South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading
Description
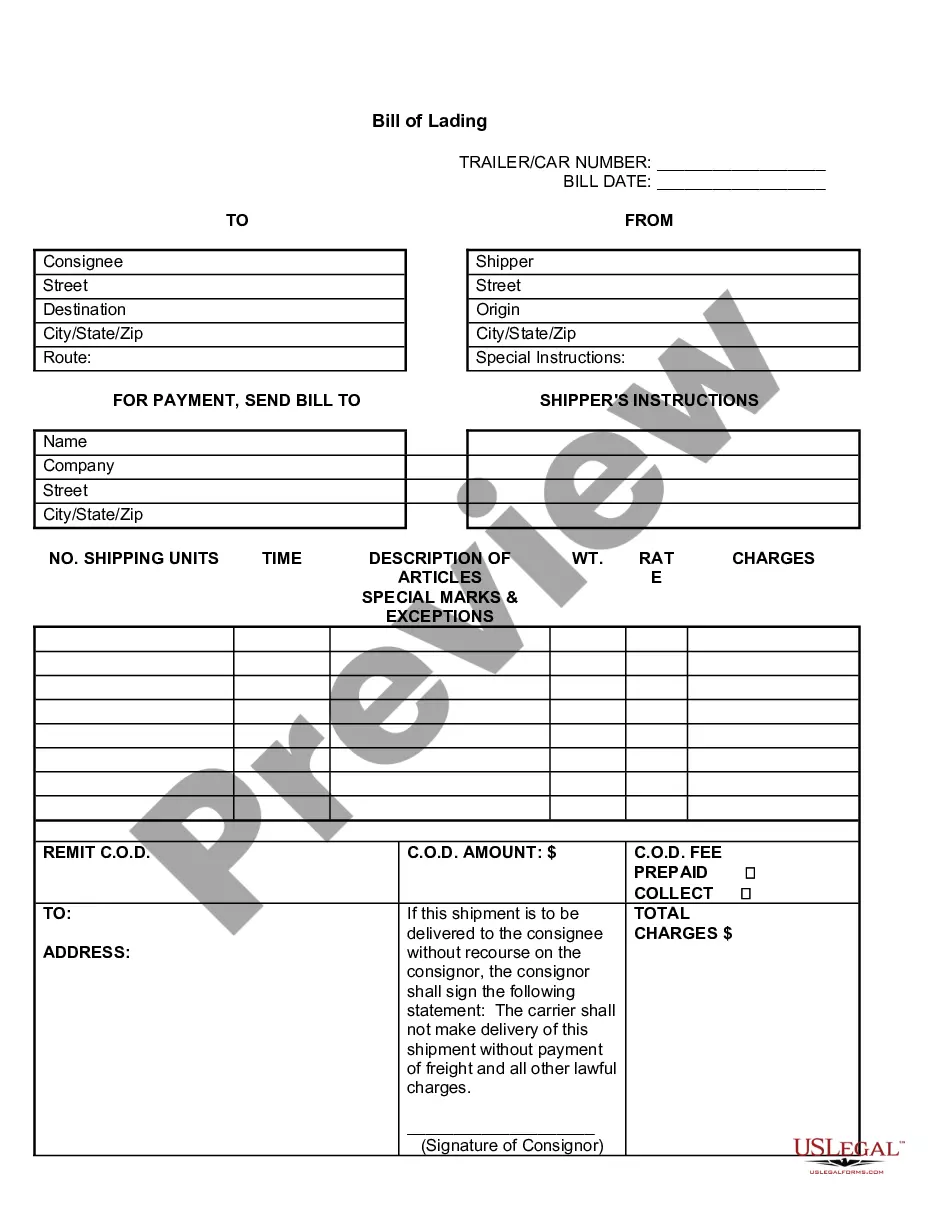
A bill of lading is a receipt given by a shipper of goods from the carrier, such as a trucking company, railroad, ship or air freighter, for shipment to a particular buyer. It is a contract protecting the shipper by guaranteeing payment and ensures the carrier that the recipient has proof of the right to the goods. The bill of lading is then sent to the buyer by the shipper upon payment for the goods, and constitutes proof that the recipient is entitled to the goods when received.
How to fill out Receipt For Bill Of Lading?
Are you in a circumstance where you will require documentation for potential business or specific operations almost every day? There are countless legal document templates accessible on the internet, but finding trustworthy ones is not easy.
US Legal Forms offers a vast array of form templates, including the South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading, which can be tailored to comply with both federal and state regulations.
If you are already acquainted with the US Legal Forms website and possess an account, simply Log In. Then, you can download the South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading template.
- Obtain the form you need and ensure it is appropriate for the correct city/region.
- Use the Preview feature to inspect the document.
- Check the description to confirm that you have selected the correct form.
- If the form is not what you're looking for, utilize the Lookup field to find the template that matches your needs.
- When you find the correct form, click Buy now.
- Choose the pricing plan you prefer, complete the necessary information to create your account, and finalize your purchase using your PayPal or credit card.
- Select a convenient file format and download your copy.
Form popularity
FAQ
The gross receipts test evaluates total business income to assess tax obligations and compliance. When dealing with your South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading, you should include all sources of income generated through your business operations. This understanding enables you to meet legal requirements effectively.
No, gross receipts do not include reimbursed expenses. These are repayments to businesses for costs already incurred and do not count as income. When using a South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading, it is vital to distinguish between actual income and amounts reimbursed for clarity in financial reporting.
In South Dakota, shipping charges may be taxable depending on the nature of the sale. If your South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading includes shipping costs tied directly to the sale of taxable goods, these charges might also be taxable. It is essential to clarify this aspect to ensure compliance with state tax laws.
Yes, South Dakota imposes a gross receipts tax, which businesses must consider when filing returns. Understanding how this tax applies to your South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading can help you manage your financial obligations effectively. Utilizing resources like US Legal Forms simplifies the process of understanding and filing for this tax.
Total gross receipts typically include all income generated from sales, services, and other business activities before any deductions. For those managing a South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading, it’s important to capture all relevant income sources to ensure proper reporting. Including every income stream contributes to accurate financial analysis.
Expense reimbursements are generally not included in gross income because they are funds returned to the taxpayer for costs incurred on behalf of the business. When preparing your South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading, recognize that only net income contributes to your gross receipts. Accurate categorization helps in maintaining clear financial records.
A gross receipts return is a form filed by businesses to report their total income generated, including sales and service revenue. For those dealing with a South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading, understanding your gross receipts is key to staying compliant with state regulations. This return is crucial for calculating any applicable taxes.
Refunds are typically not included in gross receipts as they represent a return of funds rather than income. When considering your South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading, it's essential to account for only the amount received that reflects your business's income. This helps ensure accurate reporting and compliance with South Dakota tax laws.
A bill of lading and packing slip serve different purposes, although they both relate to shipments. A bill of lading acts as a contract and receipt, detailing the terms of transportation for the goods, while a packing slip lists the items included in the shipment. Understanding this distinction is important, especially when using the South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading, to ensure all shipping documentation is accurate and comprehensive.
Essential entries on a bill of lading include the names and addresses of the shipper and receiver, a detailed description of the cargo, and terms of payment. Additionally, include the shipment's weight, any special handling instructions, and the type of transportation used. Make sure to utilize the South Dakota Receipt for Bill of Lading to cover all necessary aspects and ensure compliance with local shipping laws.