South Dakota Affidavit of Heirship for House
Description
How to fill out Affidavit Of Heirship For House?
Are you currently within a place the place you will need documents for possibly enterprise or individual functions nearly every day time? There are plenty of legitimate papers themes available online, but discovering types you can trust is not easy. US Legal Forms provides a large number of type themes, just like the South Dakota Affidavit of Heirship for House, which can be published to meet state and federal specifications.
Should you be already familiar with US Legal Forms internet site and have your account, simply log in. Afterward, you may download the South Dakota Affidavit of Heirship for House design.
Unless you have an account and wish to begin using US Legal Forms, follow these steps:
- Find the type you want and ensure it is for your right area/area.
- Take advantage of the Preview key to analyze the form.
- Browse the information to ensure that you have chosen the proper type.
- When the type is not what you are seeking, take advantage of the Research field to find the type that fits your needs and specifications.
- Whenever you obtain the right type, simply click Acquire now.
- Select the pricing program you desire, submit the required details to produce your bank account, and purchase the order using your PayPal or Visa or Mastercard.
- Decide on a practical document file format and download your version.
Locate all the papers themes you might have purchased in the My Forms food list. You can aquire a further version of South Dakota Affidavit of Heirship for House whenever, if needed. Just select the required type to download or produce the papers design.
Use US Legal Forms, one of the most considerable collection of legitimate forms, to conserve some time and stay away from mistakes. The services provides expertly created legitimate papers themes which can be used for a range of functions. Create your account on US Legal Forms and initiate generating your life easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
A formal probate requires additional court intervention and is required if the decedent passed away more than three years before the filing of the probate. An informal probate in South Dakota is often handled by the clerk of courts rather than a judge. A probate can also be testate or intestate. Do I need a Probate? - Legacy Law Firm legacylawfirmpc.com ? blog ? do-i-need-a-... legacylawfirmpc.com ? blog ? do-i-need-a-...
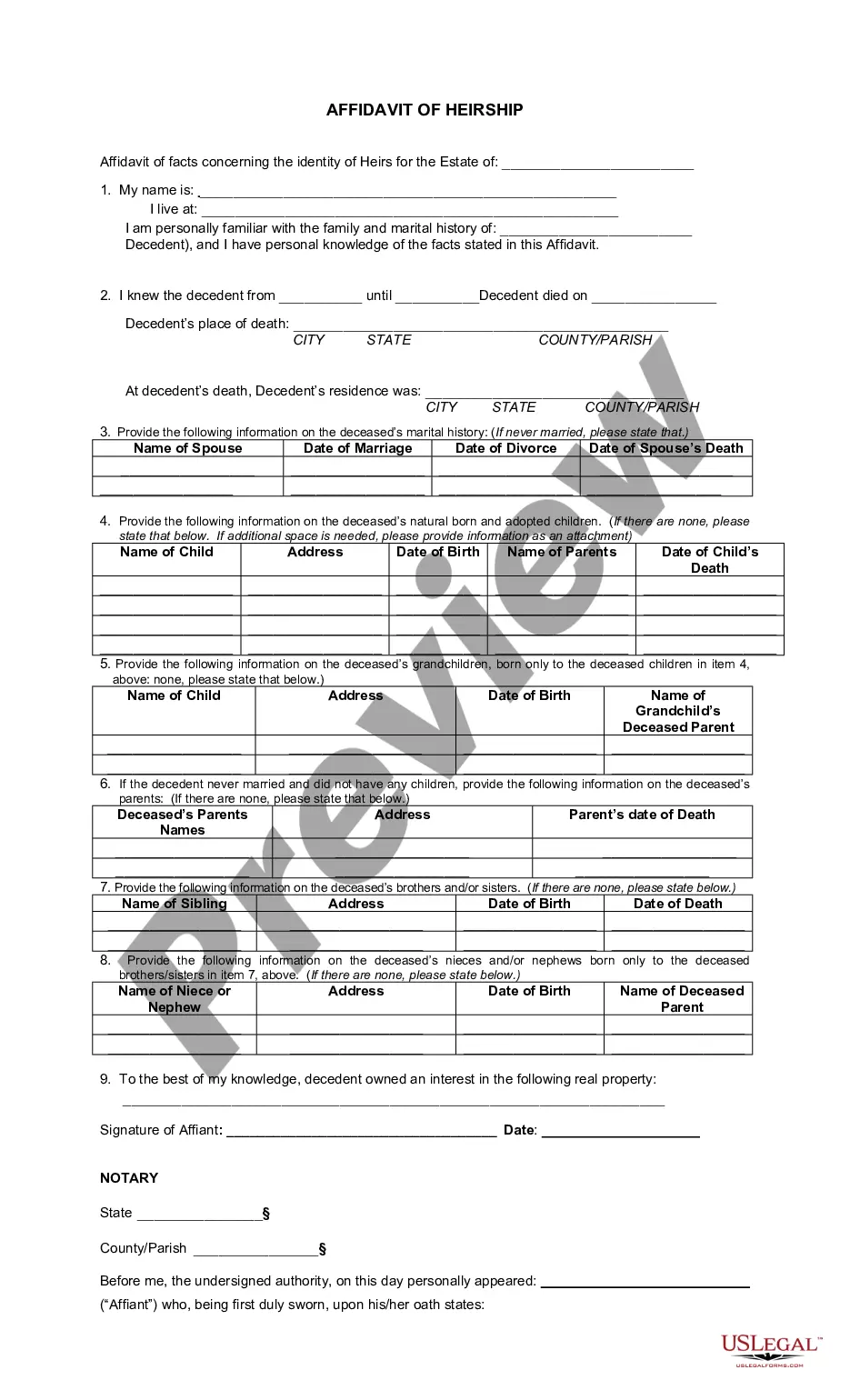
Hear this out loud PauseSixty days after the death of a decedent, any person claiming to be a successor to the decedent's interest in real property in this state may file, or cause to be filed on their behalf, an affidavit describing the real property owned by the decedent and the interest of the decedent in the property.
A South Dakota small estate affidavit is a document that can help a person using it, known as an ?affiant,? avoid traditional probate proceedings. South Dakota Small Estate Affidavit | Collection of Personal ... eForms ? Small Estate Affidavit eForms ? Small Estate Affidavit
If you die intestate in South Dakota without a spouse but you have children, then your estate goes to your children in equal shares. If you don't have children, then your entire estate goes to your parents, if they are living. If you don't have surviving parents, then your siblings inherit everything. A Guide to South Dakota Inheritance Laws | SmartAsset smartasset.com ? financial-advisor ? south-dakota-... smartasset.com ? financial-advisor ? south-dakota-...
Hear this out loud PauseOnce the affidavit has been recorded, the heirs are identified in the property records as the new owners of the property. Thereafter, the heir or heirs may transfer or sell the property if they choose to do so.
Hear this out loud PauseA South Dakota small estate affidavit aids the transfer of personal property of a deceased individual (the ?decedent?) to their successors without formal probate proceedings. Any beneficiary entitled to the decedent's property may fill out this affidavit and use it to collect the assets from its current custodians.