Pennsylvania Personnel File Inspection Requirements for Companies
Description
How to fill out Personnel File Inspection Requirements For Companies?
You might spend numerous hours online attempting to locate the sanctioned document template that adheres to the state and federal criteria you need.
US Legal Forms provides thousands of legal forms that are evaluated by experts.
You can download or print the Pennsylvania Personnel File Inspection Requirements for Companies from our platform.
If available, utilize the Review option to examine the document template as well. If you wish to obtain another version of the form, use the Search field to find the template that suits your requirements and criteria.
- If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and select the Download option.
- Afterward, you can complete, edit, print, or sign the Pennsylvania Personnel File Inspection Requirements for Companies.
- Every legal document template you purchase is yours permanently.
- To obtain an additional copy of the acquired form, navigate to the My documents tab and select the corresponding option.
- If this is your first time using the US Legal Forms website, follow the simple steps below.
- First, ensure you have chosen the correct document template for the region/city of your preference.
- Review the form description to confirm you have selected the right form.
Form popularity
FAQ
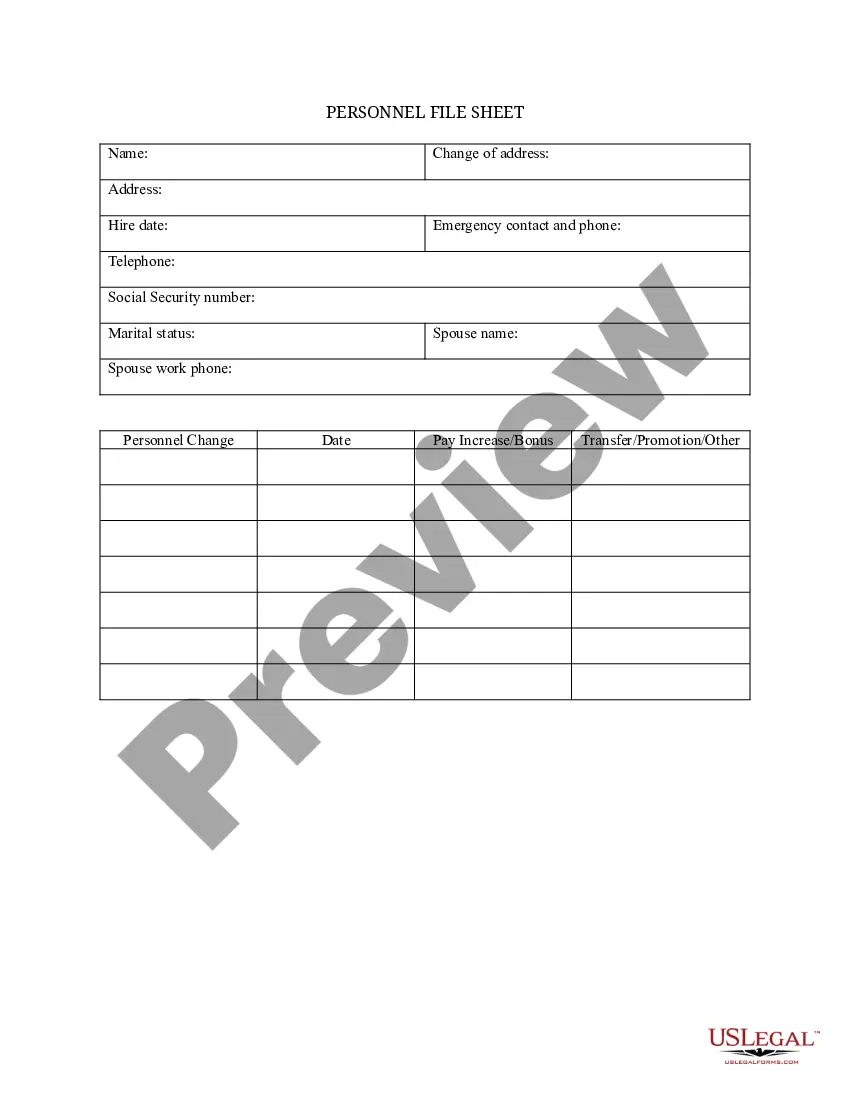
9 forms should always be maintained separately from personnel files and retained according to the U.S. Citizenship and mmigration Services (USCS) retention requirements: "9 forms should be retained for three years after the date of hire, or one year after the date employment endswhichever is later." The Form 9
What to Keep in a Personnel Filejob description for the position.job application and/or resume.offer of employment.IRS Form W-4 (the Employee's Withholding Allowance Certificate)receipt or signed acknowledgment of employee handbook.performance evaluations.forms relating to employee benefits.More items...
Medical information and records obtained as part of the interactive process must be maintained separate from the employee's personnel file and kept confidential. 2 CCR § 11069(g) Employers must keep information obtained regarding the medical or physical conditions or history of the employee confidential.
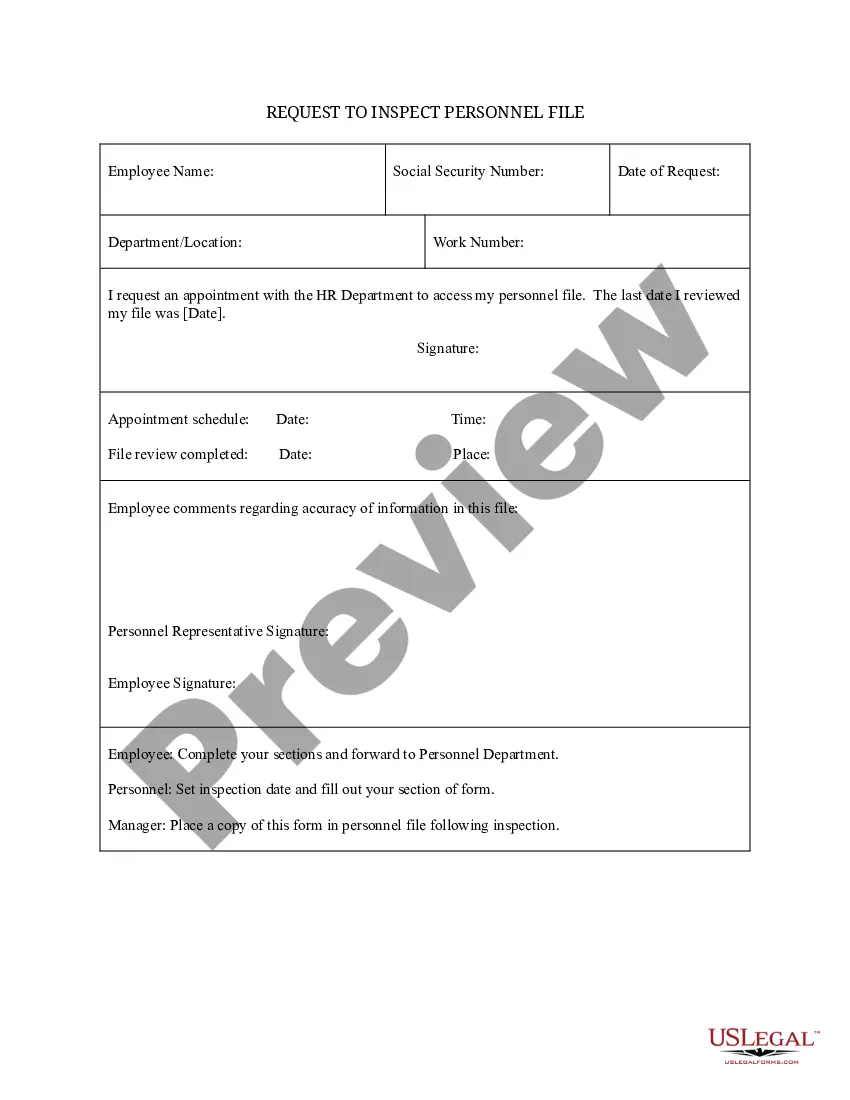
An employee has the right to review a personnel file if maintained by the employer, any application for employment, wage or salary information, notices of commendations, warnings or discipline administered, authorization for a deduction or withholding of pay or fringe benefits, leave records, employment history
Employers should keep all job-related documentation such as hiring records, performance reviews, disciplinary actions and job descriptions in an employee's general personnel file. Consider whether the document would be relevant to a supervisor who may review this file when making employment decisions.
Medical. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requires that employee medical records be maintained confidentially and separate from an employee's general personnel file.
Personnel Files Generally Are Not Discoverable Because They Contain Confidential Information About Both Employees and Employers.
The legal documents that every employee personnel file must have are: Basic employee information: Name, address, phone number, and emergency contact details. IRS tax withholding forms: W-4s and/or W-9s. Payroll and compensation information: Any paycheck or pay card data.
Examples of items that should not be included in the personnel file are:Pre-employment records (with the exception of the application and resume)Monthly attendance transaction documents.Whistleblower complaints, notes generated from informal discrimination complaint investigations, Ombuds, or Campus Climate.More items...
As an employee, do I have a right to see my personnel files? The short answer is 'yes'. You have a right to make a SAR to your employer, asking to see your personnel files, at any time. Your employer has the right to ask why you want to see your files, but must then provide all your records to you.