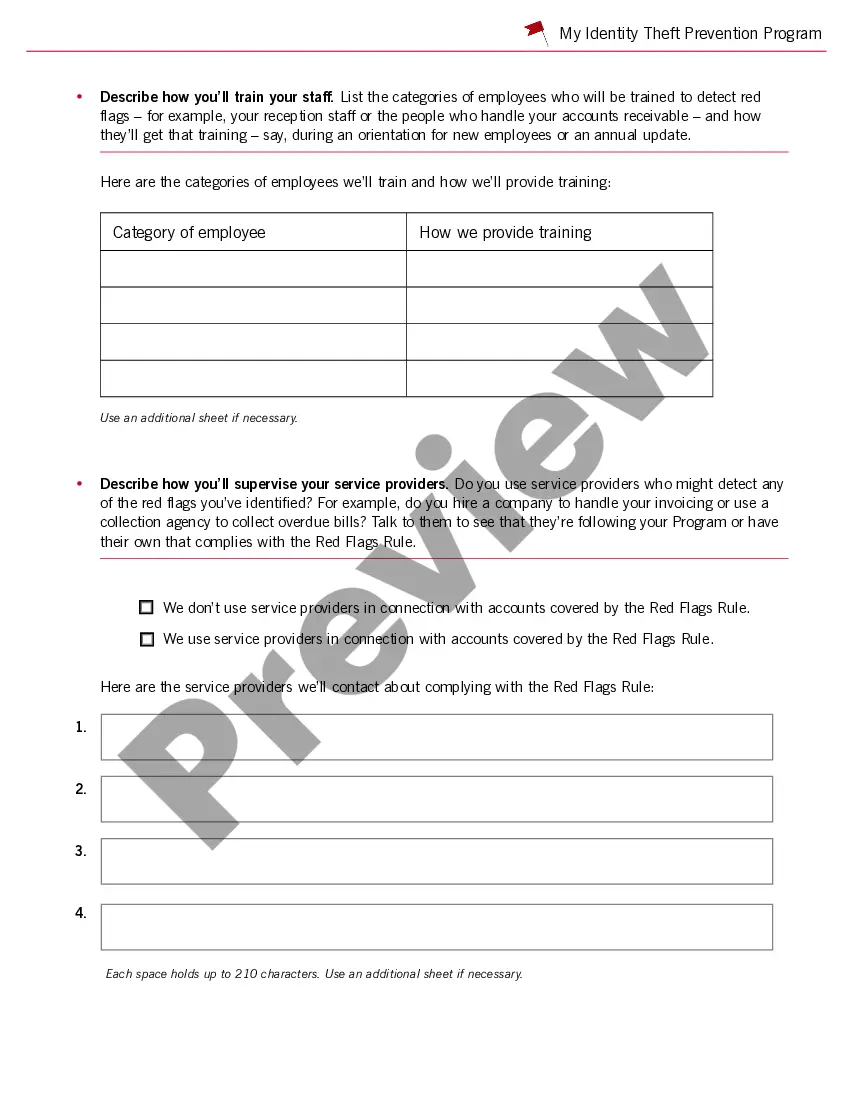
This guide has two parts: Part A to help you determine whether your business or organization is at low risk, and Part B to help you design your written Identity Theft Prevention Program if your business is in the low risk category.
Note: The preview only shows the 1st page of the document.
Title: Pennsylvania Guide to Complying with the Red Flags Rule under FCRA and FACT Introduction: In Pennsylvania, businesses that handle consumer data must adhere to the Red Flags Rule under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and the Fair and Accurate Credit Transactions Act (FACT). This comprehensive guide provides a detailed description of the requirements imposed by these regulations and offers practical insights to help Pennsylvania businesses comply effectively. Read on to understand various aspects related to compliance with the Red Flags Rule, under both FCRA and FACT. 1. Understanding the Red Flags Rule: This section explains the Red Flags Rule and its ultimate goal of preventing identity theft and protecting consumers against fraudulent activities. It defines key terms and concepts, such as "creditor," "covered account," and "identity theft red flags," to provide a clear foundation for further understanding. 2. Identifying Red Flags in Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania businesses need to be aware of the red flags that indicate potential identity theft incidents. This section discusses the common red flags prevalent in the state, emphasizing the importance of customer identification, documentation, and verification processes. 3. Effective Program Development: To comply with the Red Flags Rule, businesses in Pennsylvania must develop and implement a comprehensive Identity Theft Prevention Program (IPP). This section provides step-by-step guidance for creating an effective IPP tailored to the specific needs of Pennsylvania businesses. 4. Applicability to Different Industries: Businesses in different sectors may have distinct compliance requirements when it comes to the Red Flags Rule. This section explores industry-specific guidelines, including healthcare, financial institutions, and retail, outlining the nuances that Pennsylvania businesses in these sectors need to consider. 5. Employee Training and Awareness: The success of a Red Flags Rule compliance program lies in the hands of well-trained employees. This section highlights the importance of training staff to recognize red flag indicators and report potential identity theft incidents promptly. 6. Periodic Review and Updates: Compliance with the Red Flags Rule is an ongoing process that necessitates regular reviews and updates. This section explains how Pennsylvania businesses should conduct periodic assessments to identify any gaps or changes in their existing Identity Theft Prevention Program. 7. Consequences of Non-Compliance: Failure to comply with the Red Flags Rule can result in severe consequences for businesses operating in Pennsylvania. This section outlines potential penalties, legal implications, and reputational damage that may arise from non-compliance. Conclusion: Complying with the Red Flags Rule under FCRA and FACT is crucial for businesses in Pennsylvania to safeguard consumer information and prevent identity theft. This comprehensive guide equips Pennsylvania businesses with the necessary knowledge and tools to develop a robust Identity Theft Prevention Program, recognize red flags, and maintain compliance in accordance with state-specific regulations. By implementing these measures, businesses can ensure the protection of their customers' sensitive data while building trust and maintaining their reputation. Additional types of Pennsylvania Guides to Complying with the Red Flags Rule under FCRA and FACT could include: — Red Flags Rule Compliance Guide for Small Businesses in Pennsylvania — Red Flags Rule Compliance Guide for Healthcare Providers in Pennsylvania — Red Flags Rule Compliance Guide for Financial Institutions in Pennsylvania.Title: Pennsylvania Guide to Complying with the Red Flags Rule under FCRA and FACT Introduction: In Pennsylvania, businesses that handle consumer data must adhere to the Red Flags Rule under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and the Fair and Accurate Credit Transactions Act (FACT). This comprehensive guide provides a detailed description of the requirements imposed by these regulations and offers practical insights to help Pennsylvania businesses comply effectively. Read on to understand various aspects related to compliance with the Red Flags Rule, under both FCRA and FACT. 1. Understanding the Red Flags Rule: This section explains the Red Flags Rule and its ultimate goal of preventing identity theft and protecting consumers against fraudulent activities. It defines key terms and concepts, such as "creditor," "covered account," and "identity theft red flags," to provide a clear foundation for further understanding. 2. Identifying Red Flags in Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania businesses need to be aware of the red flags that indicate potential identity theft incidents. This section discusses the common red flags prevalent in the state, emphasizing the importance of customer identification, documentation, and verification processes. 3. Effective Program Development: To comply with the Red Flags Rule, businesses in Pennsylvania must develop and implement a comprehensive Identity Theft Prevention Program (IPP). This section provides step-by-step guidance for creating an effective IPP tailored to the specific needs of Pennsylvania businesses. 4. Applicability to Different Industries: Businesses in different sectors may have distinct compliance requirements when it comes to the Red Flags Rule. This section explores industry-specific guidelines, including healthcare, financial institutions, and retail, outlining the nuances that Pennsylvania businesses in these sectors need to consider. 5. Employee Training and Awareness: The success of a Red Flags Rule compliance program lies in the hands of well-trained employees. This section highlights the importance of training staff to recognize red flag indicators and report potential identity theft incidents promptly. 6. Periodic Review and Updates: Compliance with the Red Flags Rule is an ongoing process that necessitates regular reviews and updates. This section explains how Pennsylvania businesses should conduct periodic assessments to identify any gaps or changes in their existing Identity Theft Prevention Program. 7. Consequences of Non-Compliance: Failure to comply with the Red Flags Rule can result in severe consequences for businesses operating in Pennsylvania. This section outlines potential penalties, legal implications, and reputational damage that may arise from non-compliance. Conclusion: Complying with the Red Flags Rule under FCRA and FACT is crucial for businesses in Pennsylvania to safeguard consumer information and prevent identity theft. This comprehensive guide equips Pennsylvania businesses with the necessary knowledge and tools to develop a robust Identity Theft Prevention Program, recognize red flags, and maintain compliance in accordance with state-specific regulations. By implementing these measures, businesses can ensure the protection of their customers' sensitive data while building trust and maintaining their reputation. Additional types of Pennsylvania Guides to Complying with the Red Flags Rule under FCRA and FACT could include: — Red Flags Rule Compliance Guide for Small Businesses in Pennsylvania — Red Flags Rule Compliance Guide for Healthcare Providers in Pennsylvania — Red Flags Rule Compliance Guide for Financial Institutions in Pennsylvania.