policy is essential for anyone engaging with Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, as it forms the basis of exploitation and ownership.
An assignment of prior inventions is a document where an inventor formally assigns ownership rights of previously created inventions to another party, such as an employer. This is particularly important in the realm of Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, as it ensures that all inventions are accounted for and ownership is clear. Clear agreements prevent future misunderstandings.
An employee assignment agreement is a contract between an employer and an employee, wherein the employee agrees to assign any inventions they create during employment to the employer. This agreement is essential to outline the expectations regarding ownership rights. In the context of Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, this contract helps prevent disputes over who owns inventions.
A confidentiality and invention agreement is a contract that combines the protection of confidential information with the assignment of invention rights. This agreement ensures that an employer retains ownership of any inventions made by employees while also keeping sensitive business information confidential. Such agreements are critical in the context of Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application.
Assignment of invention refers to the legal process where an inventor transfers their ownership rights of an invention to another party, typically an employer or organization. This process is vital in Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, as it clarifies who holds the rights to the invention. Proper documentation ensures both parties understand their rights and responsibilities.
Executing a confidentiality agreement means that all parties are formally agreeing to keep specific information private and secure. This ensures that sensitive details about inventions or business processes are not disclosed without consent. Such agreements are often essential in contexts like Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application to safeguard proprietary information.
Prior inventions refer to any inventions created by an inventor before entering into an assignment agreement or prior to the execution of a patent application. These inventions do not belong to the new employer or entity unless an explicit agreement states otherwise. Understanding prior inventions is crucial for anyone involved in Pennsylvania Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application to ensure clarity on ownership.