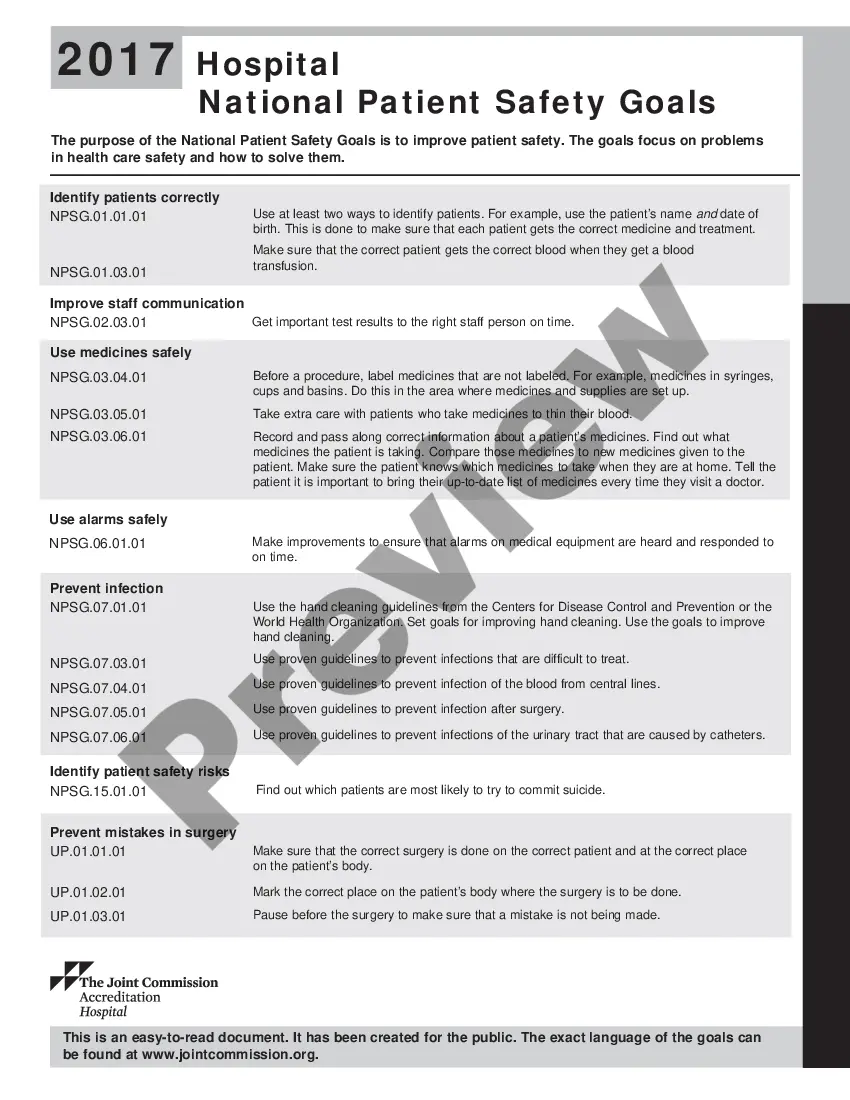
The Tennessee Hospital National Patient Safety Goals (Nests) are a set of guidelines and standards established by The Joint Commission specifically for hospitals in Tennessee. These goals aim to improve patient safety and enhance the overall quality of care provided to patients in healthcare facilities across the state. Complying with these goals ensures that hospitals maintain a safe environment and minimize potential risks to patients. The Tennessee Hospital Nests cover a wide range of areas and highlight specific objectives that hospitals should strive to achieve. These goals are based on extensive research, evidence-based practices, and best-known methods in order to promote patient safety. Adhering to these goals helps hospitals reduce medical errors, prevent healthcare-associated infections, and improve communication between healthcare providers and patients. Here are some of the key Tennessee Hospital National Patient Safety Goals: 1. Identify patients correctly: Hospitals must implement procedures to accurately identify patients throughout their stay, ensuring the right procedures and medications are administered to the correct individual. 2. Improve staff communication: Enhancing communication among healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurses, and other staff members, is crucial to avoid errors and misunderstandings that may compromise patient safety. 3. Use medications safely: Hospitals should establish comprehensive medication safety procedures, including processes for prescribing, dispensing, and administering medications, as well as educating patients on their proper use. 4. Prevent surgical site infections: By implementing evidence-based practices, hospitals can minimize the risk of surgical site infections, such as maintaining proper hygiene, using sterile equipment, and administering antibiotics when necessary. 5. Prevent central line-associated bloodstream infections: Hospitals should focus on measures to reduce infections related to central lines, such as proper insertion and maintenance techniques, as well as staff training and surveillance. 6. Prevent falls: Hospitals should assess and implement effective fall prevention strategies, including regular patient assessments, ensuring a safe patient environment, and educating both patients and their families on preventing falls. 7. Improve hand hygiene compliance: Ensuring proper hand hygiene among healthcare providers is crucial to preventing the spread of infections. Hospitals must establish protocols and monitor compliance to promote optimal hand hygiene practices. 8. Reduce the risk of pressure ulcers: Implementing strategies to assess, prevent, and treat pressure ulcers is essential. Hospitals should develop protocols for early identification and proper interventions to minimize the occurrence and severity of pressure ulcers. By focusing on these goals, Tennessee hospitals can enhance patient safety and improve outcomes for individuals seeking medical care in the state. Regularly evaluating and improving their adherence to these goals allows hospitals to provide the highest standard of care and ensure the well-being of patients.
Tennessee Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
Choosing the right legitimate file template might be a have a problem. Naturally, there are a variety of themes available online, but how would you find the legitimate type you need? Make use of the US Legal Forms web site. The services provides 1000s of themes, for example the Tennessee Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, that can be used for company and private needs. Every one of the kinds are checked out by pros and meet federal and state demands.
When you are previously authorized, log in in your profile and click on the Obtain option to obtain the Tennessee Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. Use your profile to check from the legitimate kinds you may have purchased previously. Check out the My Forms tab of your profile and get one more backup of the file you need.
When you are a fresh end user of US Legal Forms, here are straightforward directions that you can follow:
- Very first, make sure you have chosen the appropriate type for the area/region. You may look over the form using the Preview option and study the form information to guarantee this is the right one for you.
- In the event the type will not meet your preferences, make use of the Seach industry to get the correct type.
- When you are certain the form is proper, click on the Buy now option to obtain the type.
- Choose the prices plan you need and enter in the needed details. Build your profile and pay for your order using your PayPal profile or bank card.
- Choose the document file format and acquire the legitimate file template in your device.
- Complete, modify and printing and indicator the acquired Tennessee Hospital National Patient Safety Goals.
US Legal Forms is the greatest library of legitimate kinds where you can find various file themes. Make use of the company to acquire appropriately-made files that follow status demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
What Are the 7 National Patient Safety Goals for Hospitals in 2021?Identify patients correctly.Improve staff communication.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.Prevent infection.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...
Goal. Prevent, reduce, and ultimately eliminate healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.
20172021 versionsGoal 1: Identify patients correctly.Goal 2: Improve effective communication.Goal 3: Improve the safety of high-alert medications.Goal 4: Ensure safe surgery.Goal 5: Reduce the risk of health care-associated infections.Goal 6: Reduce the risk of patient harm resulting from falls.
Goal 6: Reduce patient harm associated with clinical alarm systems.
Measures of infection control include identifying patients at risk of nosocomial infections, observing hand hygiene, following standard precautions to reduce transmission and strategies to reduce VAP, CR-BSI, CAUTI. Environmental factors and architectural lay out also need to be emphasized upon.
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
2022 Joint Commission National Patient Safety Goals1 Identify Patients Correctly.2 Improve Staff Communication.3 Use Medicines Safely.4 Use Alarms Safely.5 Prevent Infection.6 Surgery Verification.