South Dakota Mineral Owner's Subordination (of Rights to Make Use of Surface Estate) is a legal arrangement that allows mineral owners in South Dakota to surrender or subordinate their rights to make use of the surface estate to another party. This agreement grants the surface owner the authority to use the land for various purposes while protecting the mineral rights of the subordinating party. In South Dakota, there are two primary types of Mineral Owner's Subordination that can be used: 1. Temporary Subordination: This type of subordination involves a temporary surrender of surface rights by the mineral owner. It allows the surface owner to engage in activities such as construction, agriculture, or other land use purposes while preserving the mineral rights for future extraction. Temporary subordination typically specifies a specific timeframe during which the surface owner may exercise their rights. 2. Permanent Subordination: In some cases, mineral owners in South Dakota may decide to permanently subordinate their rights to use the surface estate. This means that the surface owner gains complete control over the land and is no longer restricted by the mineral rights. Permanent subordination is usually pursued when the mineral owner has no intention of utilizing their mineral rights or when there is a conflict of interest between the two parties. In both types of subordination, it is crucial to establish clear terms and conditions to protect the rights of both the surface owner and the mineral owner. Such agreements typically outline the specific scope of surface activities permissible, compensation arrangements, environmental protections, and termination clauses. South Dakota Mineral Owner's Subordination (of Rights to Make Use of Surface Estate) plays a vital role in managing the coexistence of surface and subsurface interests. By allowing the surface owner to utilize the land without compromising the mineral rights, it fosters effective land use planning, economic development, and resource extraction, while ensuring the protection of valuable mineral deposits for future exploitation.
South Dakota Mineral Rights
Description
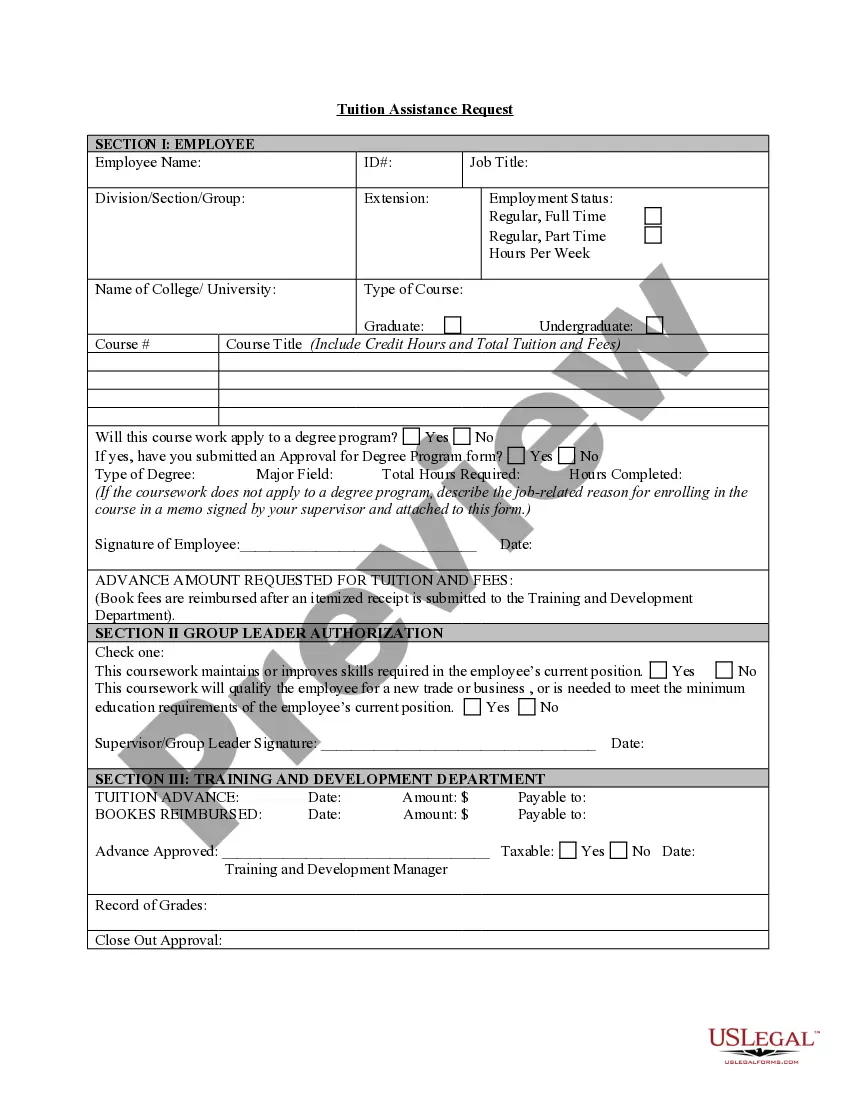
How to fill out South Dakota Mineral Owner's Subordination (of Rights To Make Use Of Surface Estate)?
Are you currently within a place that you need to have paperwork for possibly enterprise or individual purposes nearly every day time? There are a lot of legal record web templates available on the net, but discovering types you can rely is not straightforward. US Legal Forms provides thousands of type web templates, like the South Dakota Mineral Owner's Subordination (of Rights to Make Use of Surface Estate), that are published in order to meet state and federal demands.
When you are already informed about US Legal Forms web site and possess an account, simply log in. Afterward, you can obtain the South Dakota Mineral Owner's Subordination (of Rights to Make Use of Surface Estate) web template.
Should you not have an bank account and need to begin using US Legal Forms, adopt these measures:
- Discover the type you require and ensure it is for your right area/county.
- Utilize the Review option to review the shape.
- Read the information to actually have selected the correct type.
- In the event the type is not what you`re trying to find, make use of the Lookup area to find the type that meets your needs and demands.
- Once you find the right type, click on Acquire now.
- Pick the rates strategy you want, fill in the necessary information to create your bank account, and buy your order using your PayPal or credit card.
- Choose a hassle-free data file file format and obtain your backup.
Find all the record web templates you may have purchased in the My Forms menus. You may get a extra backup of South Dakota Mineral Owner's Subordination (of Rights to Make Use of Surface Estate) whenever, if needed. Just select the essential type to obtain or printing the record web template.
Use US Legal Forms, one of the most substantial assortment of legal varieties, to save time and avoid faults. The assistance provides skillfully created legal record web templates which you can use for a variety of purposes. Create an account on US Legal Forms and begin producing your lifestyle a little easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
A landowner may own the rights to everything on the surface, but not the rights to underground resources such as oil, gas, and minerals. In the United States, landowners possess both surface and mineral rights unless they choose to sell the mineral rights to someone else.
The cost basis for inherited mineral rights is ?fair value.? It's simply the book value of what you receive on the day you acquire it. If you sell your rights afterward, you'll have to pay capital gains tax on the difference between your cost basis and the sale price.
If you collect royalty income of $100,000, you could pay $30,000+ in taxes and only keep $70,000 and it would takes years to collect. Your basis in mineral rights can affect how much tax you owe when selling mineral rights vs collecting royalties. If you inherited mineral rights, it nearly always makes sense to sell.
One quick and dirty approach is the ?rule of thumb.? Those following the rule of thumb say that mineral rights are worth a multiple of three to five times the yearly income produced. For example, a mineral right that produces $1,000 a year in royalties would be worth between $3,000 and $5,000 under the rule of thumb.
The IRS views the profits from the sale of mineral rights as a capital gain, not income. To figure out how much you might need to pay as a capital gains tax, you need to figure out your cost basis in the mineral rights. The cost basis is the original price or value of the asset ? in this case, mineral rights.
As a mineral rights value rule of thumb, the 3X cash flow method is often used. To calculate mineral rights value, multiply the 12-month trailing cash flow by 3. For a property with royalty rights, a 5X multiple provides a more accurate valuation (stout.com).
In the United States, mineral rights can be sold or conveyed separately from property rights. As a result, owning a piece of land does not necessarily mean you also own the rights to the minerals beneath it. If you didn't know this, you're not alone. Many property owners do not understand mineral rights.
Dominance of Mineral Estate This means that the owner of the mineral estate has the right to freely use the surface estate to the extent reasonably necessary for the exploration, development, and production of the oil and gas under the property.