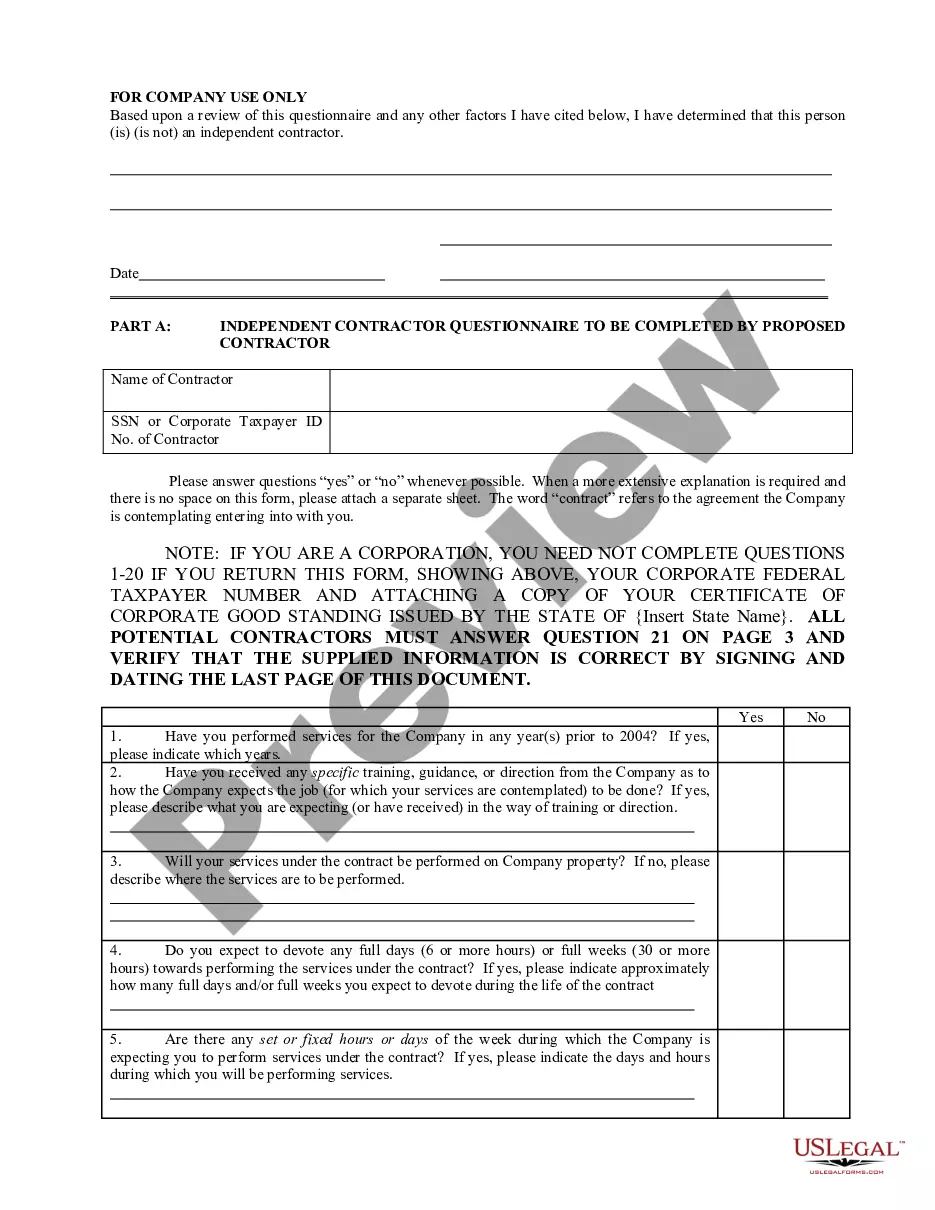
Tennessee Determining Self-Employed Independent Contractor Status
Description
How to fill out Determining Self-Employed Independent Contractor Status?
It is feasible to dedicate time online attempting to locate the valid form template that satisfies the federal and state requirements you require.
US Legal Forms offers a vast array of legitimate documents that have been reviewed by experts.
You can obtain or print the Tennessee Determining Self-Employed Independent Contractor Status through our service.
If available, utilize the Review button to inspect the document template as well. If you wish to find another version of the form, use the Search field to locate the template that fulfills your needs and specifications. Once you have identified the template you desire, click Acquire now to continue. Choose the pricing plan you prefer, enter your credentials, and register for an account on US Legal Forms. Complete the transaction using your credit card or PayPal account to purchase the legal document. Select the format of the document and download it to your device. Make adjustments to your document if necessary. You can complete, modify, sign, and print the Tennessee Determining Self-Employed Independent Contractor Status. Obtain and print numerous document templates using the US Legal Forms website, which provides the largest collection of legal forms. Utilize professional and state-specific templates to manage your business or personal needs.
- If you possess a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and click on the Obtain button.
- Then, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the Tennessee Determining Self-Employed Independent Contractor Status.
- Every legal document template you buy is yours permanently.
- To access another copy of a purchased form, navigate to the My documents tab and click on the corresponding button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the basic instructions below.
- First, ensure you have chosen the correct document template for your county/region of choice.
- Review the document outline to confirm that you have selected the appropriate form.
Form popularity
FAQ
Claimants currently eligible for unemployment through the federal Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) and Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Compensation (PEUC) programs will continue to receive benefits through the week ending July 3, 2021.
Small business owners qualify for unemployment in the same way that other individuals do through the CARES Act. In short, you must be out of work due to direct COVID-19 impacts such as required business closure.
Four ways to verify your income as an independent contractorIncome-verification letter. The most reliable method for proving earnings for independent contractors is a letter from a current or former employer describing your working arrangement.Contracts and agreements.Invoices.Bank statements and Pay stubs.
The three types of self-employed individuals include:Independent contractors. Independent contractors are individuals hired to perform specific jobs for clients, meaning that they are only paid for their jobs.Sole proprietors.Partnerships.
Tennessee's unemployment system is completely online. Individuals can apply, check the status of their claim, and complete weekly certifications at .
Simply put, being an independent contractor is a way of being self-employed. Is an independent contractor self-employed? Yes. Independent contractors are self-employed who earn an income but do not work as employees.
To be eligible for this benefit program, you must a resident of Tennessee and meet all of the following: Unemployed, and. Worked in Tennessee during the past 12 months (this period may be longer in some cases), and. Earned a minimum amount of wages determined by Tennessee guidelines, and.
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
Typically, most self-employed individuals and independent contractors working in Tennessee are not authorized to obtain regular Tennessee Unemployment Compensation (TUC). However, self-employed individuals and independent contractors may be eligible for benefits under Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA).
Becoming an independent contractor is one of the many ways to be classified as self-employed. By definition, an independent contractor provides work or services on a contractual basis, whereas, self-employment is simply the act of earning money without operating within an employee-employer relationship.