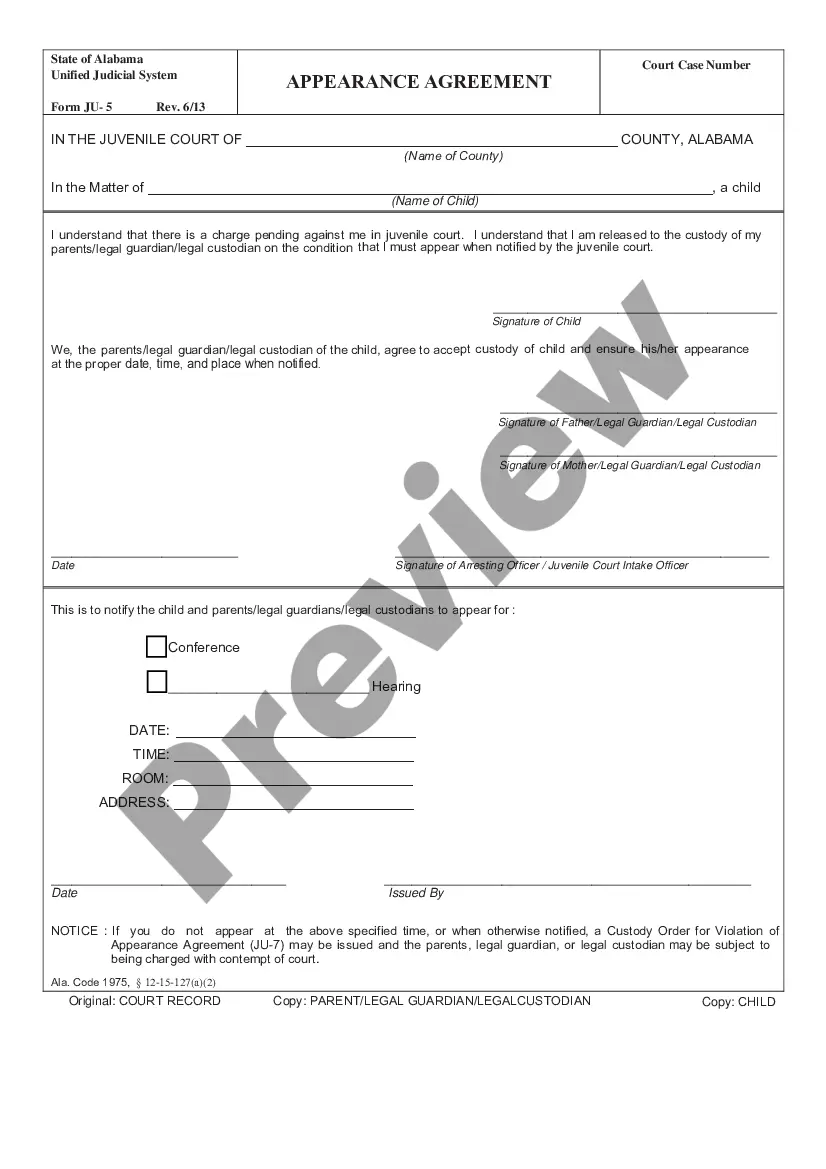
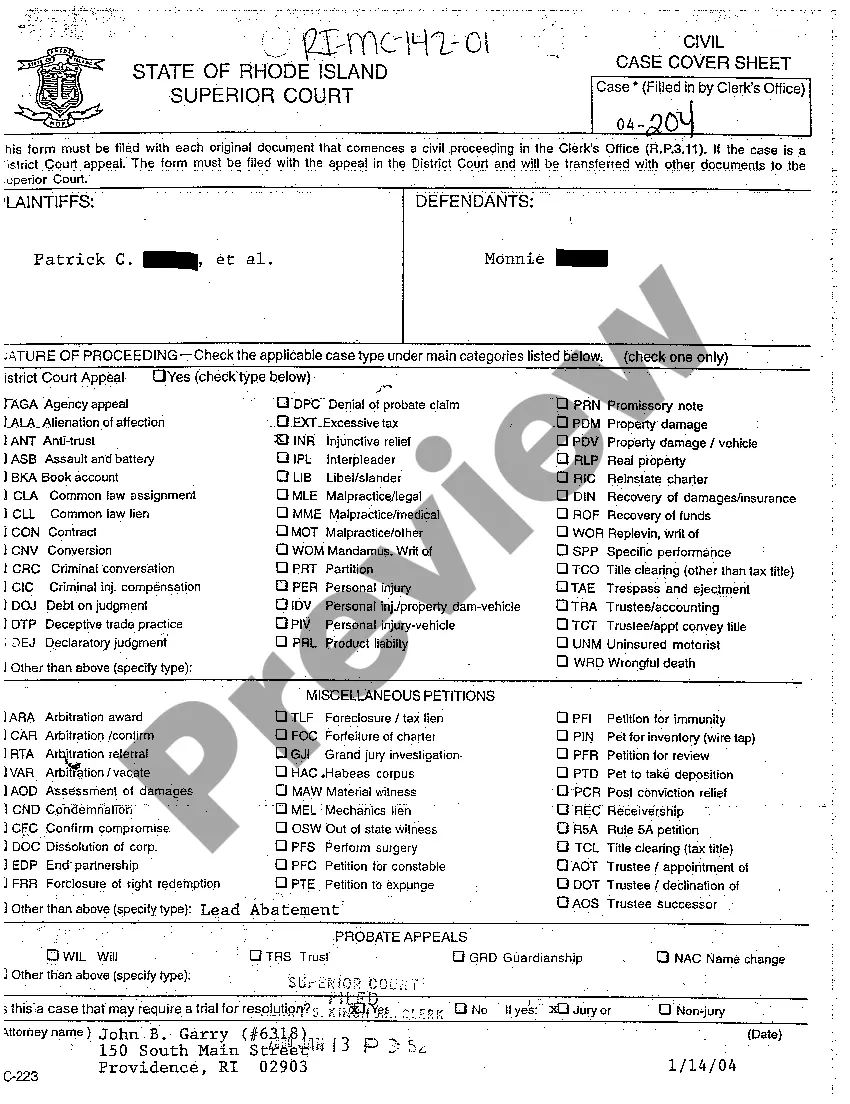
The Texas Case Screening Instrument (CSI) is a standardized assessment tool developed by the Texas Department of Family and Protective Services (DIPS) to evaluate the risk of child abuse and neglect in a family. It is designed to be used by caseworkers when investigating a family or evaluating whether a family should be referred to intervention services. The CSI assesses the level of risk posed by the family by measuring factors such as family dynamics, parenting skills, family history of abuse, substance abuse, and mental health. The CSI is composed of four different instruments: the Protective Factors Screening Scale (PASS), the Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM), the Family Strengths Assessment (FSA), and the Service Needs Assessment (SNA). The PASS assesses protective factors in the family such as a supportive social network, knowledge of parenting skills, and the availability of resources. The RAM assesses the risk posed by the family by measuring the presence of risk factors such as poverty, substance abuse, mental health issues, and violence. The FSA assesses the family's strengths such as family cohesion, parental involvement, and community support. The SNA assesses the family's service needs such as parenting skills, mental health services, and substance abuse treatment.
The Texas Case Screening Instrument (CSI) is a standardized assessment tool developed by the Texas Department of Family and Protective Services (DIPS) to evaluate the risk of child abuse and neglect in a family. It is designed to be used by caseworkers when investigating a family or evaluating whether a family should be referred to intervention services. The CSI assesses the level of risk posed by the family by measuring factors such as family dynamics, parenting skills, family history of abuse, substance abuse, and mental health. The CSI is composed of four different instruments: the Protective Factors Screening Scale (PASS), the Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM), the Family Strengths Assessment (FSA), and the Service Needs Assessment (SNA). The PASS assesses protective factors in the family such as a supportive social network, knowledge of parenting skills, and the availability of resources. The RAM assesses the risk posed by the family by measuring the presence of risk factors such as poverty, substance abuse, mental health issues, and violence. The FSA assesses the family's strengths such as family cohesion, parental involvement, and community support. The SNA assesses the family's service needs such as parenting skills, mental health services, and substance abuse treatment.