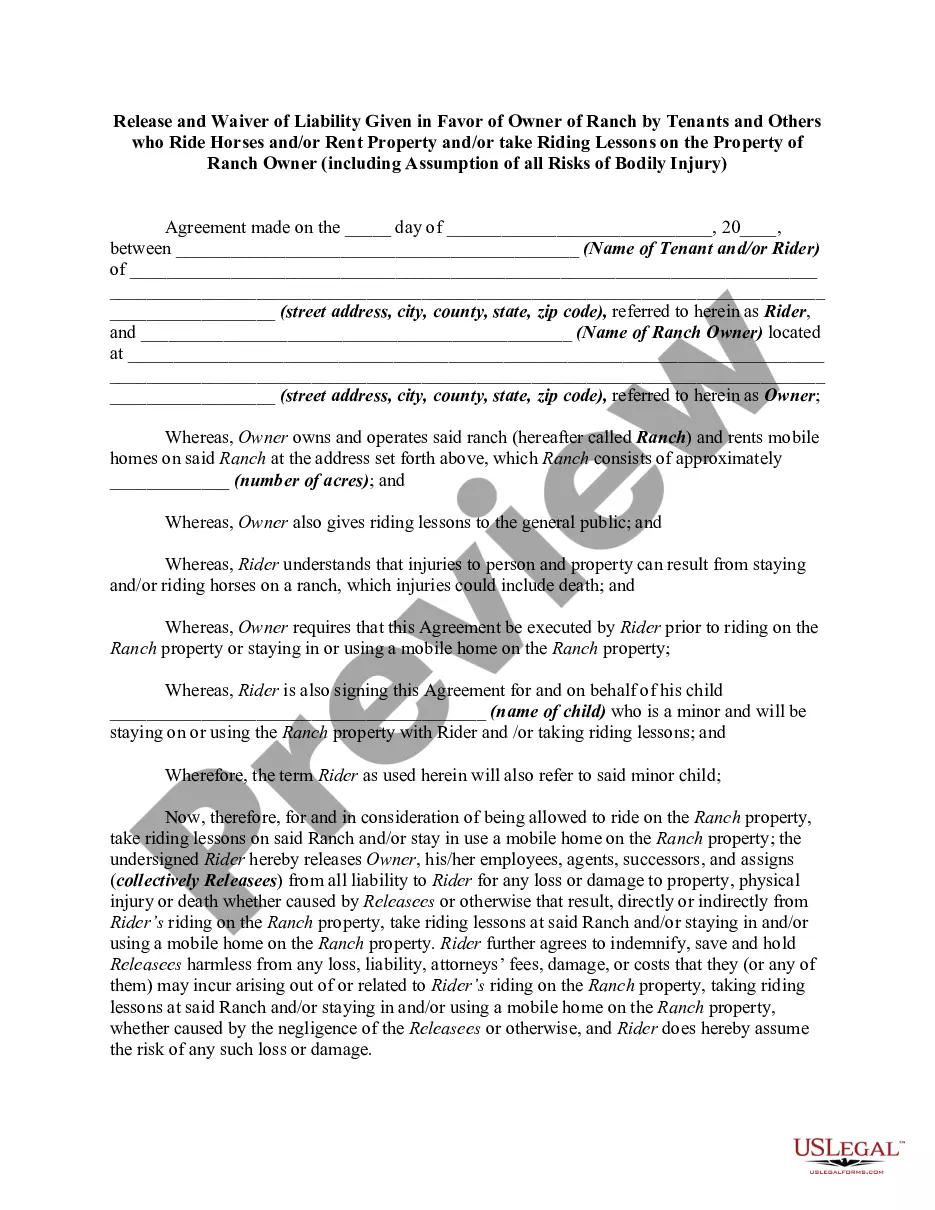
South Dakota Borrower Security Agreement regarding the extension of credit facilities
Description
How to fill out Borrower Security Agreement Regarding The Extension Of Credit Facilities?
US Legal Forms - among the largest libraries of lawful varieties in America - gives a wide range of lawful document themes you can download or print. Utilizing the web site, you may get a large number of varieties for business and specific purposes, categorized by types, says, or keywords.You will find the newest types of varieties just like the South Dakota Borrower Security Agreement regarding the extension of credit facilities within minutes.
If you have a registration, log in and download South Dakota Borrower Security Agreement regarding the extension of credit facilities in the US Legal Forms collection. The Acquire button will appear on every single kind you perspective. You have access to all previously downloaded varieties from the My Forms tab of your own profile.
In order to use US Legal Forms the first time, allow me to share easy recommendations to get you started off:
- Be sure to have picked out the correct kind to your town/state. Click on the Review button to analyze the form`s information. Browse the kind information to actually have chosen the correct kind.
- If the kind does not satisfy your requirements, utilize the Research field at the top of the display to discover the the one that does.
- In case you are satisfied with the shape, verify your decision by clicking on the Purchase now button. Then, choose the prices program you prefer and give your accreditations to register on an profile.
- Procedure the financial transaction. Make use of your charge card or PayPal profile to perform the financial transaction.
- Find the file format and download the shape on your gadget.
- Make alterations. Load, edit and print and signal the downloaded South Dakota Borrower Security Agreement regarding the extension of credit facilities.
Each and every web template you put into your account does not have an expiry date which is your own property permanently. So, if you would like download or print one more copy, just go to the My Forms section and click on around the kind you will need.
Gain access to the South Dakota Borrower Security Agreement regarding the extension of credit facilities with US Legal Forms, one of the most substantial collection of lawful document themes. Use a large number of professional and state-particular themes that fulfill your company or specific requires and requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
If the debtor defaults, the lender can gain all rights to the property, as laid under the security agreement. Mortgage is different from a security agreement. A mortgage is used to secure the lender's rights by placing a lien against the title of the property.
Also known as a loan or credit facility agreement or facility letter. An agreement or letter in which a lender (usually a bank or other financial institution) sets out the terms and conditions (including the conditions precedent) on which it is prepared to make a loan facility available to a borrower.
Collateral guarantees a loan, so it needs to be an item of value. For example, it can be a piece of property, such as a car or a home, or even cash that the lender can seize if the borrower does not pay.
Key Takeaways. A security agreement is a document that provides a lender a security interest in a specified asset or property that is pledged as collateral. Security agreements often contain covenants that outline provisions for the advancement of funds, a repayment schedule, or insurance requirements.
While the tax is net income-based, SDCL 10-43-90 imposes a minimum financial institution tax specific to South Dakota chartered trust companies. The minimum financial institution tax applied to South Dakota chartered trust companies is tiered over the first five years of operations.
A ?SECURITY AGREEMENT? is an agreement that. creates or provides for an interest in personal property. that secures payment or performance of an obligation.
A security interest exists when a borrower enters into a contract that allows the lender or secured party to take collateral that the borrower owns in the event that the borrower cannot pay back the loan. The term security interest is often used interchangeably with the term lien in the United States.
Standards may differ from lender to lender, but there are four core components ? the four C's ? that lenders will evaluate in determining whether they will make a loan: capacity, capital, collateral and credit.