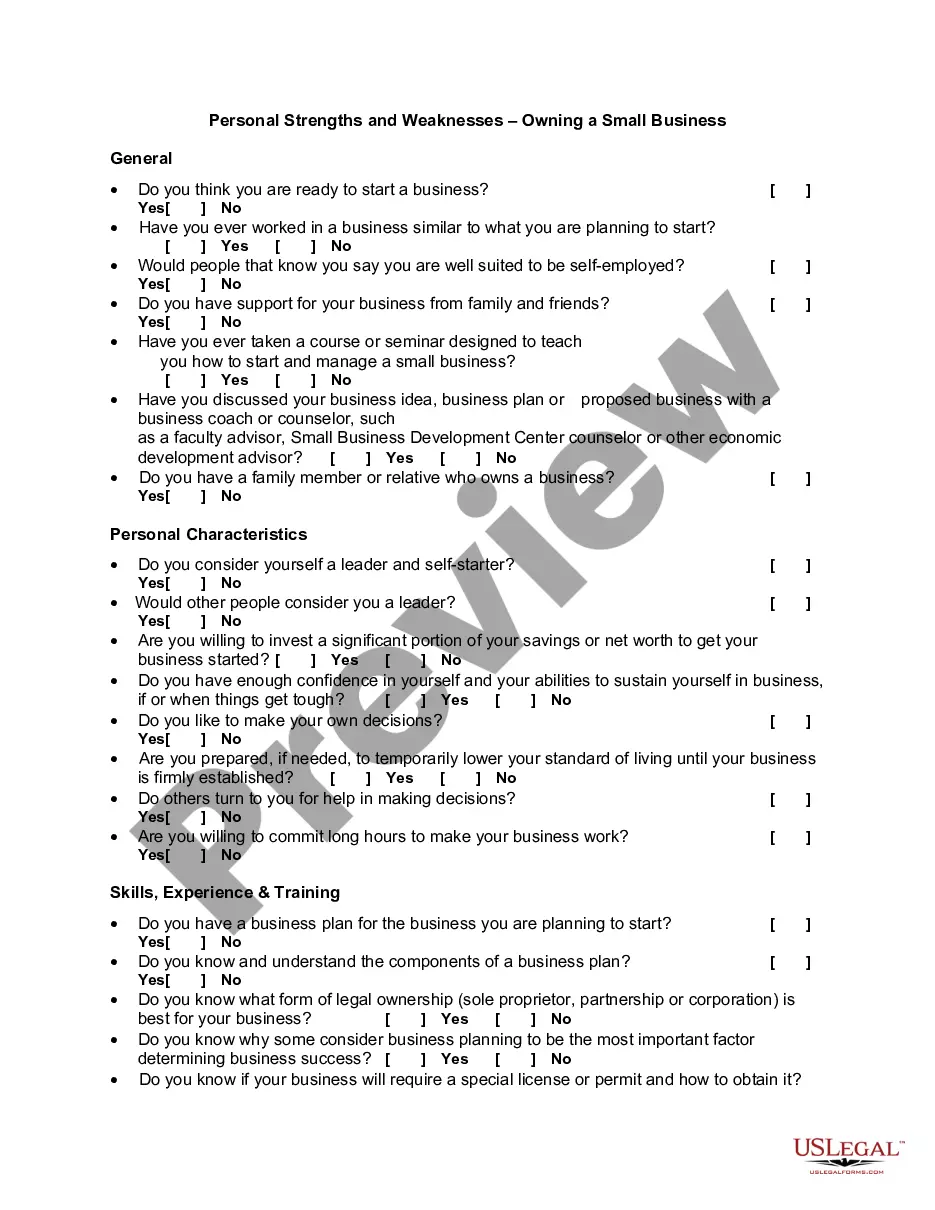
Title: South Carolina Employee Rights Under the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) Introduction: The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) of 1993 is a federal law that provides eligible employees with certain rights and protections when they need time off from work due to family or medical reasons. South Carolina employees are entitled to these rights, which ensure job security and leave benefits during challenging circumstances. This article will provide a detailed description of the South Carolina Employee Rights Under the Family and Medical Leave Act, highlighting different types of leave available and their key provisions. Important keywords include: South Carolina, Employee Rights, Family and Medical Leave Act, FMLA, leave benefits. 1. Eligibility for FMLA Leave: Under South Carolina Employee Rights, workers are eligible for FMLA leave if they meet specific criteria. These include being employed by a private company with 50 or more employees within a 75-mile radius, working for a public agency, or being employed by an elementary or secondary school. 2. Types of FMLA Leave: South Carolina employees are entitled to different types of leave under the FMLA, including: a. Family Leave: This allows employees to take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for the birth, adoption, or foster care placement of a child, or to care for a family member with a serious health condition. b. Personal Medical Leave: Employees can take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave for their own serious health condition that renders them unable to perform their job. c. Family Military Leave: South Carolina Employee Rights extend to providing up to 26 weeks of unpaid leave to care for a family member who is a covered service member with a serious illness or injury. 3. Job Protection and Benefits during FMLA Leave: South Carolina employees who take FMLA leave are entitled to certain job protections and benefits, such as: a. Job Security: Companies covered by the FMLA must guarantee that employees returning from leave will be reinstated to their original position or an equivalent job with the same pay, benefits, and conditions. b. Continuation of Health Insurance: Employers must maintain health insurance coverage for employees on FMLA leave under the same terms as if they were actively working. c. Accruing Leave and Benefits: Employees continue to accrue seniority, paid leave, and other benefits during their FMLA leave. 4. Notice and Documentation Requirements: South Carolina Employee Rights include a responsibility to provide their employers with reasonable notice and documentation when requesting FMLA leave. Employees must inform their employer of the need for leave in advance, whenever possible. 5. South Carolina Pregnancy Accommodation Act (SCP AA): In addition to federal FMLA rights, South Carolina has its own law, known as the South Carolina Pregnancy Accommodation Act. This act provides additional protections for pregnant workers, including reasonable accommodations related to pregnancy, childbirth, and related medical conditions. Conclusion: South Carolina Employee Rights Under the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) ensure that workers are protected and supported during significant life events and health-related issues. Knowing the different types of leave available and the accompanying benefits is crucial for employees to exercise their rights effectively and strike a balance between work and personal responsibilities. Employers should also be well-versed in these rights to adequately support their employees in times of need.
South Carolina Employee Rights Under the Family and Medical Leave Act
Description
How to fill out South Carolina Employee Rights Under The Family And Medical Leave Act?
Choosing the right authorized record template might be a have a problem. Needless to say, there are a variety of layouts available on the net, but how can you get the authorized develop you want? Utilize the US Legal Forms web site. The assistance provides 1000s of layouts, including the South Carolina Employee Rights Under the Family and Medical Leave Act, that can be used for company and private needs. All the forms are checked by pros and meet federal and state requirements.
When you are previously signed up, log in to your account and click the Down load button to have the South Carolina Employee Rights Under the Family and Medical Leave Act. Use your account to look with the authorized forms you may have bought earlier. Visit the My Forms tab of the account and have yet another duplicate in the record you want.
When you are a whole new end user of US Legal Forms, allow me to share straightforward directions that you can comply with:
- Initially, be sure you have selected the proper develop to your metropolis/county. You may look over the form while using Review button and browse the form explanation to make certain it is the right one for you.
- In case the develop fails to meet your requirements, make use of the Seach discipline to discover the proper develop.
- When you are certain the form is proper, click the Get now button to have the develop.
- Pick the costs plan you want and enter the needed information and facts. Build your account and purchase an order using your PayPal account or credit card.
- Opt for the document formatting and download the authorized record template to your gadget.
- Complete, revise and print and indication the obtained South Carolina Employee Rights Under the Family and Medical Leave Act.
US Legal Forms is definitely the most significant catalogue of authorized forms that you will find numerous record layouts. Utilize the company to download professionally-produced files that comply with condition requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
In order to be eligible to take leave under the FMLA, an employee must (1) work for a covered employer, (2) work 1,250 hours during the 12 months prior to the start of leave, (3) work at a location where 50 or more employees work at that location or within 75 miles of it, and (4) have worked for the employer for 12
The FMLA entitles eligible employees to take up to 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave in a 12-month period, with an exception for military caregiver leave. Eligible employees who take military caregiver leave can take up to 26 weeks of protected leave in a 12-month period.
Yes, you can. If your doctor feels that a shortened workweek or other accommodation is vital to help you with your serious stress condition, intermittent FMLA is possible. FMLA allows eligible employees to take up to 60 days off per year, and you do not have to take the days off consecutively.
FMLA is designed to help employees balance their work and family responsibilities by allowing them to take reasonable unpaid leave for certain family and medical reasons. It also seeks to accommodate the legitimate interests of employers and promote equal employment opportunity for men and women.
While the employee is on leave, an employer can ask the employee to provide status updates, including asking the employee to obtain a second opinion regarding her condition. The caveat is that you may only ask the employee; you cannot ask anyone else about a particular employee's leave.
The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) provides certain employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave per year. It also requires that their group health benefits be maintained during the leave.
Key Employees and Their Rights. Under certain circumstances, an employer may deny job restoration to "key employees." A "key employee" is a salaried, FMLA-eligible employee who is among the highest paid 10 percent of all the employees employed by the employer within 75 miles of the employee's worksite.
In South Carolina, workers have the right to organize and the right to designate representatives of their own choosing to negotiate the terms and conditions of employment. No employer may discharge or discriminate in the payment of wages against any person because of his or her membership in a labor organization.
The FMLA entitles eligible employees of covered employers to take unpaid, job-protected leave for specified family and medical reasons with continuation of group health insurance coverage under the same terms and conditions as if the employee had not taken leave.
Employees must make reasonable efforts to schedule leave for planned medical treatment so as not to unduly disrupt the employer's operations. Leave due to qualifying exigencies may also be taken on an intermittent basis. Employees may choose or employers may require use of accrued paid leave while taking FMLA leave.