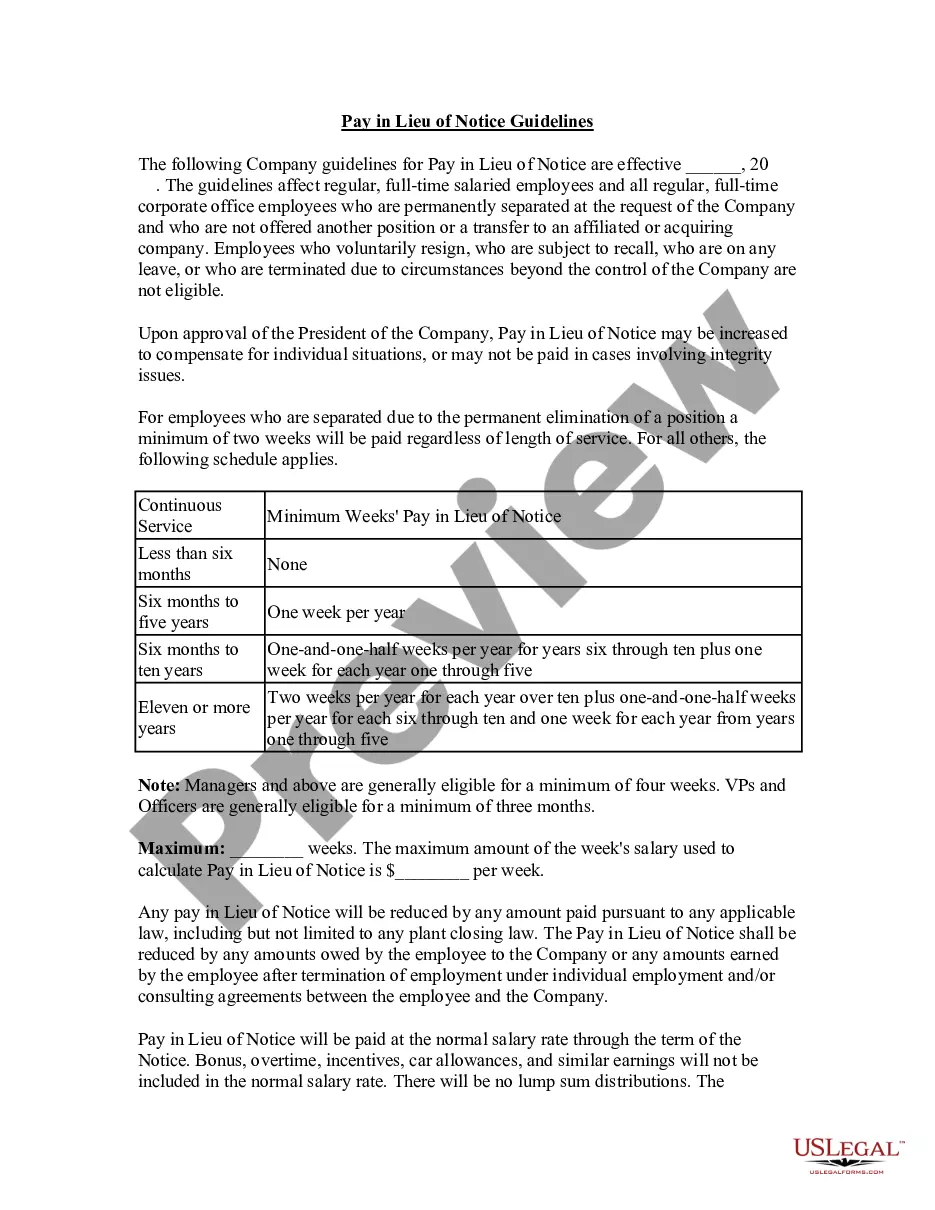
Tennessee Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines, also known as the Tennessee WARN Act, establish rules and regulations pertaining to compensation when an employer terminates an employee without providing the full notice period required by law. This compensation, commonly referred to as pay in lieu of notice, serves to mitigate the adverse impact on employees who face sudden job loss. According to the guidelines, Tennessee employers with 100 or more employees are subject to the Tennessee WARN Act. The act requires employers to provide affected employees with a minimum of 60 days' notice before implementing a mass layoff or plant closure. Failure to comply with this requirement makes employers liable for providing pay in lieu of notice to affected employees. Pay in lieu of notice, as determined by the Tennessee WARN Act, encompasses wages, salary, commissions, accrued holiday pay, and other compensation employees would have earned if they had not experienced sudden job loss. However, it does not include severance pay or any other benefits. In addition to the general Tennessee Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines, different types of guidelines may apply depending on the specific circumstances of the termination. For example, different guidelines may exist for layoffs resulting from temporary plant closures, permanent plant closures, or reductions in workforce due to financial constraints. Employers should familiarize themselves with Tennessee Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines to ensure compliance with the law and to properly compensate affected employees. It is crucial for employers to understand that failure to follow the guidelines can result in legal consequences, including potential lawsuits and financial penalties. In summary, the Tennessee Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines require employers to provide a minimum of 60 days' notice or compensation to affected employees in the event of a mass layoff or plant closure. This compensation covers wages, salary, commissions, and other similar payments employees would have earned during the notice period. Different types of guidelines may apply depending on the circumstances, such as temporary or permanent closures or workforce reductions due to financial constraints. Compliance with these guidelines is essential for Tennessee employers to avoid legal issues and safeguard the rights of their employees.
Tennessee Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines
Description
How to fill out Tennessee Pay In Lieu Of Notice Guidelines?
You can invest hrs on the web attempting to find the legitimate papers template which fits the state and federal demands you will need. US Legal Forms supplies a huge number of legitimate types that happen to be examined by specialists. You can actually obtain or printing the Tennessee Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines from my support.
If you already have a US Legal Forms accounts, you may log in and click the Down load key. Next, you may full, modify, printing, or indicator the Tennessee Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines. Every single legitimate papers template you buy is your own property for a long time. To have an additional duplicate of any purchased type, go to the My Forms tab and click the corresponding key.
Should you use the US Legal Forms internet site for the first time, follow the easy directions beneath:
- First, ensure that you have selected the proper papers template for that region/area of your choice. See the type description to ensure you have picked the appropriate type. If accessible, make use of the Preview key to search through the papers template too.
- If you want to find an additional variation of your type, make use of the Search field to discover the template that meets your needs and demands.
- Once you have located the template you want, simply click Get now to move forward.
- Choose the pricing program you want, type in your references, and register for a merchant account on US Legal Forms.
- Comprehensive the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal accounts to purchase the legitimate type.
- Choose the structure of your papers and obtain it for your product.
- Make alterations for your papers if possible. You can full, modify and indicator and printing Tennessee Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines.
Down load and printing a huge number of papers layouts using the US Legal Forms web site, which offers the greatest selection of legitimate types. Use expert and status-particular layouts to take on your company or personal demands.