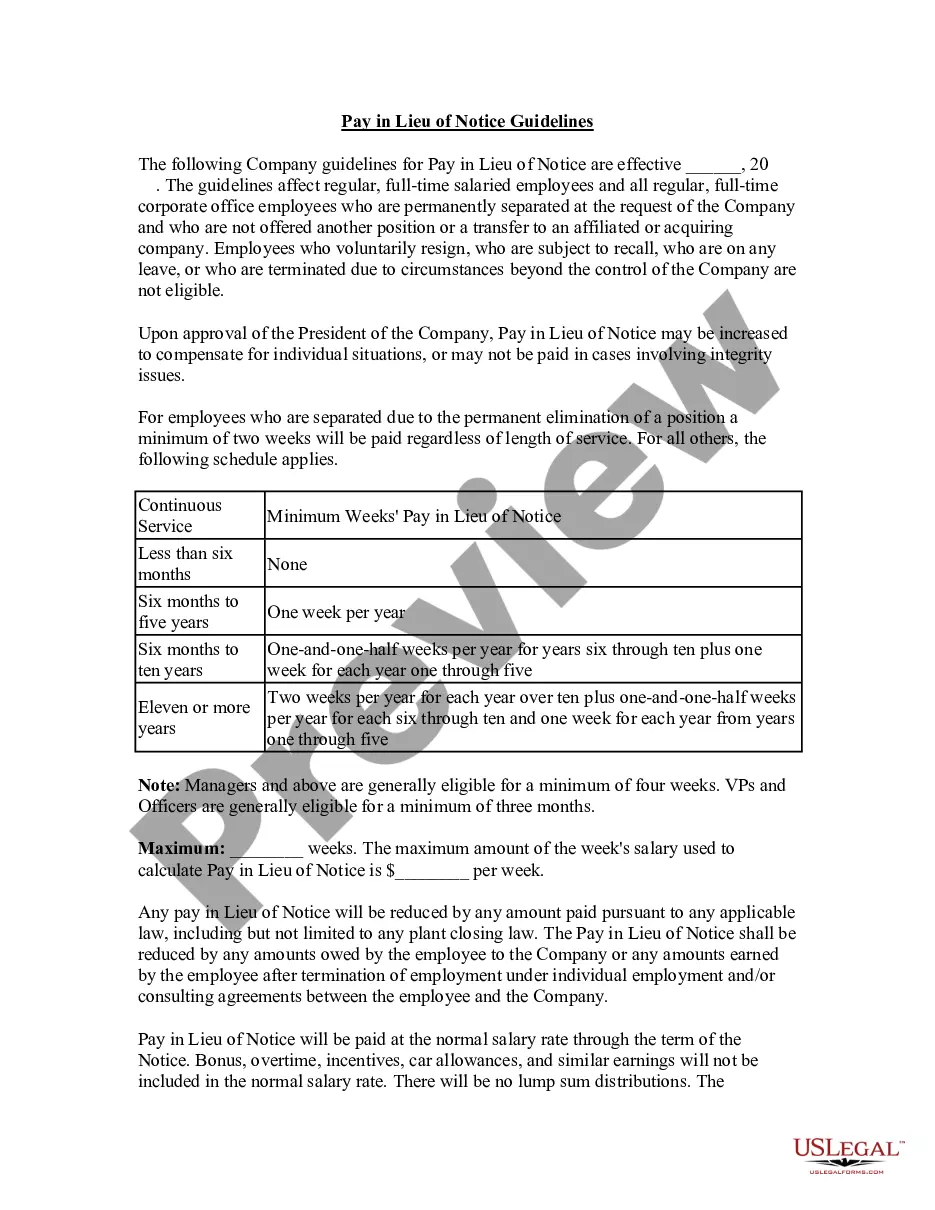
South Carolina Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines
Description
How to fill out Pay In Lieu Of Notice Guidelines?
If you want to aggregate, acquire, or create valid document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the largest selection of legal forms, which are accessible online.
Take advantage of the site’s straightforward and convenient search to locate the documents you require.
Various templates for business and personal purposes are categorized by divisions and indicates, or keywords.
Step 4. After you have located the form you need, click the Buy now button. Choose the payment plan you prefer and input your details to create an account.
Step 5. Complete the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to finish the purchase.
- Utilize US Legal Forms to find the South Carolina Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines with just a few clicks.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms user, Log In to your account and click the Acquire button to obtain the South Carolina Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines.
- You can also access forms you previously saved from the My documents section of your account.
- If this is your first time using US Legal Forms, adhere to the following steps.
- Step 1. Confirm you have chosen the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Use the Preview feature to go through the form’s content. Make sure to read the overview.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, utilize the Search field at the top of the screen to find other versions of the legal form template.
Form popularity
FAQ
When you don’t receive a termination letter, it can lead to confusion and uncertainty regarding your employment status. Without formal notification, you may not know your rights, especially concerning the South Carolina Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines. This can affect your ability to seek unemployment benefits or plan your next steps. Consider consulting resources like US Legal Forms to better understand your situation and ensure you receive any due compensation.
In South Carolina, the law does not require employees to provide a specific notice period before leaving a job. However, many employers expect a two-week notice as a professional courtesy. If you choose not to give notice, you may be subject to the South Carolina Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines, which can affect your eligibility for benefits. Understanding these guidelines can help you make informed decisions about your employment transition.
Payment in lieu of leave occurs when an employer compensates an employee for unused leave days instead of allowing them to take the time off. This concept aligns closely with the South Carolina Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines, as it addresses financial compensation in employment matters. Understanding this can help both employers and employees navigate their rights and options; using resources like US Legal Forms can provide additional guidance.
A letter payment in lieu of notice, as outlined in the South Carolina Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines, is a formal document issued by an employer to inform an employee of the compensation they will receive instead of serving a notice period. This letter typically includes details such as the payment amount and the reason for its issuance. Utilizing US Legal Forms can streamline the creation of these documents, ensuring all necessary information is included.
Yes, according to the South Carolina Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines, payments made in lieu of notice generally attract certain contributions to the employee's retirement plan, known as 'super.' Employers should ensure they calculate the necessary contributions accurately to comply with legal requirements. Engaging with legal resources or consultants can help clarify obligations and ensure compliance with retirement fund regulations.
To process payment in lieu of notice under the South Carolina Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines, employers typically provide written notification to the employee, outlining the details of the payment. This payment should equal the wages the employee would have earned during the notice period, ensuring compliance with local labor laws. You may consider using platforms like US Legal Forms, which offer templates and resources to help you manage this process efficiently and correctly.
Employees are sometimes under the impression that two weeks' notice is required by law. Neither federal nor South Carolina law requires that two weeks' notice be given, but both the employer and the employee may be contractually bound by a written policy implemented by the employer.
Employees are sometimes under the impression that two weeks' notice is required by law. Neither federal nor South Carolina law requires that two weeks' notice be given, but both the employer and the employee may be contractually bound by a written policy implemented by the employer.
Job abandonment occurs when an employee does not report to work as scheduled and has no intention of returning to the job but does not notify the employer of his or her intention to quit. Employers should develop a policy defining how many days of no-call/no-show will be considered job abandonment.
Which means if the employee does not give one month notice or as many months as prescribed, in the letter of appointment, he/she has to pay one month salary or as many months salary as prescribed in the letter of appointment.