2.76.6 RACKETEER INFLUENCED AND CORRUPT ORGANIZATIONS ACT-"SECTION C" (Unanimity on Racketeering Acts) is a federal law that was enacted in 1970 as part of the RICO Act. Section C of this law prohibits any person or organization from participating in or engaging in a pattern of racketeering activities, such as bribery, fraud, embezzlement, extortion, or obstruction of justice. It also prohibits the use of any enterprise or organization for the purpose of committing these activities. The primary purpose of Section C is to ensure that all persons and organizations are held to the same standard of criminal accountability for racketeering activities, regardless of their size or power. Under this section, individuals and organizations can be held criminally liable for their involvement in a pattern of racketeering activities, even if they do not personally commit the crimes. Furthermore, it also prohibits any person or organization from aiding or abetting another person or organization in the commission of these activities. There are two primary types of 2.76.6 RACKETEER INFLUENCED AND CORRUPT ORGANIZATIONS ACT-"SECTION C" (Unanimity on Racketeering Acts): criminal liability and civil liability. Under criminal liability, individuals and organizations can be prosecuted and punished for their involvement in a pattern of racketeering activities. Under civil liability, individuals and organizations can be held liable for damages that they caused due to their involvement in a pattern of racketeering activities. Overall, 2.76.6 RACKETEER INFLUENCED AND CORRUPT ORGANIZATIONS ACT-"SECTION C" (Unanimity on Racketeering Acts) is an important law that provides a uniform standard of criminal and civil accountability for individuals and organizations that engage in racketeering activities. It is a key part of the RICO Act and is designed to protect against organized crime and corruption.
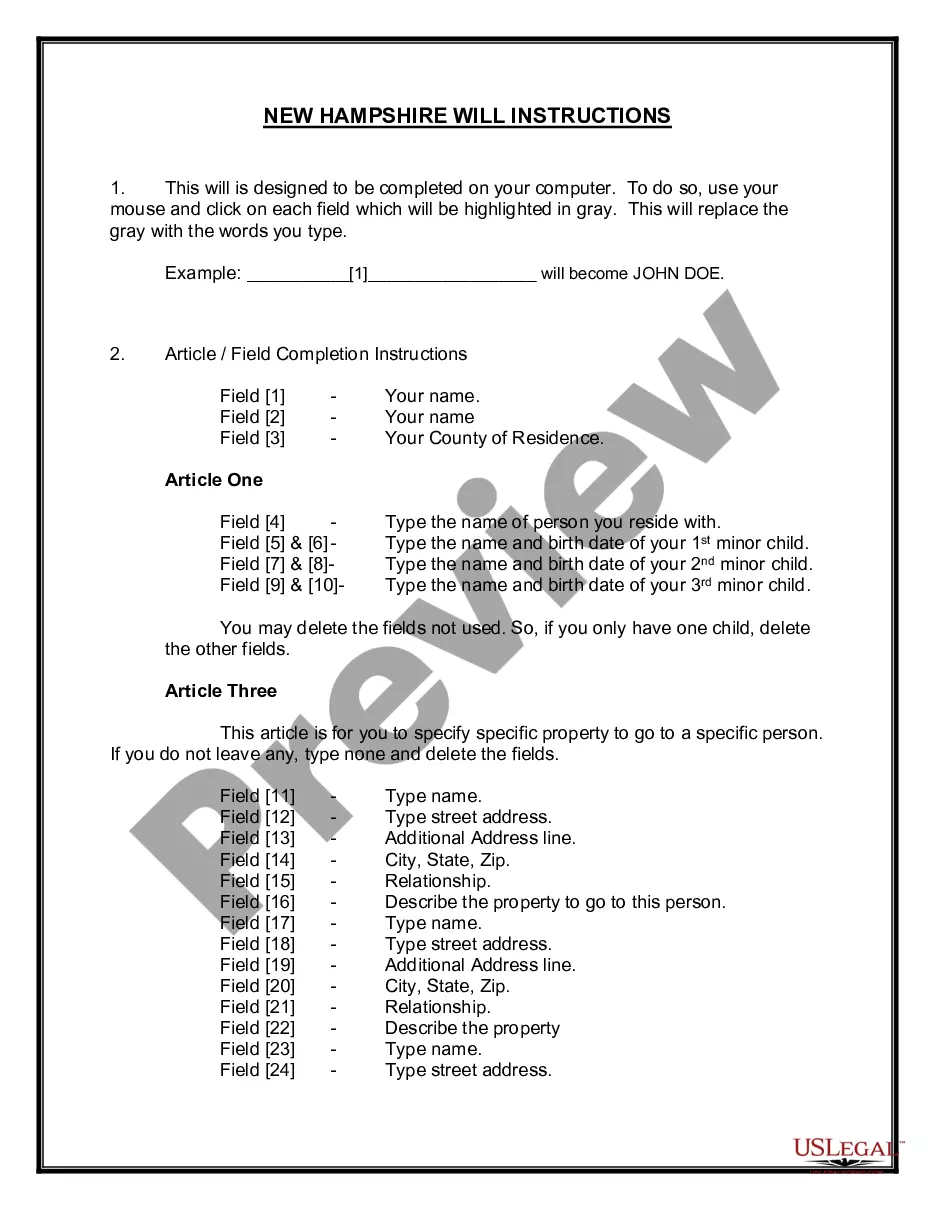
2.76.6 RACKETEER INFLUENCED AND CORRUPT ORGANIZATIONS ACT-"SECTION C" (Unanimity on Racketeering Acts)
Description
How to fill out 2.76.6 RACKETEER INFLUENCED AND CORRUPT ORGANIZATIONS ACT-"SECTION C" (Unanimity On Racketeering Acts)?
Dealing with legal documentation requires attention, precision, and using properly-drafted blanks. US Legal Forms has been helping people countrywide do just that for 25 years, so when you pick your 2.76.6 RACKETEER INFLUENCED AND CORRUPT ORGANIZATIONS ACT-"SECTION C" (Unanimity on Racketeering Acts) template from our service, you can be sure it meets federal and state laws.
Dealing with our service is straightforward and quick. To obtain the required document, all you’ll need is an account with a valid subscription. Here’s a brief guide for you to obtain your 2.76.6 RACKETEER INFLUENCED AND CORRUPT ORGANIZATIONS ACT-"SECTION C" (Unanimity on Racketeering Acts) within minutes:
- Make sure to attentively examine the form content and its correspondence with general and legal requirements by previewing it or reading its description.
- Search for an alternative official template if the previously opened one doesn’t match your situation or state regulations (the tab for that is on the top page corner).
- Log in to your account and save the 2.76.6 RACKETEER INFLUENCED AND CORRUPT ORGANIZATIONS ACT-"SECTION C" (Unanimity on Racketeering Acts) in the format you prefer. If it’s your first experience with our service, click Buy now to continue.
- Register for an account, select your subscription plan, and pay with your credit card or PayPal account.
- Decide in what format you want to save your form and click Download. Print the blank or add it to a professional PDF editor to submit it electronically.
All documents are created for multi-usage, like the 2.76.6 RACKETEER INFLUENCED AND CORRUPT ORGANIZATIONS ACT-"SECTION C" (Unanimity on Racketeering Acts) you see on this page. If you need them in the future, you can fill them out without re-payment - simply open the My Forms tab in your profile and complete your document whenever you need it. Try US Legal Forms and accomplish your business and personal paperwork quickly and in full legal compliance!