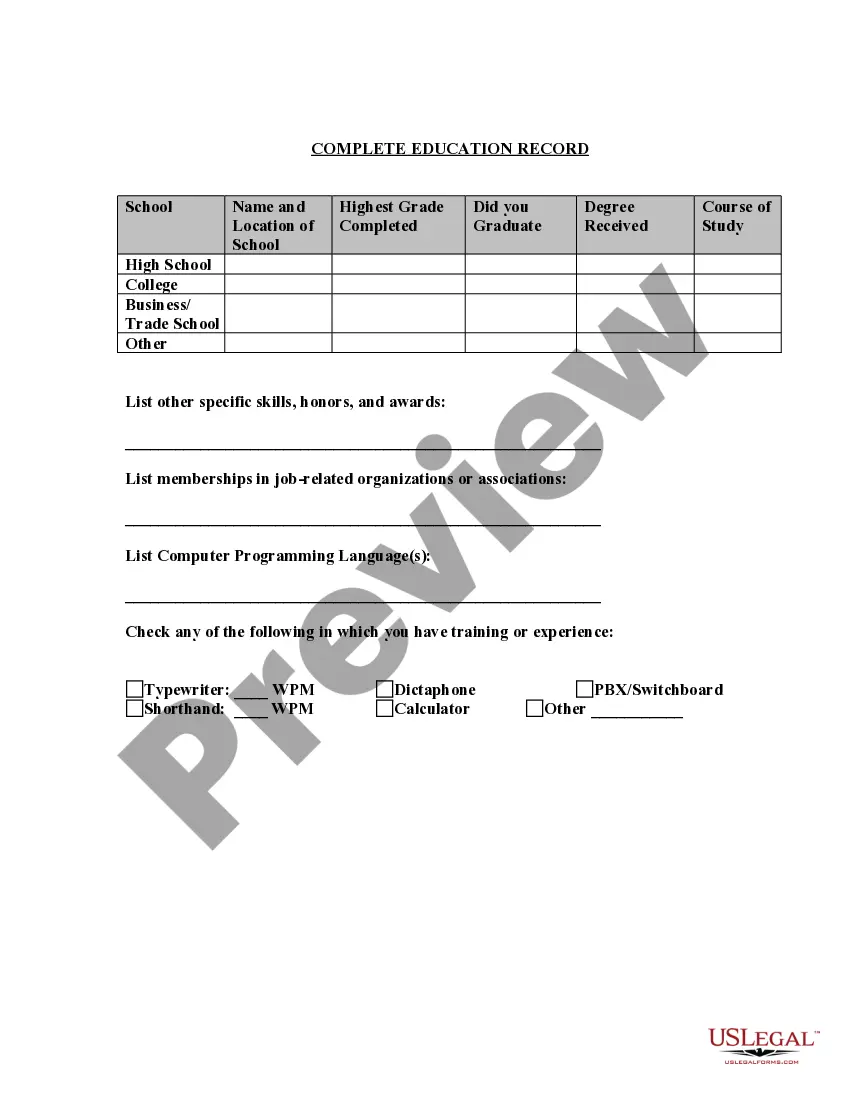
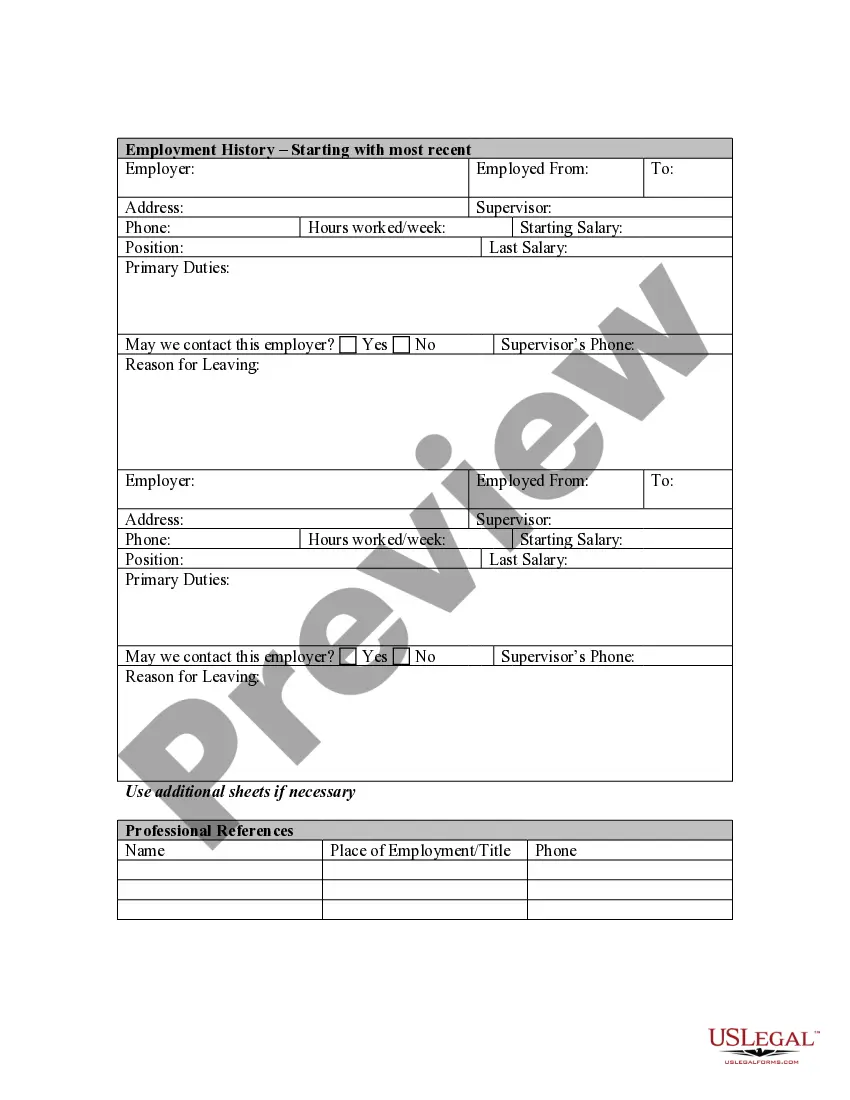
Application Employment
Description Exempt Position
How to fill out Work Nonexempt?
- Log in to your existing US Legal Forms account to access your dashboard. Ensure your subscription is active; if not, renew it as needed.
- Browse the extensive library. Utilize the Preview mode to check the details and ensure your selected template meets local jurisdiction requirements.
- Conduct a search in case of inconsistencies. Use the Search tab to find alternative templates that better suit your needs.
- Purchase the document by clicking the Buy Now button. Select a subscription plan that aligns with your requirements and create an account if you're new.
- Complete your payment via credit card or PayPal, and proceed to download your form. Save it on your device for easy access.
By following these steps, you empower yourself to handle your employment documentation efficiently. US Legal Forms not only offers a robust collection of legal forms but also connects users with premium experts to ensure precision in your documents.
Don't let legal paperwork overwhelm you. Start using US Legal Forms today to simplify your application process and secure your dream job!
Application Employment Online Form popularity
Work Exempt Nonexempt Other Form Names
Work Employment Exempt Nonexempt FAQ
In general, the office manager is often responsible for and credited with keeping the entire office running smoothly. Because of that, the position is often classified as exempt from overtime.
Salary level test. Employees who are paid less than $23,600 per year ($455 per week) are nonexempt. (Employees who earn more than $100,000 per year are almost certainly exempt.)
Managers generally are exempt from overtime compensation under state and federal wage and hour laws. However, it is important to remember that it is job duties and not job titles that determine whether or not an employee actually is exempt from this important source of increased compensation.
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.
Further, the FLSA regulations clearly state that executive or administrative assistants will only qualify as exempt if they assist business owners or senior executives of large organizations. Thus, if the administrative employee is one of several assistants in the office performing general administrative duties and
Examples of non-exempt employees include contractors, freelancers, interns, servers, retail associates and similar jobs. Even if non-exempt employees earn more than the federal minimum wage, they still take direction from supervisors and do not have administrative or executive positions.
What Is a Non-Exempt Employee? Non-exempt employees are workers who are entitled to earn the federal minimum wage and qualify for overtime pay, which is calculated as one-and-a-half times their hourly rate, for every hour they work, above and beyond a standard 40-hour workweek.
The primary difference in status between exempt and non-exempt employees is their eligibility for overtime. Under federal law, that status is determined by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Exempt employees are not entitled to overtime, while non-exempt employees are.
Employees who meet the thresholds of both the Duties and Salary tests are considered exempt from overtime pay or salaried. All other employees, with some exceptions listed below, are considered nonexempt, or eligible for overtime wages.