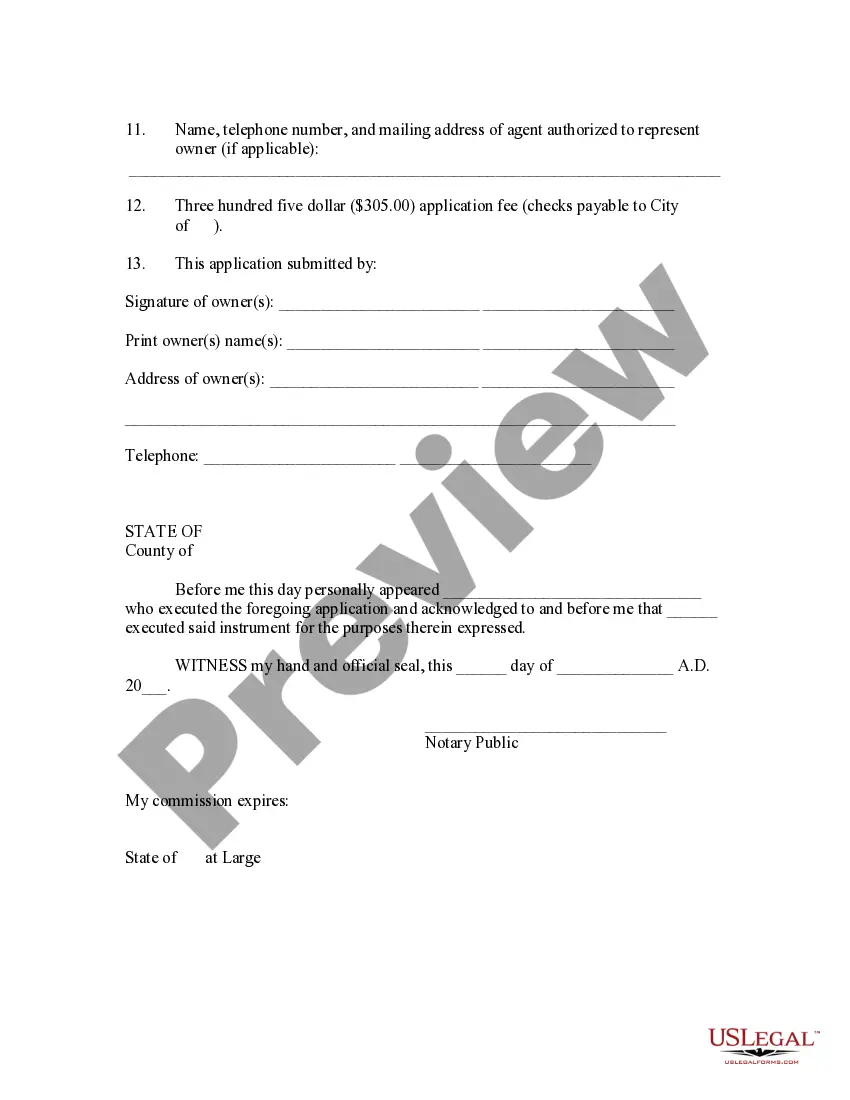
The Texas Petition for Voluntary Annexation is a legal process that allows certain entities to request the annexation of their property into a nearby municipality. Annexation is the process of incorporating unincorporated areas, such as land or properties, into a city or town, which brings them under the jurisdiction and governance of that municipality. The Texas Local Government Code provides guidelines and requirements for Petitions for Voluntary Annexation. Property owners or legitimate associations representing property owners can initiate the process by submitting a petition to the city or town requesting annexation. The petition must meet specific criteria and follow the prescribed format outlined in the Texas statutes. The Texas Petition for Voluntary Annexation is an important tool for property owners who wish to obtain the benefits and services offered by being part of a municipality. By voluntarily annexing their land, property owners gain access to essential services, including water supply, sewage systems, public transportation, police and fire protection, road maintenance, zoning regulations, and other amenities provided by the local government. There are different types of Texas Petitions for Voluntary Annexation, depending on the characteristics of the property and the specific circumstances of the annexation. Some common types include residential annexations, commercial or industrial annexations, agricultural annexations, and even extraterritorial jurisdiction (ETC) annexations. Residential annexations involve incorporating residential properties, such as homes or apartment complexes, into a nearby city or town. Commercial or industrial annexations, on the other hand, involve the annexation of commercial buildings, manufacturing facilities, or other non-residential properties. Agricultural annexations typically involve the annexation of rural or agricultural land into a municipality, which can be beneficial for farmers or ranchers who can access services and resources provided by the local government to assist in land management and agriculture-related activities. Extraterritorial jurisdiction (ETC) annexations refer to the process of extending the regulatory control of a municipality beyond its municipal boundaries. This allows municipalities to have some jurisdiction and control over land located just outside their city limits, to manage their growth effectively. In summary, the Texas Petition for Voluntary Annexation is a legal tool that enables property owners or associations to request their property's incorporation into a municipality. This process offers various benefits, services, and protections to the annexed properties, ensuring access to municipal amenities and governance. The different types of Petitions for Voluntary Annexation include residential, commercial or industrial, agricultural, and extraterritorial jurisdiction annexations, each serving different purposes as per the nature and location of the property in question.
Texas Petition for Voluntary Annexation
Description
How to fill out Texas Petition For Voluntary Annexation?
Choosing the right legal file template might be a have a problem. Naturally, there are a lot of web templates available on the net, but how would you obtain the legal develop you need? Take advantage of the US Legal Forms web site. The services provides a huge number of web templates, for example the Texas Petition for Voluntary Annexation, that can be used for company and private requires. Every one of the kinds are checked out by specialists and meet up with federal and state specifications.
In case you are already registered, log in for your accounts and click on the Acquire button to have the Texas Petition for Voluntary Annexation. Make use of your accounts to appear with the legal kinds you possess acquired previously. Proceed to the My Forms tab of the accounts and acquire yet another copy in the file you need.
In case you are a brand new end user of US Legal Forms, listed below are straightforward guidelines so that you can comply with:
- First, ensure you have chosen the proper develop to your city/county. It is possible to look over the shape using the Preview button and browse the shape outline to make certain this is basically the best for you.
- If the develop is not going to meet up with your preferences, make use of the Seach discipline to get the appropriate develop.
- When you are certain that the shape is suitable, click the Get now button to have the develop.
- Opt for the rates plan you want and enter the needed details. Design your accounts and pay money for an order with your PayPal accounts or bank card.
- Opt for the submit format and obtain the legal file template for your device.
- Complete, change and printing and indication the attained Texas Petition for Voluntary Annexation.
US Legal Forms may be the biggest collection of legal kinds that you can find various file web templates. Take advantage of the service to obtain skillfully-produced documents that comply with express specifications.